继承的引出
概念:
继承(inheritance)机制是面向对象程序设计使代码可以复用的最重要的手段,它允许程序员在保持原有类特 性的基础上进行扩展,增加功能,这样产生新的类,称派生类。继承呈现了面向对象程序设计的层次结构, 体现了由简单到复杂的认知过程。以前我们接触的复用都是函数复用,继承是类设计层次的复用。
例子:
-
网页 有很多公共部分
-
导致实现时候有很多重复的代码
-
引出继承,基类(父类)公共网页
-
具体子类(派生类),实现不同的内容
-
语法 class 子类 :继承方式 父类
#include<iostream> using namespace std; //class News //{ //public: // void header() // { // cout << "公共的头部" << endl; // } // // void footer() // { // cout << "公共底部" << endl; // } // void left() // { // cout << "左侧列表" << endl; // } // void content() // { // cout << "新闻播报:白百合.." << endl; // } //}; //class Yule //{ //public: // void header() // { // cout << "公共的头部" << endl; // } // // void footer() // { // cout << "公共底部" << endl; // } // void left() // { // cout << "左侧列表" << endl; // } // void content() // { // cout << "新闻播报:白百合.." << endl; // } //}; /* void test01() { //新闻类 News news; news.header(); news.footer(); news.left(); news.content(); //娱乐类 Yule y1; y1.header(); y1.footer(); y1.left(); y1.content(); }*/ //继承写法 //抽象一个 基类的网页 重复的代码都写到这个网页上 class BasePage { public: void header() { cout << "公共的头部" << endl; } void footer() { cout << "公共底部" << endl; } void left() { cout << "左侧列表" << endl; } void content() { cout << "新闻播报:白百合.." << endl; } }; class News :public BasePage //继承 News类继承 BasePage类 { public: void content() { cout << "新闻播报" << endl; } }; class YULE :public BasePage { public: void content() { cout << "白百合.." << endl; } }; class Game :public BasePage { public: void content() { cout << "kpl直播" << endl; } }; void test02() { cout << "新闻网页内容:" << endl; News news; news.header(); news.footer(); news.left(); news.content(); cout << "娱乐网页内容:" << endl; YULE y1; y1.header(); y1.footer(); y1.left(); y1.content(); cout << "游戏网页内容:" << endl; Game y2; y2.header(); y2.footer(); y2.left(); y2.content(); } //继承 减少代码重复内容 //BasePage 基类 (父类) News 派生类 (子类) int main() { test02(); system("pause"); return 0; }
继承的方式
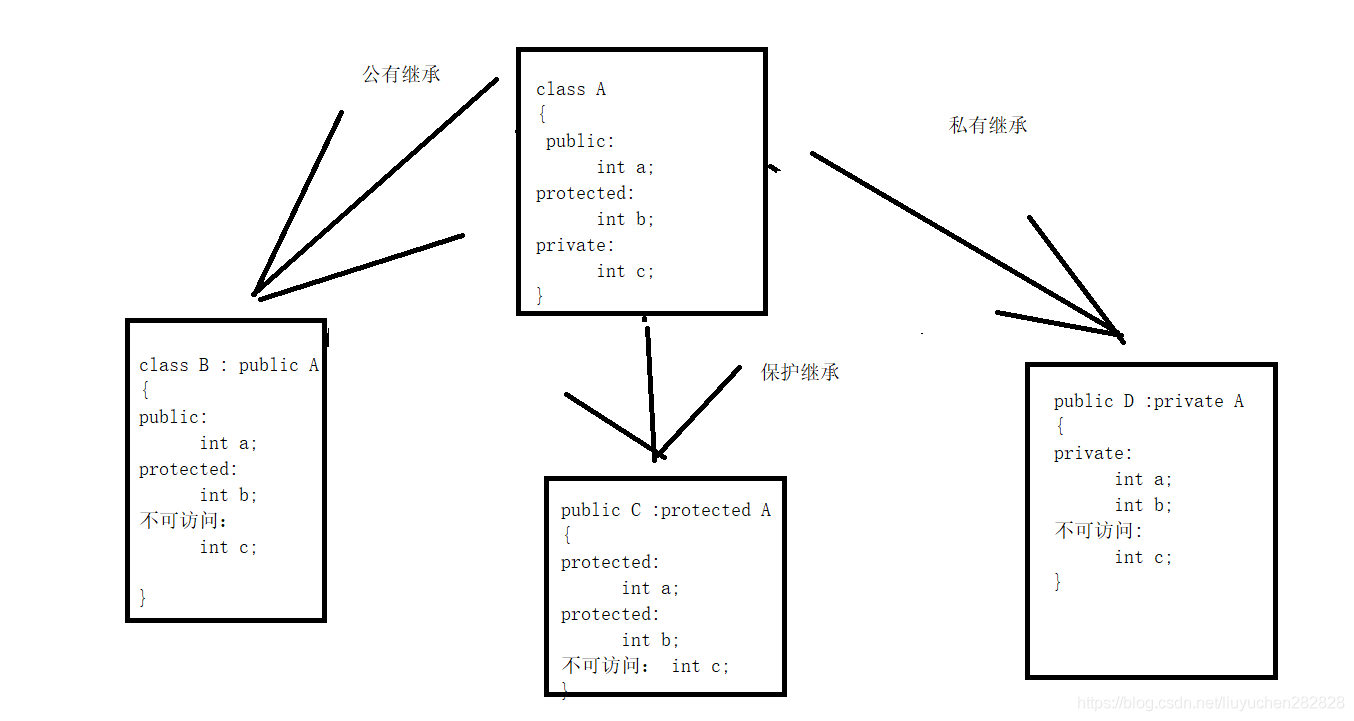
- 不管公有继承 ,保护,还是私有,基类中的私有属性,都不可以继承下去
- 公有继承 父类中的protected在子类中是protected,父类中的public在子类中还是public
- 保护继承,父类中的protected在子类中是protected,父类中的public在子类中是protected
- 私有继承,父类中的protected在子类中是private,父类中的public在子类中是prviate
注意:
-
基类private成员在派生类中无论以什么方式继承都是不可见的。这里的不可见是指基类的私有成员还是 被继承到了派生类对象中,但是语法上限制派生类对象不管在类里面还是类外面都不能去访问它。
