1、多线程相关概念
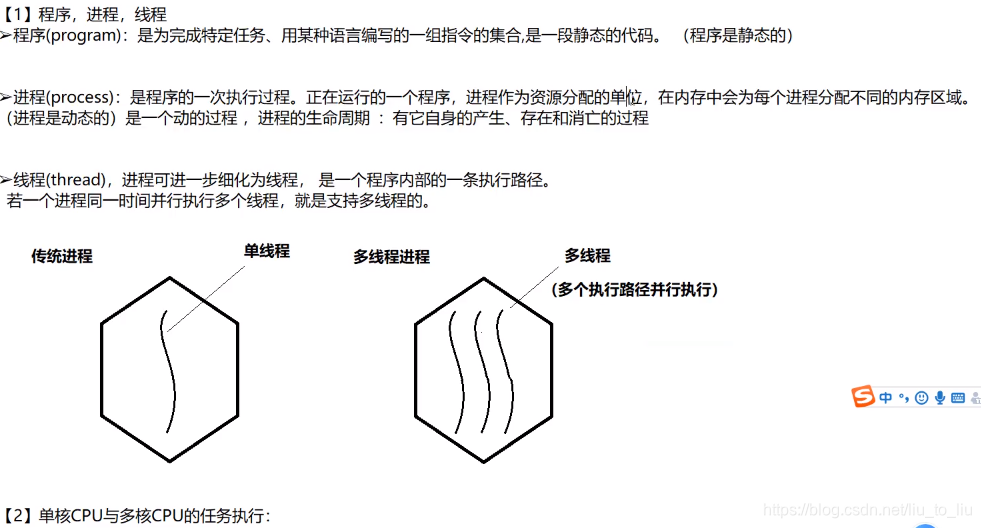
-
线程的组成部分

-
线程特点

-
单核CPU
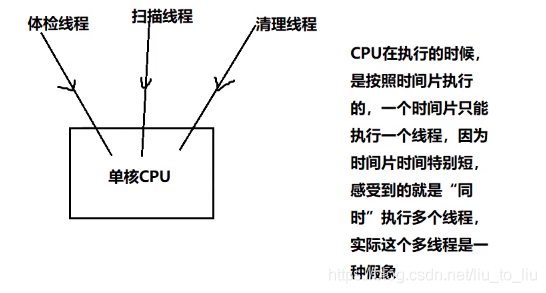
-
多核CPU
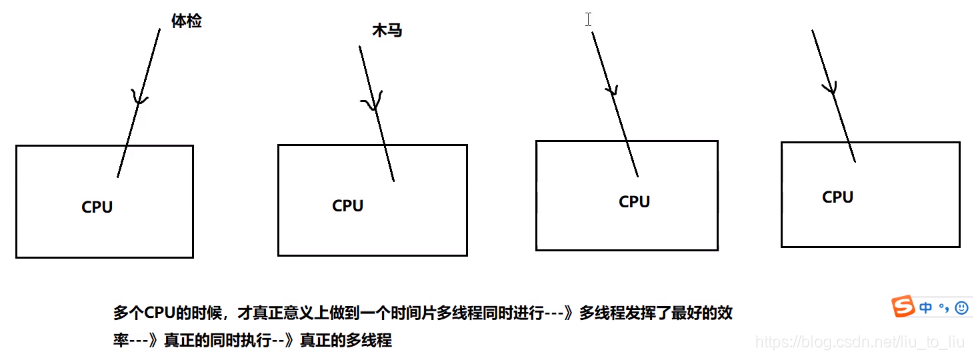
-
并行:多个CPU同时执行多个任务
-
并发:一个CPU”同时“执行多个任务(采用时间片切换)
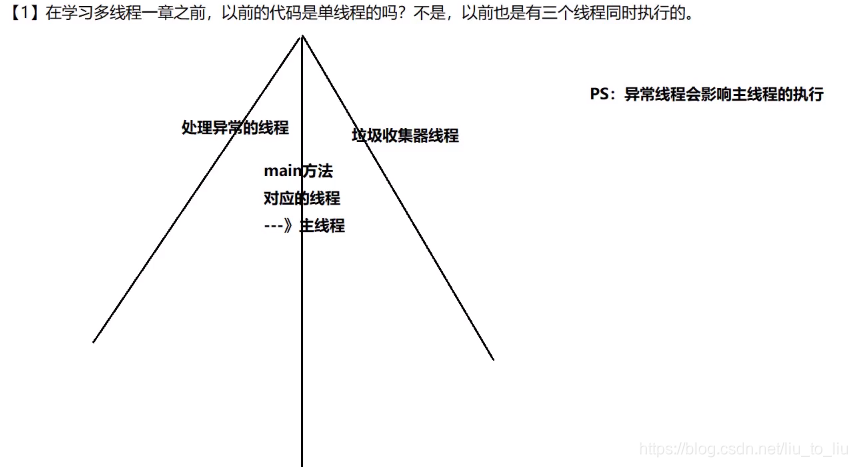
2、创建线程
2.1 第一种方式
- 继承Thread类
/**
* 不是说名字中带线程单词就具备多线程的能力了(争抢资源)
* 继承Thread类,才具备了争抢资源的能力
*/
public class TestThread extends Thread{
//必须重写Thread类中的run方法,线程的任务/逻辑必须写在该方法中
@Override
public void run() {
//输出1-10
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(this.getName() + i);
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//主线程1
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main1...." + i);
}
//创建其他线程,跟主线程2争抢资源,不会与主线程1争抢资源,因为程序是从上往下执行的
TestThread tt = new TestThread();
// tt.run();//调用run方法,想要执行线程中的任务--->这个run方法不能直接调用,直接调用会当成普通方法
//启动线程,必须调用父类Thread类start方法
tt.start();
//主线程2
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main2...." + i);
}
}
}
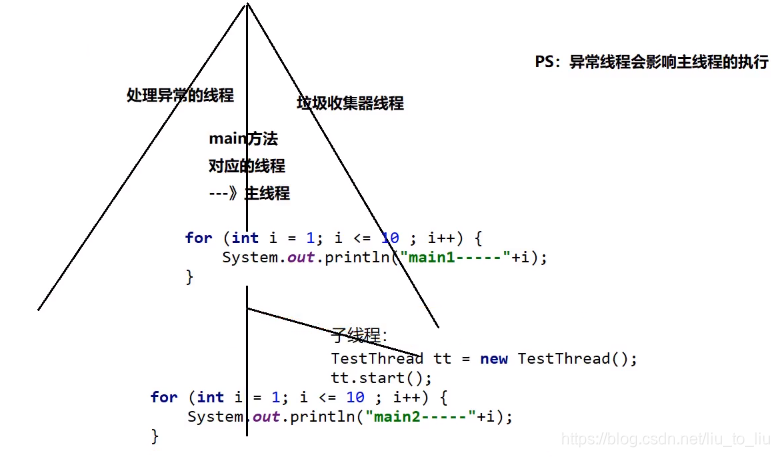
2.1.1 设置线程的名字
-
子线程名字的设置:子线程对象.setName(“子线程名字”);线程的名字获取:this.getName();
-
主线程名字的设置:Thread.currentThread().setName(“主线程名字”);线程的名字获取:Thread.currentThread().getName()

