时间:2012
网络的亮点:
(1)首次利用GPU进行网络加速训练。
(2)使用ReLU激活函数,而不是传统的Sigmoid激活函数以及Tanh激活函数
(3)使用LRN局部相应归一化。
(4)在全连接层的前两层中使用了Dropout随机失活神经元操作,以减少过拟合。
概念
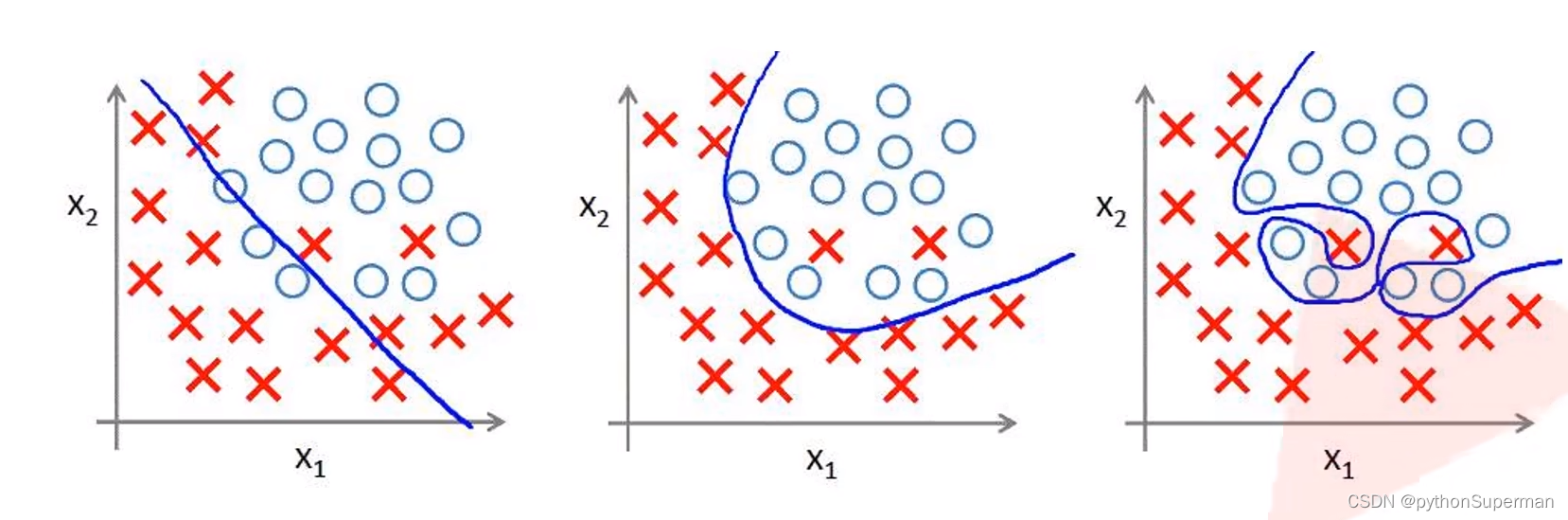
过拟合:
根本原因是特征维度过多,模型假设过于复杂,参数过多,训练数据过少,噪声过多,导致拟合的函数完美的预测训练集,但对新数据的测试集预测结果差。 过度的拟合了训练数据,而没有考虑到泛化能力。
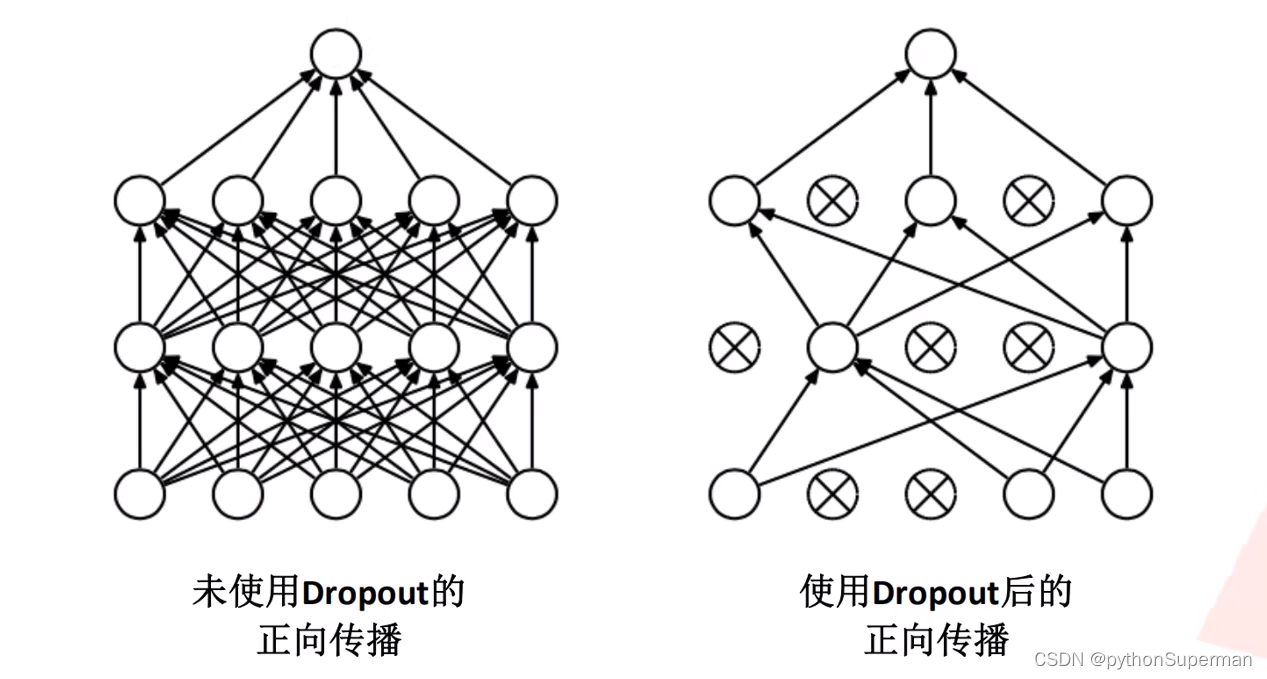
Dropout
使用Dropout的方式在网络正向传播过程,在每一层随机失活一部分神经元。可以理解为dropout可以减少网络训练的参数从而达到一个减少过拟合的这个一个作用。
代码
model.py
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, init_weights=False):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 48, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2), # input[3, 224, 224] output[48, 55, 55]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[48, 27, 27]
nn.Conv2d(48, 128, kernel_size=5, padding=2), # output[128, 27, 27]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[128, 13, 13]
nn.Conv2d(128, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[192, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[192, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(192, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[128, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[128, 6, 6]
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(128 * 6 * 6, 2048),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(2048, 2048),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(2048, num_classes),
)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
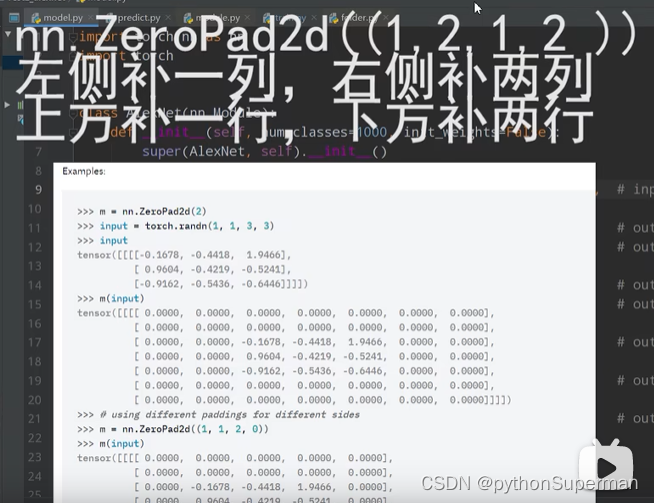
padding:
只能传入两种形式的变量,int整形,tuple类型。
比如int整形传入1,就会在图像的左上右下分别添上一层0。
比如tuple(1,2):1代表上下方各补一行零,2代表左右两侧各补两列零。
或者:
nn.ReLU(inplace=True):inplace=True增加计算量,减少内存使用
Dropout:失活。Dropout 是为了让全连接层部分失活,所以需要dropout的全连接层前配置Dropout()
激活:每一层都要激活。激活属于非线性操作,如果不激活,每层就是纯线性变换,连续的多层和只有一层是等效的,没有任何区别。