-
. 基类private成员在派生类中是不能被访问,如果基类成员不想在类外直接被访问,但需要在派生类中能 访问,就定义为protected。可以看出保护成员限定符是因继承才出现的。
-
实际上面的表格我们进行一下总结会发现,基类的私有成员在子类都是不可见。基类的其他成员在子类 的访问方式 == Min(成员在基类的访问限定符,继承方式),public > protected > private。
-
使用关键字class时默认的继承方式是private,使用struct时默认的继承方式是public,不过最好显示的 写出继承方式。
-
在实际运用中一般使用都是public继承,几乎很少使用protetced/private继承,也不提倡使用 protetced/private继承,因为protetced/private继承下来的成员都只能在派生类的类里面使用,实际中 扩展维护性不强。
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Base1 { public: int m_A; protected: int m_B; private: int m_C; }; //公有继承 class Son1 : public Base1 { public: void func() { //cout << m_C << endl;//基类中私有属性 不可继承 cout << m_A << endl; //基类中公有属性可继承还是public cout << m_B << endl;//基类中保护属性 可继承 还是protected } }; void testSon1() { Son1 s1; s1.m_A; //s1.m_B; 类外访问不了protected属性 } //--------------------------保护继承------------- class Base2 { public: int m_A; protected: int m_B; private: int m_C; }; class Son2 :protected Base2 { public: void func() { //cout << m_C << endl;//基类中私有属性 不可继承 cout << m_A << endl; //基类中公有属性可继承还是protected cout << m_B << endl;//基类中保护属性 可继承 还是protected } }; void func2() { Son2 s; //s.m_A;//保护继承类外不可访问 } //--------------------------私有继承------------- class Base3 { public: int m_A; protected: int m_B; private: int m_C; }; class Son3 :private Base3 { public: void func() { //cout << m_C << endl;//基类中私有属性 不可访问 cout << m_A << endl;//基类中公有属性 可继承 还是private } }; class GrandSon3 :public Son3 { public: void myFunc() { ; //cout << m_A << endl;//孙子类中 访问不到m_A,因为在Son3中m_A已经是私有属性了 } }; int main() { system("pause"); return 0; }
继承中的对象模型
-
子类中会继承父类中所有的内容,包括了私有属性
-
只是我们访问不到,编译器给隐藏了
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Base { public: int m_A; protected: int m_B; private: int m_C; }; //子类中 会继承父类的私有成员 只是被编译器给隐藏起来,访问不到私有成员 class Son :public Base { public: int m_D; }; void test01() { cout << sizeof(Son) << endl; //大小为16,基类中的私有成员也在子类中被继承,只是无权访问 } int main() { test01(); system("pause"); return 0; }








 本文深入讲解C++中的继承机制,包括公有、保护和私有继承的特点与应用场景,并通过实例展示了如何利用继承来减少代码重复,提高代码复用性和扩展性。
本文深入讲解C++中的继承机制,包括公有、保护和私有继承的特点与应用场景,并通过实例展示了如何利用继承来减少代码重复,提高代码复用性和扩展性。
















 801
801

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