-
通过构造器设置线程名字
- 子类构造器传入子线程的名字的参数,然后通过super(name)获取子线程名字

- 子类构造器传入子线程的名字的参数,然后通过super(name)获取子线程名字
2.2 第二种方式
- 实现Runnable接口
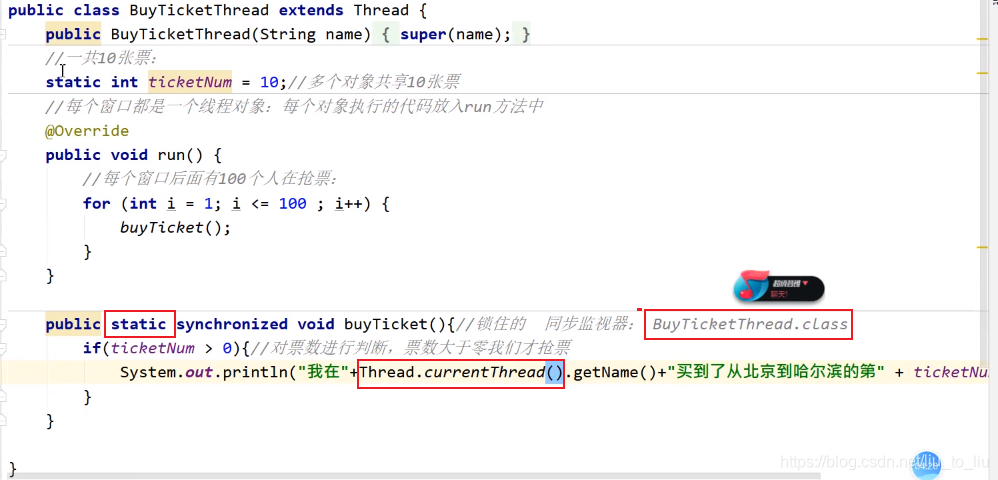
public class BuyTicketThread02 implements Runnable{
int ticketNum = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++){
if(ticketNum > 0) System.out.println("我在" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到了北京到哈尔滨的第"+ ticketNum-- +"张票");
}
}
}
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象,由于只有一个线程对象,所以车票不需要设置成静态变量,该对象也能争抢资源,实现Runnable与继承Thread类的区别
BuyTicketThread02 t = new BuyTicketThread02();
//窗口买票
Thread t1 = new Thread(t,"窗口1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(t,"窗口2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(t,"窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
- 继承Thread类:因单继承的局限性,用的比较少
- 实现Runnable接口:共享资源的能力也会强一些,不需要static修饰共享资源的变量
- 第一种方式和第二种方式, 都重写了run(),run()不足有两处:(1)、没有返回值;(2)、不能抛出异常;基于这两点不足,在JDK1.5以后出现了第三种创建线程的方式:实现Callable接口
- Thread类最终也要实现Runnable接口
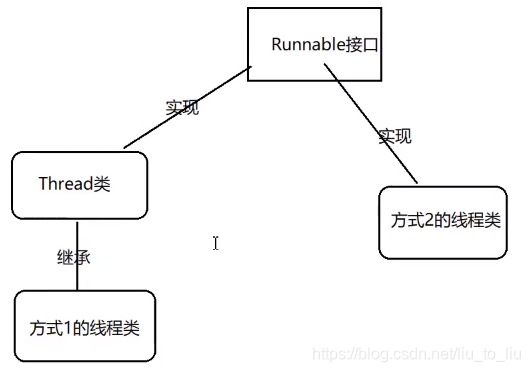
2.3 第三种方式
- 实现Callable接口
- 实现Callable接口的优点:
- (1)、有返回值
- (2)、能抛出异常
- (3)、缺点:创建线程比较麻烦
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class Test05 implements Callable<Integer> {
/**
* 实现Callable接口,可以不带泛型,如果 不带泛型,那么call方式的返回值就是Object类型
* 如果带泛型,那么call的返回值就是泛型对应的类型
* 从call方法看到: 方法有返回值,可以抛出异常
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return new Random().nextInt(10);//返回10以内的随机数
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//创建线程
Test05 t = new Test05();
FutureTask ft = new FutureTask(t);
Thread th = new Thread(ft);
th.start();
//获取线程得到的返回值
Object obj = ft.get();
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//1.创建Callable对象
Callable<Integer> callable = new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始计算。。。");
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
};
//2.把Callable对象转成可执行任务
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(callable);
//3.创建线程
Thread thread = new Thread(task);
//4.启动线程
thread.start();
//获取结果
Integer sum = task.get();
System.out.println("结果是:" + sum);
}
}
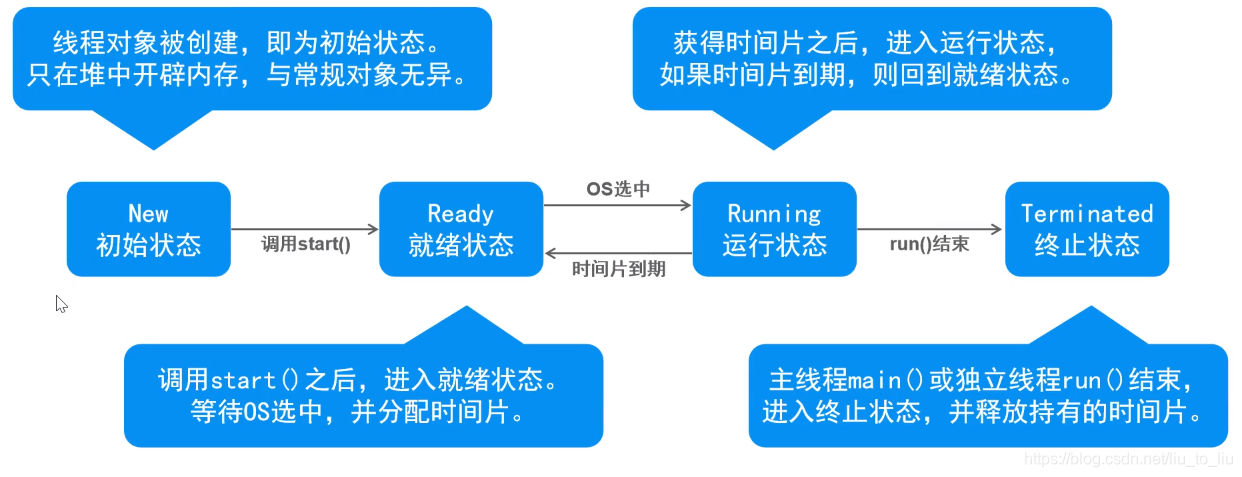
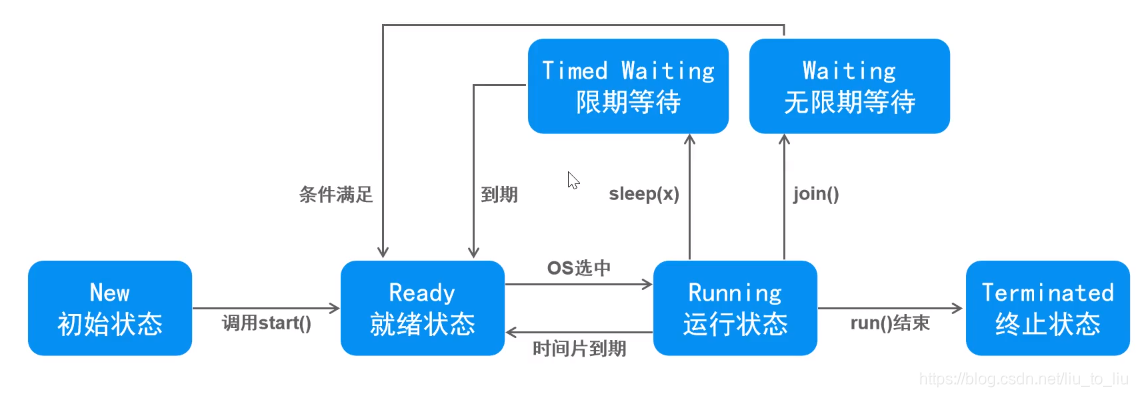
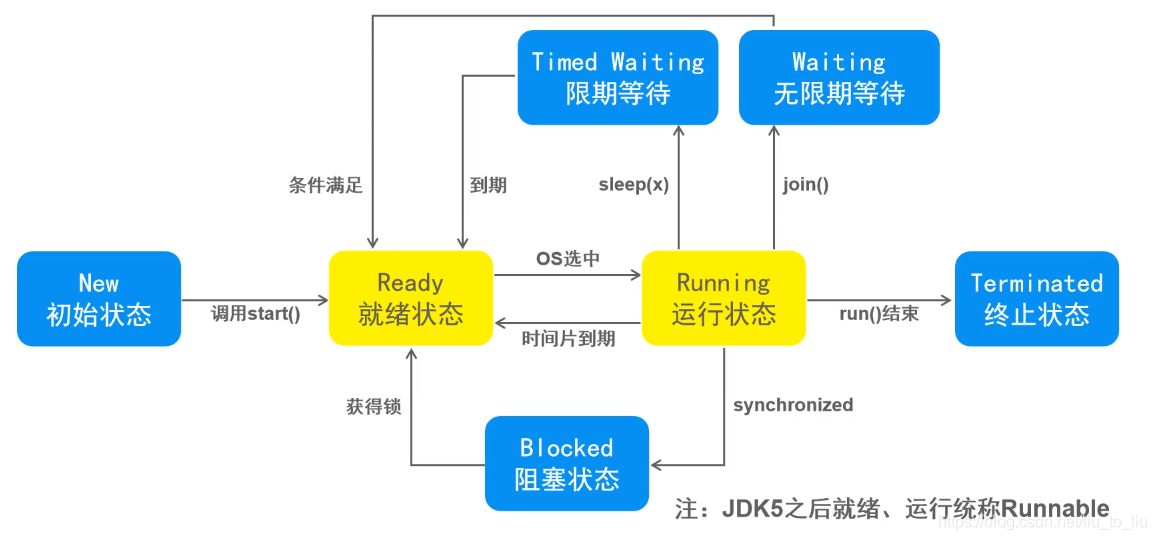
3、线程的生命周期
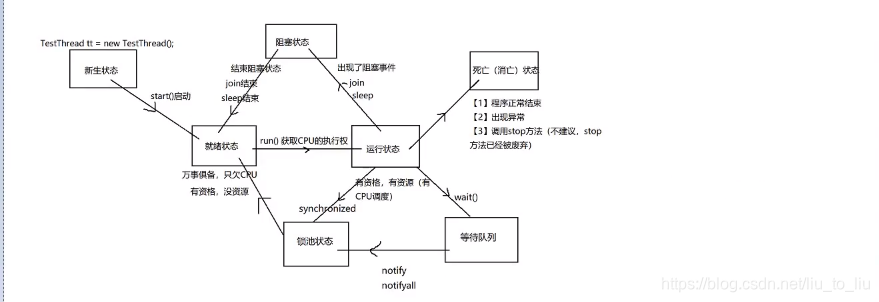
- 线程的基本状态
- 线程的状态(等待)
- 线程的状态(阻塞)
4、线程常用方法
- (1)、start():启动线程,表面上调用start(),实际在调用线程里的run()
- (2)、run():线程类继承Thread类或者实现Runnable接口的时候,都要重新实现这个run(),run()里面是线程要执行的内容
- (3)、currentThread:Thread类中一个静态方法:获取当前正在执行的线程
- (4)、setName():设置线程名称
- (5)、getName():获取线程名称
- (6)、线程优先级
- 同优先级的线程,采取的策略就是先到先服务,使用时间片celue
- 如果优先级别高,被CPU调度的概率高
- 级别:1-10 默认的级别为5