nn.Dropout(p=0.5):p代表随机失活的比例。失活是这一次训练中一半的神经元不参与训练,但神经元并没有删去。
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1):展开的是第一维,channel,展成一个一维向量。
train.py
transform
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), # 随机裁剪成224×224的大小
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 在水平方向随机水平翻转
transforms.ToTensor(), # 标准化处理
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)), # cannot 224, must (224, 224)
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])}
json类别文件
# data_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../..")) # get data root path
image_path = ("./flower_data") # flower data set path
assert os.path.exists(image_path), "{} path does not exist.".format(image_path)
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "train"),
transform=data_transform["train"])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
用flower_list来保存类别索引,在这个数据集下,图片所在的文件夹名称即为他们的索引。
然后通过dict方法联合类别和序号值
再写入json文件。
# {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items())
# write dict into json file
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
损失函数
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
nn.CrossEntropyLoss():针对多类别的损失函数
优化器
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0002)
优化器是Adam优化器,优化对象是网络中所有的可训练的参数,学习率设置的为0.0002
net.train()
使用Dropout的方式再网络正向传播过程中随机失活一部分神经元。这是再训练过程中需要的,所以会调用net.train(),再测试过程中不需要随机失活,所以会调用net.eval()关闭dropout()方法.




 本文介绍了2012年网络领域的四个重要技术亮点:GPU用于网络加速训练、ReLU激活函数、LRN局部响应归一化和Dropout防止过拟合。同时详细讲解了过拟合的概念和Dropout在模型中的应用,以AlexNet为例展示了如何在代码中实现这些技术。
本文介绍了2012年网络领域的四个重要技术亮点:GPU用于网络加速训练、ReLU激活函数、LRN局部响应归一化和Dropout防止过拟合。同时详细讲解了过拟合的概念和Dropout在模型中的应用,以AlexNet为例展示了如何在代码中实现这些技术。
















 1475
1475

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








