1.借用构造器函数进行继承
function Parent1(){
this.name="parent1";
}
function Child1(){
Parent1.call(this);
}
var s1=new Child1()
console.log(s1,s1.name) //parent1缺点:
Parent1.prototype.say=function(){
console.log(this.name);
}
s1.say(); //报错,没有say方法从上面的例子可以看出来,Child1只是继承了Parent1自身的属性,并没有继续其原型对象上的方法
2.原型链继承
这个方法是在上面方法改进得到的
function Parent2(){
this.name="parent2";
}
Parent2.prototype.say=function(){
console.log(this.name)
}
function Child2(){
}
Child2.prototype=new Parent2();
var s2=new Child2();
s2.say() //parent2
缺点:
function Parent2(){
this.name="parent2";
this.arry=[1,2,3];
}
Parent2.prototype.say=function(){
console.log(this.name)
}
function Child2(){
}
Child2.prototype=new Parent2();
var s2=new Child2();
var s3=new Child2();
s2.arry.push(4)
console.log(s2.arry) //[1,2,3,4]
console.log(s3.arry) //[1,2,3,4]我们可以看出对于继承的属性,实例改变后其他实例继承的这个属性也会随之改变
3.原型链加构造器函数进行继承
function Parent3(){
this.name="parent3";
this.arry=[1,2,3];
}
Parent3.prototype.say=function(){
console.log(this.name)
}
function Child3(){
Parent3.call(this);
}
Child3.prototype=new Parent3();
var s4=new Child3();
var s5=new Child3();
s4.arry.push(4)
console.log(s4.arry) //[1,2,3,4]
console.log(s5.arry) //[1,2,3]
s4.say() //parent3
缺点:
1.我们这个地方对于父类函数parent3调用了两次,一次在Parent3.call(this);,另一次在Child3.prototype=new Parent3();
2.打印s4.constructor 结果为Parent3,我们都知道constructor是用来返回对象的构造函数,正确结果应该为Child3,;
因为Child3.prototype=new Parent3()
所以Child3.prototype.consructor===Parent3.prototype.constructor
因为Parent3.prototype.constructor为Parent3
所以Child3.prototype.construcotr===Parent3 //★
因为s4.constructor===s4.__proto__.constructor
因为s4.__proto__===Child3.prototype
所以s4.constructor===Child3.prototype.constructor //★
所以s4.constructor===Parent3我们按照下面这样修改即可
Child3.prototype=Object.create(Parent3.prototype)
Child3.prototype.constructor=Child3;这里还需要注意一下这里用到了Object.create进行原型继承——–参考
Object.create方法创建了一个中间对象(也就是父类的原型对象),返回给了Child3.prototype。
看到过下面两种解决方法
Child3.prototype=new Parent3();
Child3.prototype.constructor=Child3;这种前面说过,会调用两次Parent3函数,存在缺点
Child3.prototype=Parent3.prototype
Child3.prototype.constructor=Child3;这种是因为对象的传递是引用传递,这里直接把父类的原型对象传递给了子类,会导致下面这种情况:
function Parent3(){
this.name="parent3";
this.arry=[1,2,3];
}
Parent3.prototype.say=function(){
console.log(this.name)
}
function Child3(){
Parent3.call(this);
}
Child3.prototype=Parent3.prototype;
Child3.prototype.constructor=Child3;
var s4=new Child3();
var s5=new Parent3();
console.log(s4.constructor) //Child3
console.log(s5.constructor) //Child3 将父类的constructor都重置了这里额外提一点:
Object.create()方法创建一个新对象,使用现有的对象来提供新创建的对象的proto。
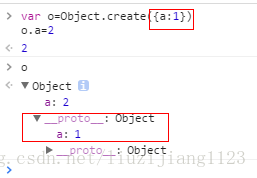
























 883
883

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