public class TestThread01 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
class TestThread02 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 20; i <= 30; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建两个子线程,让这两个子线程争抢资源
TestThread01 t1 = new TestThread01();
t1.setPriority(10);
t1.start();
TestThread02 t2 = new TestThread02();
t2.setPriority(1);
t2.start();
}
}
- (6)、join():当一个线程调用了join(),这个线程就会先被执行,它执行结束以后才可以去执行其余的线程。
注意:必须先start,再join才有效
public class TestThread extends Thread{
public TestThread(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(this.getName() + "----------" + i);
}
}
}
class Test1{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++){
if(i == 6){
//创建子线程
TestThread tt = new TestThread("子线程");
tt.start();
tt.join();
}
System.out.println("main-----" + i);
}
}
}
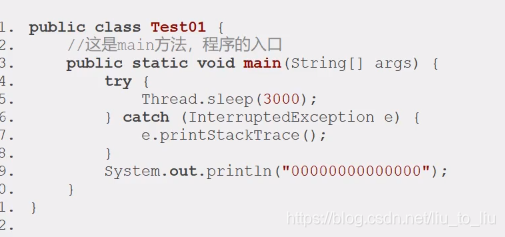
- (7)、sleep():人为的制造阻塞事件
- (8)、setDaemon():设置守护线程,子线程设置为主线程的守护线程,主线程停止了,子线程也不要继续执行了。
注意:先设置守护线程,再启动线程

public class TestThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程-----" + i);
}
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建并启动子线程
TestThread tt = new TestThread();
tt.setDaemon(true);//设置守护线程,注意:先设置,再启动
tt.start();
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main---" + i);
}
}
}
- (9)、stop():
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
if(i == 6){
Thread.currentThread().stop();//停止当前线程
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
- (10)、yield():当前线程主动放弃时间片,回到就绪状态,竞争下一次时间片
public class YieldThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ...... " + i);
Thread.yield();
}
}
}
class TestYield{
public static void main(String[] args) {
YieldThread y1 = new YieldThread();
YieldThread y2 = new YieldThread();
y1.start();
y2.start();
}
}
5、线程安全问题

-
(1)、出现了两个10张票或者3个10张票

-
(2)、出现0,1,-2的可能

-
出现了重票,错票都是线程安全引起的问题,原因:多个线程,在争抢资源的过程中 ,导致共享资源出现问题,一个线程还没执行完,另一个线程就参与进来了,开始争抢资源。
-
同步规则

解决线程安全问题:
5.1 同步代码块

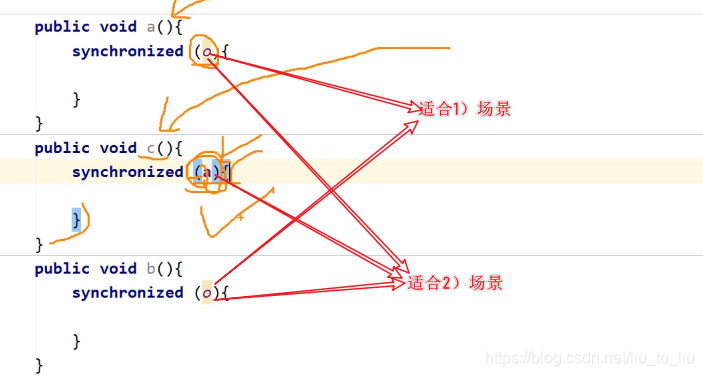
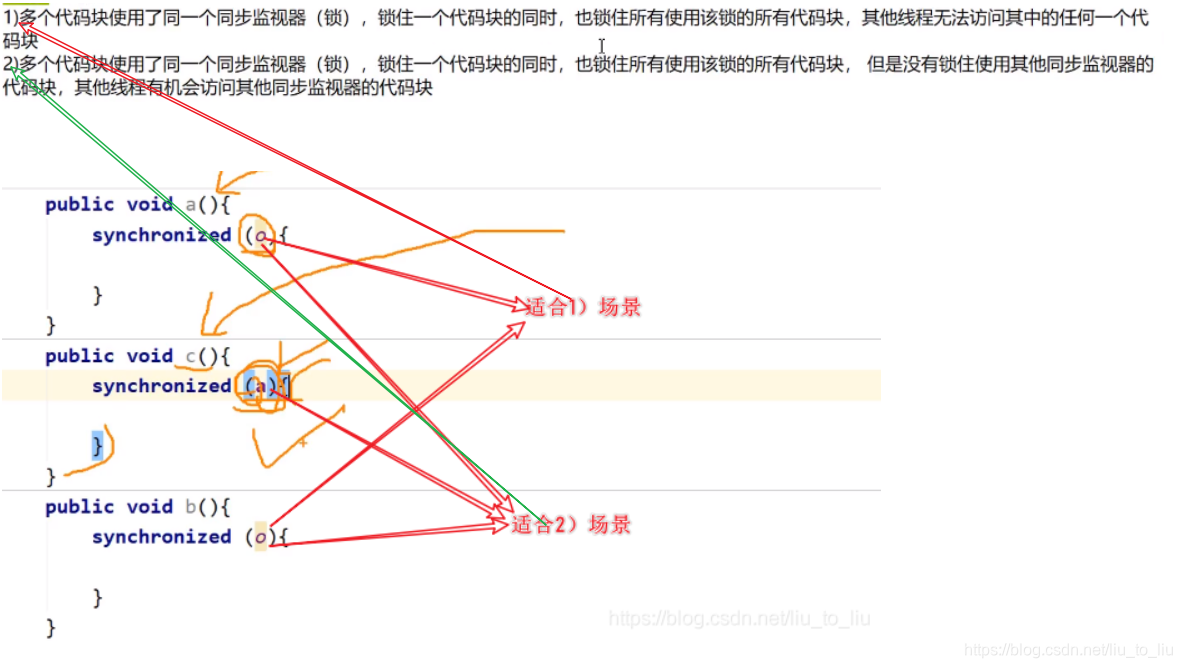
- 锁必须多个线程用的是同一把锁
- 字节码:字节码在内存中只加载一次,而且唯一。
- 字符串:字符串可作为锁,是因为在常量池独一份,但是
- this:如果是同一个对象执行的线程,可用this作为锁
- 锁的总结:

- 4)、5)对应的引用可能会改变,作为锁不友好,所以不推荐使用
- 6)对于Object来说,用final修饰后,地址是不能修改的,但是Object对象里面的属性是可以修改的,所以不推荐作为锁
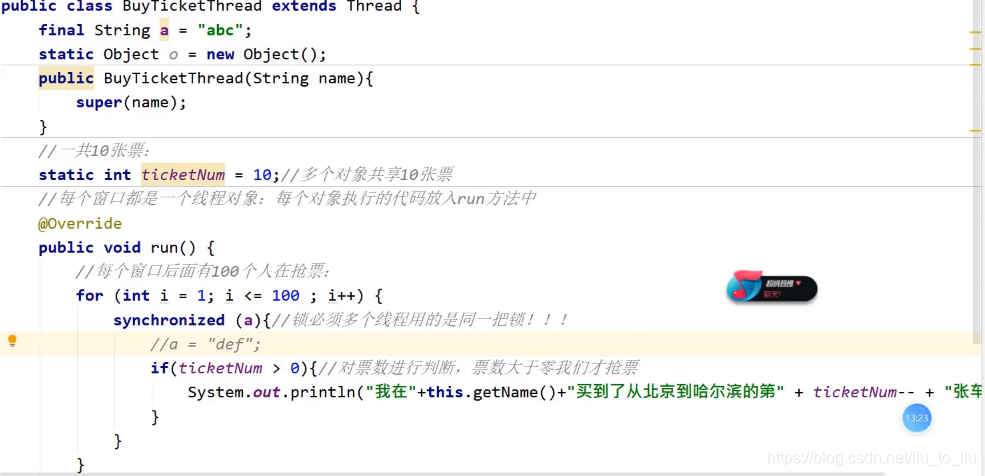
- 同步代码块的执行过程


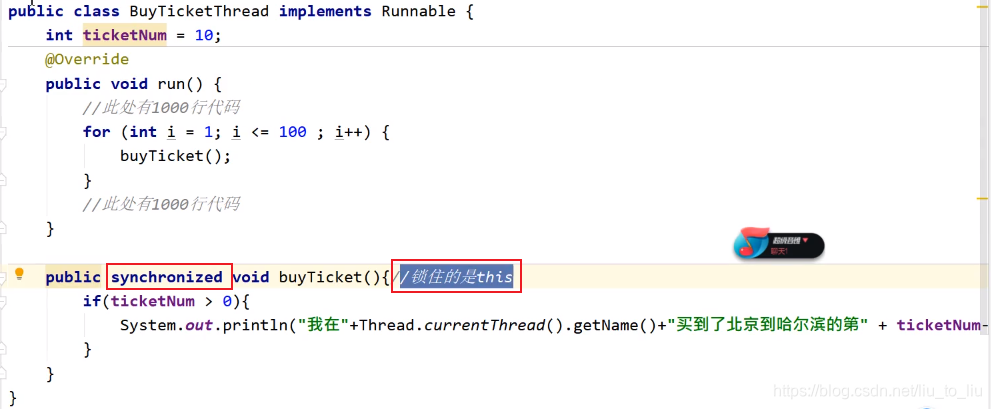
public class BuyTicketThread implements Runnable{
int ticketNum = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
synchronized(this){//把具有安全隐患的代码锁住即可,如果锁多了就会效率低
if(ticketNum > 0) System.out.println("我在" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到了北京到哈尔滨的第" + ticketNum);
}
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicketThread t = new BuyTicketThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(t,"窗口1");
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(t,"窗口2");
t2.start();
Thread t3 = new Thread(t,"窗口3");
t3.start();
}
}
5.2 同步方法



/**
* 票类(共享资源)
*/
public class Ticket implements Runnable{
private int ticket = 100;
//创建锁
private Object obj = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if(!sale()) break;
}
}
//买票方法
public synchronized boolean sale(){//锁:this
if(ticket <= 0) {
return false;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖了第" + ticket + "张票");
ticket--;
return true;
}
}
public class TestTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建票对象
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(ticket,"窗口1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(ticket,"窗口2");
Thread thread3 = new Thread(ticket,"窗口3");
Thread thread4 = new Thread(ticket,"窗口4");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread4.start();
}
}
- 死锁:尽可能避免出现死锁

/**
* 创建两个锁对象
*
*/
public class MyLock {
//两个锁
public static Object a = new Object();
public static Object b = new Object();
}
class Boy extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (MyLock.a){
System.out.println("男孩拿到了a");
synchronized (MyLock.b){
System.out.println("男孩拿到了b");
System.out.println("男孩可以吃东西了");
}
}
}
}
class Girl extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized(MyLock.b){
System.out.println("女孩拿到了b");
synchronized (MyLock.a){
System.out.println("女孩拿到了a");
System.out.println("女孩可以吃东西了");
}
}
}
}
class TestDeadLock{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boy boy = new Boy();
boy.start();
Girl girl = new Girl();
girl.start();
}
}
5.3 Lock
- JDK1.5后,新增Lock锁,与synchronized相比,lock可提供多种锁方案,更灵活
- Lock和synchronized的区别

5.3.1 ReetrantLock(重入锁)
- 重入锁:ReentrantLock---->Lock接口的实现类,与synchronized一样具有互斥锁功能

5.3.2 ReetrantReadWritedLock(读写锁)


5.3.3 线程安全的集合
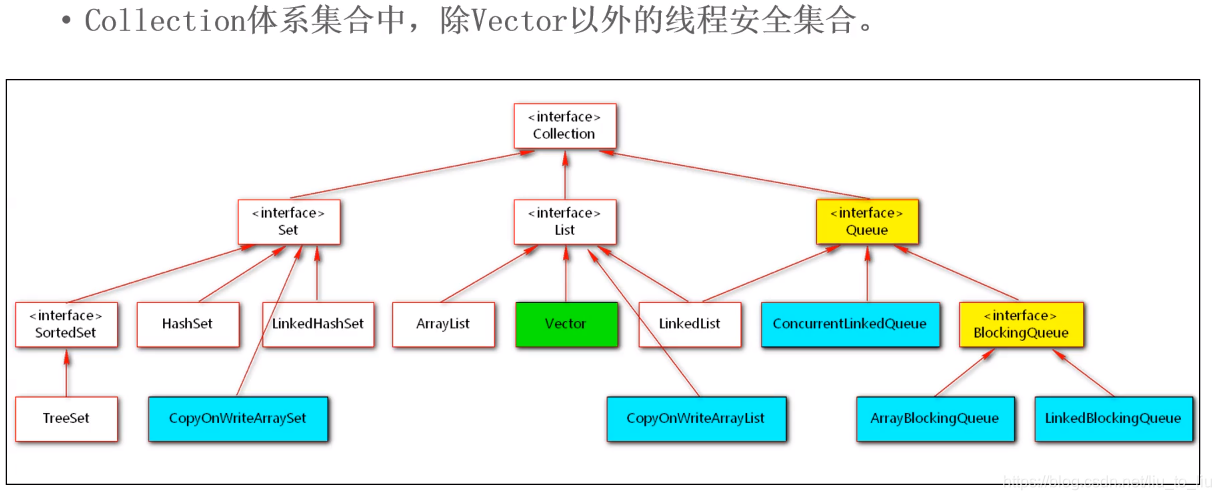
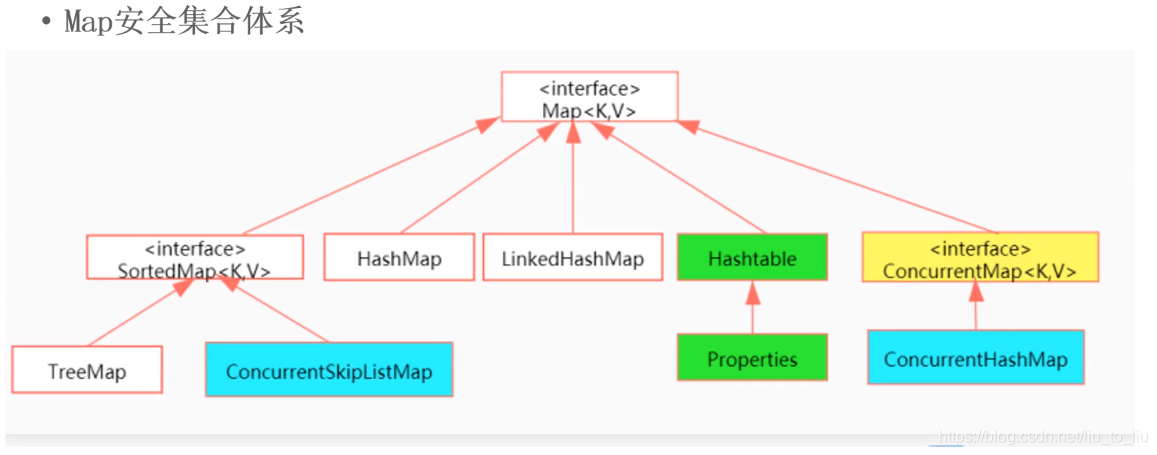
- Collections中的工具方法(以下方法均是JDK1.2提供的,不常用)

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建arrayList
// ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
//1.1使用Collections中的线程安全方法转成线程安全的集合(JDK1.5之前解决线程安全的方法)
// List<String> synList = Collections.synchronizedList(arrayList);
//1.2使用CopyOnWriteArrayList(JDK1.5之后)
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> arrayList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
//创建线程
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
int temp = i;
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
arrayList.add(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "====" + temp + "======" + j);
System.out.println(arrayList.toString() );
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
5.3.3.1 CopyOnWriteArrayList

import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* 使用多线程操作CopyOnWriteArrayList
*/
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
//使用多线程操作
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//提交任务
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
es.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==========" + new Random().nextInt(1000));
}
});
}
//关闭线程池
es.shutdown();
while(!es.isTerminated()){
}
System.out.println("元素个数:" + list.size());
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
5.3.3.2 CopyOnWriteArraySet

/**
* CopyOnWriteArraySet
*/
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
CopyOnWriteArraySet<String> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
//添加元素
set.add("pingguo");
set.add("tiaozi");
set.add("pingguo");
System.out.println("元素个数:" + set.size());
System.out.println(set.toString());
}
}
- 优先顺序
Lock----同步代码块(已经进入了方法体,分配了相应资源)----同步方法(在方法体之外)
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class BuyTicketThread implements Runnable{
int ticketNum = 10;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();//多态,接口=实现类 ,可以使用不同的实现类,扩展性好
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
lock.lock();
try {
if(ticketNum > 0) System.out.println("我在" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到了北京到哈尔滨的第" +
ticketNum-- + "张票");
}finally {
//关闭锁:--->即使有异常,这个锁也可以得到释放
lock.unlock();//使用try...finally,能保证lock锁关闭
}
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicketThread t = new BuyTicketThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(t,"窗口1");
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(t,"窗口2");
t2.start();
Thread t3 = new Thread(t,"窗口3");
t3.start();
}
}
应用案例
- 同步代码块
public class Product {//商品类
//品牌
private String brand;
//名字
private String name;
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class ProducerThread extends Thread{//生产者线程
//共享商品
private Product p;
public ProducerThread(Product p){
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {//生产10个商品
synchronized (p){
if((1&i) == 0){
//生产费列罗巧克力
p.setBrand("费列罗");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
p.setName("巧克力");
}else{
//生产哈尔滨啤酒
p.setBrand("哈尔滨");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
p.setName("啤酒");
}
//将生产信息做一个打印
System.out.println("生产者生产了:" + p.getBrand() + "-----------" + p.getName());
}
}
}
}
public class CustomerThread extends Thread{
//共享商品
private Product p;
public CustomerThread(Product p){
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (p){
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println("消费者消费了:" + p.getBrand() + "---------" + p.getName());
}
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//共享商品
Product p = new Product();
ProducerThread pt = new ProducerThread(p);
CustomerThread ct = new CustomerThread(p);
pt.start();
ct.start();
}
}
- 同步方法
public class Product {//商品类
//品牌
private String brand;
//名字
private String name;
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//生产商品
public synchronized void setProduct(String brand,String name){
this.setBrand(brand);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.setName(name);
//将生产信息做一个打印
System.out.println("生产者生产了:" + this.getBrand() + "-----------" + this.getName());
}
//消费商品
public synchronized void getProduct(){
System.out.println("消费者消费了:" + this.getBrand() + "---------" + this.getName());
}
}
public class ProducerThread extends Thread{//生产者线程
//共享商品
private Product p;
public ProducerThread(Product p){
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {//生产10个商品
if((1&i) == 0){
p.setProduct("费列罗","巧克力");
}else{
p.setProduct("哈尔滨","啤酒");
}
}
}
}
public class CustomerThread extends Thread{
//共享商品
private Product p;
public CustomerThread(Product p){
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
p.getProduct();
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//共享商品
Product p = new Product();
ProducerThread pt = new ProducerThread(p);
CustomerThread ct = new CustomerThread(p);
pt.start();
ct.start();
}
}
- 生产和消费交替执行
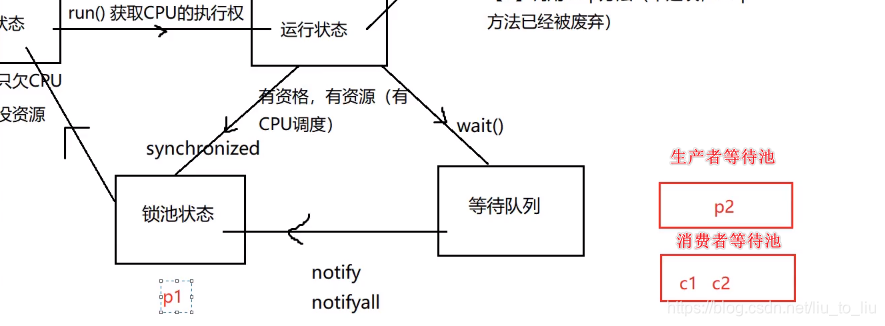
- 在java对象中,有两种池:
- (1)锁池—synchronized;
- (2)等待池—wait()、notify()、notifyAll(),
- 如果一个线程调用了某个对象的wait方法,那么该线程进入到对象的等待池中(并且已经将锁释放),如果未来的某一时刻,另外一个线程调用了 相同对象的notify方法或者notifyAll方法,那么该等待池中的线程就会被唤醒,然后进入到对象的锁池里面去获得该对象的锁,如果获得锁成功后,那么该线程就会沿着wait方法之后的路径继续执行。注意是沿着wait方法之后
- sleep和wait的区别
- sleep进入阻塞状态不释放锁
- wait进入阻塞状态释放锁
public class Product {//商品类
//品牌
private String brand;
//名字
private String name;
//判断是否有商品,false:无商品;true:有商品
boolean flag = false;//默认情况下没有商品 ,让生产者先生产,然后消费
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//生产商品
public synchronized void setProduct(String brand,String name){
//flag为true,表示有商品,生产者不生产,等消费者消费
if(flag == true){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.setBrand(brand);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.setName(name);
//将生产信息做一个打印
System.out.println("生产者生产了:" + this.getBrand() + "-----------" + this.getName());
//生产完成后,证明有商品
flag = true;
//通知消费者消费
notify();
}
//消费商品
public synchronized void getProduct(){
if(flag == false){//没有商品,等待生产者生产
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("消费者消费了:" + this.getBrand() + "---------" + this.getName());
//商品消费完
flag = false;
//通知生产者生产商品
notify();
}
}
public class ProducerThread extends Thread{//生产者线程
//共享商品
private Product p;
public ProducerThread(Product p){
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {//生产10个商品
if((1&i) == 0){
p.setProduct("费列罗","巧克力");
}else{
p.setProduct("哈尔滨","啤酒");
}
}
}
}
public class CustomerThread extends Thread{
//共享商品
private Product p;
public CustomerThread(Product p){
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
p.getProduct();
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//共享商品
Product p = new Product();
ProducerThread pt = new ProducerThread(p);
CustomerThread ct = new CustomerThread(p);
pt.start();
ct.start();
}
}
- 在JDK1.5中出现了Condition



import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Product {//商品类
//品牌
private String brand;
//名字
private String name;
//声明Lock锁
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//创建生产者的等待队列
Condition produceCondition = lock.newCondition();
//创建消费者的等待队列
Condition consumeCondition = lock.newCondition();
//判断是否有商品,false:无商品;true:有商品
boolean flag = false;//默认情况下没有商品 ,让生产者先生产,然后消费
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//生产商品
public void setProduct(String brand,String name){
lock.lock();
try {
//flag为true,表示有商品,生产者不生产,等消费者消费
if(flag == true){
try {
// wait();
//生产阻塞,生产者进入等待队列
produceCondition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.setBrand(brand);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.setName(name);
//将生产信息做一个打印
System.out.println("生产者生产了:" + this.getBrand() + "-----------" + this.getName());
//生产完成后,证明有商品
flag = true;
//通知消费者消费
// notify();
consumeCondition.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//消费商品
public void getProduct(){
lock.lock();
try {
if(flag == false){//没有商品,等待生产者生产
try {
// wait();
//消费者等待,消费者线程进入等待队列
consumeCondition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("消费者消费了:" + this.getBrand() + "---------" + this.getName());
//商品消费完
flag = false;
//通知生产者生产商品
// notify();
produceCondition.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class ProducerThread extends Thread{//生产者线程
//共享商品
private Product p;
public ProducerThread(Product p){
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {//生产10个商品
if((1&i) == 0){
p.setProduct("费列罗","巧克力");
}else{
p.setProduct("哈尔滨","啤酒");
}
}
}
}
public class CustomerThread extends Thread{
//共享商品
private Product p;
public CustomerThread(Product p){
this.p = p;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
p.getProduct();
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//共享商品
Product p = new Product();
ProducerThread pt = new ProducerThread(p);
CustomerThread ct = new CustomerThread(p);
pt.start();
ct.start();
}
}
5.4 线程通信

/**
* 银行卡
*/
public class BankCard {
//余额
private double money;
//标记
private boolean flag;//true:表示有钱可以取钱;false:表示没钱乐意存钱
//存钱
public synchronized void save(double m){//锁:this
if(flag){
try {
this.wait();//进入等待队列,同时也释放锁和CPU
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
money = money + m;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "存了 " + m + " 余额是:" + money);
flag = true;//有钱;修改标记
this.notify();//唤醒取钱线程
}
//取钱
public synchronized void take(double m){//锁:this
if(!flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
money = money - m;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "取了 " + m + " 余额是:" + money);
flag = false;//没钱;修改标记
this.notify();//唤醒存钱线程
}
}
/**
* 存钱
*/
class AddMoney implements Runnable{
private BankCard card;
public AddMoney(BankCard card){
this.card = card;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
card.save(1000);
}
}
}
/**
* 取钱
*/
class SubMoney implements Runnable{
private BankCard card;
public SubMoney(BankCard card){
this.card = card;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
card.take(1000);
}
}
}
/**
* 测试
*/
class TestBankCard{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建银行卡
BankCard card = new BankCard();
//创建存钱线程
AddMoney add = new AddMoney(card);
Thread t1 = new Thread(add,"小李");
t1.start();
//创建取钱线程
SubMoney sub = new SubMoney(card);
Thread t2 = new Thread(sub,"小红");
t2.start();
}
}
- 多存多取问题
/**
* 银行卡
*/
public class BankCard {
//余额
private double money;
//标记
private boolean flag;//true:表示有钱可以取钱;false:表示没钱乐意存钱
//存钱
public synchronized void save(double m){//锁:this
if(flag){
try {
this.wait();//进入等待队列,同时也释放锁和CPU
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
money = money + m;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "存了 " + m + " 余额是:" + money);
flag = true;//有钱;修改标记
this.notify();//唤醒取钱线程
}
//取钱
public synchronized void take(double m){//锁:this
if(!flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
money = money - m;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "取了 " + m + " 余额是:" + money);
flag = false;//没钱;修改标记
this.notify();//唤醒存钱线程
}
}
/**
* 存钱
*/
class AddMoney implements Runnable{
private BankCard card;
public AddMoney(BankCard card){
this.card = card;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
card.save(1000);
}
}
}
/**
* 取钱
*/
class SubMoney implements Runnable{
private BankCard card;
public SubMoney(BankCard card){
this.card = card;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
card.take(1000);
}
}
}
/**
* 测试
*/
class TestBankCard{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建银行卡
BankCard card = new BankCard();
//创建线程
AddMoney add = new AddMoney(card);
SubMoney sub = new SubMoney(card);
Thread t1 = new Thread(add,"晨晨");
Thread t2 = new Thread(add,"明明");
Thread t3 = new Thread(sub,"冰冰");
Thread t4 = new Thread(sub,"莉莉");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}
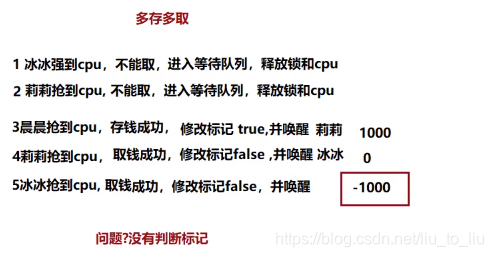
- 全部等待问题
/**
* 银行卡
*/
public class BankCard {
//余额
private double money;
//标记
private boolean flag;//true:表示有钱可以取钱;false:表示没钱乐意存钱
//存钱
public synchronized void save(double m){//锁:this
while(flag){
try {
this.wait();//进入等待队列,同时也释放锁和CPU
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
money = money + m;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "存了 " + m + " 余额是:" + money);
flag = true;//有钱;修改标记
//this.notify();//唤醒取钱线程
this.notifyAll();
}
//取钱
public synchronized void take(double m){//锁:this
while(!flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
money = money - m;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "取了 " + m + " 余额是:" + money);
flag = false;//没钱;修改标记
//this.notify();//唤醒存钱线程
this.notifyAll();
}
}
/**
* 存钱
*/
class AddMoney implements Runnable{
private BankCard card;
public AddMoney(BankCard card){
this.card = card;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
card.save(1000);
}
}
}
/**
* 取钱
*/
class SubMoney implements Runnable{
private BankCard card;
public SubMoney(BankCard card){
this.card = card;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
card.take(1000);
}
}
}
/**
* 测试
*/
class TestBankCard{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建银行卡
BankCard card = new BankCard();
//创建线程
AddMoney add = new AddMoney(card);
SubMoney sub = new SubMoney(card);
Thread t1 = new Thread(add,"晨晨");
Thread t2 = new Thread(add,"明明");
Thread t3 = new Thread(sub,"冰冰");
Thread t4 = new Thread(sub,"莉莉");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}
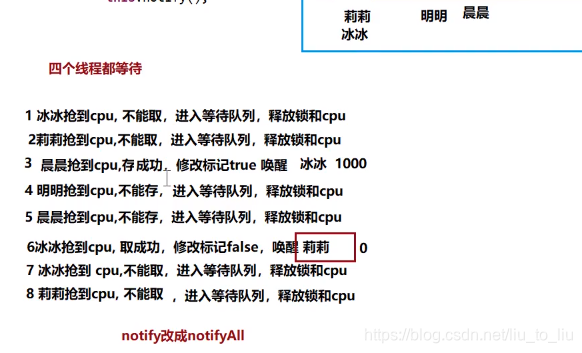
- 经典问题

5.5 Queue接口(队列)

import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建队列,线程不安全
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//入队
queue.offer("苹果");
queue.offer("AA");
queue.offer("BB");
//出队
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println("元素个数:" + queue.size());
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
System.out.println("出队完毕:" + queue.size());
}
}
5.5.1 ConcurrentLinkedQueue
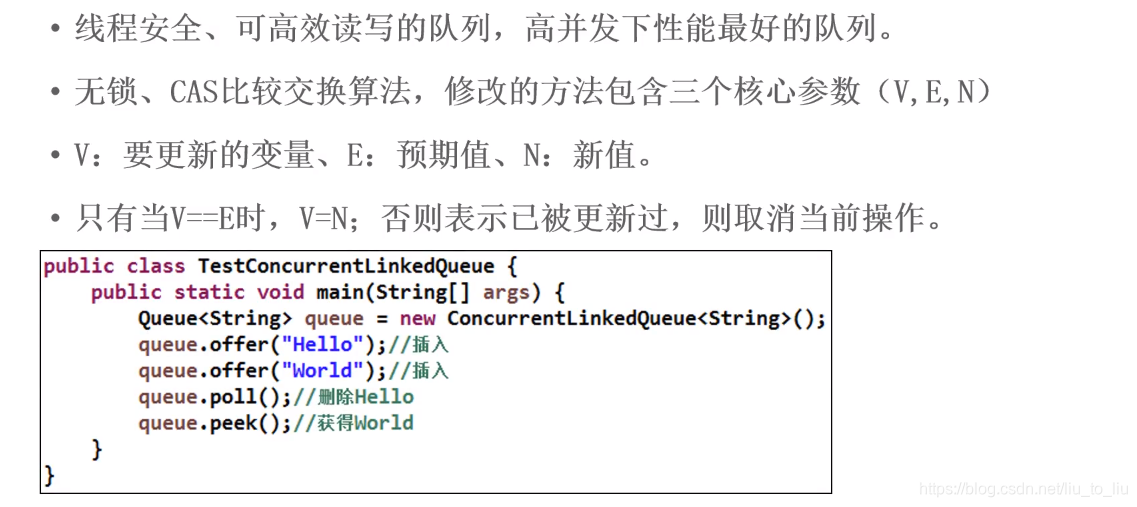
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建安全队列
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Integer> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
//入队操作
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
queue.offer(i);
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 6;i <= 10;i++){
queue.offer(i);
}
}
});
//启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
//出队操作
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}
}
5.5.2 BlockingQueue接口(阻塞队列)


import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
/**
* 阻塞队列
* 案例1:创建一个有界队列,添加元素
*
*/
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建一个有界队列,添加数据
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5);
//添加元素
queue.put("aaaa");
queue.put("abaa");
queue.put("asaaa");
queue.put("baaa");
queue.put("baaa");
//删除元素
queue.take();
System.out.println(queue);
queue.put("hhhhhhhh");
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
5.5.3 ConcurrentHashMap

import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
ConcurrentHashMap<String,String> hashMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//使用多线程添加数据
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) {
hashMap.put(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---" + k,k + "");
System.out.println(hashMap);
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
6、线程池

6.1 线程池原理
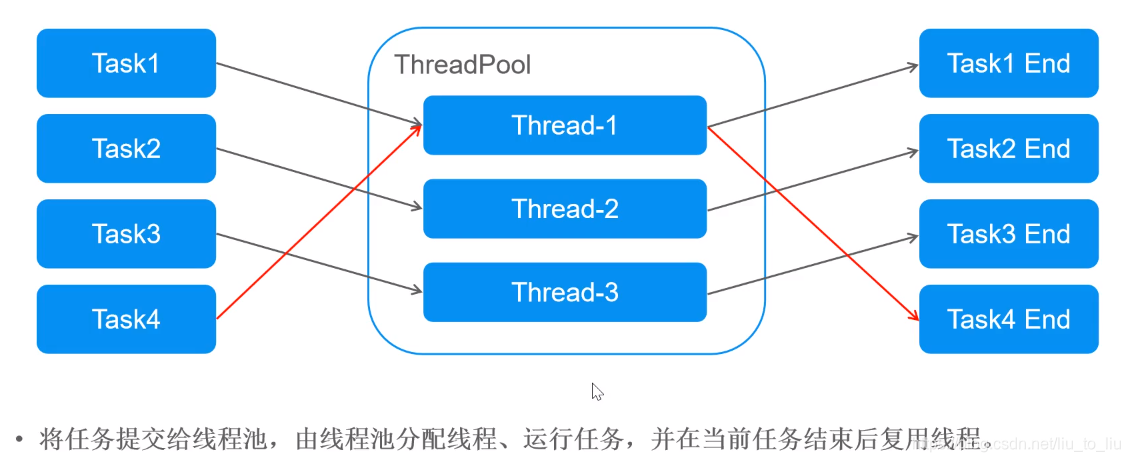
6.2 创建线程池
- 常用的线程池接口和类(所在包java.util.concurrent)
- Executor:线程池的顶级接口
- ExecutorService:线程池接口,可通过submit(Runnable task)提交任务代码
- Executors工厂类:通过此类可以获得一个线程池
- 通过newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)获取固定数量的线程池。参数:指定线程池中线程的数量
- 通过newCachedThreadPool()获得动态数量的线程池,如不够则创建新的,没有上限
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* Executor:线程池的根接口
* ExecutorService:包含管理线程池的一些方法,submit shutdown
* ThreadPoolExecutor
* ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
* Executors:创建线程池的工具类
* (1)创建固定线程个数线程池
* (2)创建缓存线程池,由任务的多少决定
* (3)创建单线程池
* (4)创建调度线程池 调度:周期、定时执行
*/
public class ThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.1 创建固定线程个数
//ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
//1.2 创建缓存线程池,线程个数是由任务决定的
ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//1.3 创建单线程池(使用较少)
//ExecutorService es = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//1.4 创建调度线程池
//Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(corePoolSize);
//创建任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
private int ticket = 100;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if(ticket <= 0){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买了第" + ticket + "张票");
ticket--;
}
}
};
//提交任务
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
es.submit(runnable);
}
//关闭线程池
es.shutdown();//等待所有任务执行完毕,关闭线程池
//es.shutdownNow();//立即关闭
}
}
6.3 Callable与线程池结合使用
- Future接口
-
表示将要完成任务的结果
-
表示ExecutorService.submit()所返回的状态结果,就是call()的返回值
-
方法:V get()以阻塞形式等待Future中的异步处理结果(call()的返回值)
-
线程同步:形容一次方法调用,同步一旦开始,调用者必须等待该方法返回,才能继续,单条执行路径
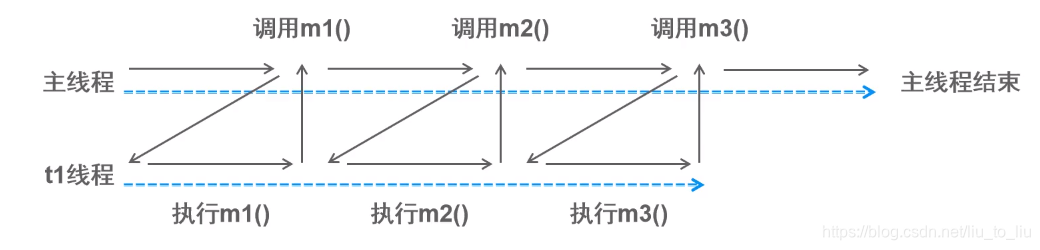
-
线程异步:形容一次方法调用,异步一旦开始,像是一次消息传递,调用者告知之后立刻返回。二者竞争时间片,并发执行,多条执行路径
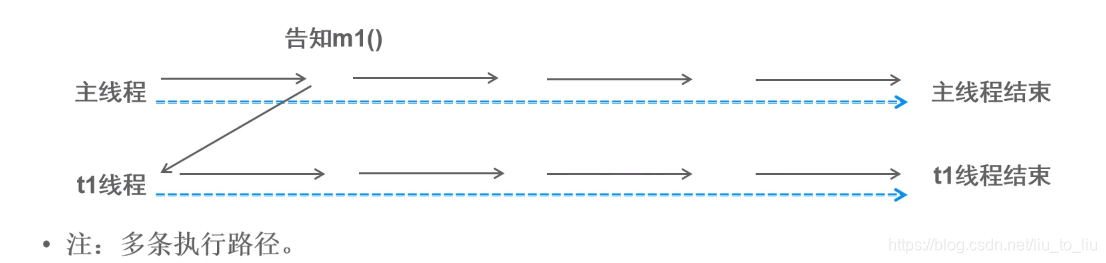
-
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* 使用线程池计算100以内的和
*
*/
public class ThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//创建线程池
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
//提交任务;Future:表示将要执行的结果
Future<Integer> future = es.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始计算了。。。");
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
});
//获取任务结果,get()等待call()任务执行完毕才会返回
System.out.println(future.get());
//关闭线程池
es.shutdown();
}
}





 本文深入探讨了Java中的多线程,包括线程的创建方式(继承Thread、实现Runnable、实现Callable)、线程生命周期、常用方法、线程安全问题(同步代码块、同步方法、Lock接口)、线程池的工作原理及创建,以及Callable与线程池的结合使用。通过实例展示了如何解决线程安全问题,如死锁和线程通信,还介绍了并发集合(CopyOnWriteArrayList、CopyOnWriteArraySet)以及阻塞队列 BlockingQueue。最后,文章讲解了线程池的ExecutorService和ThreadPoolExecutor,强调了线程池在管理线程资源中的重要性。
本文深入探讨了Java中的多线程,包括线程的创建方式(继承Thread、实现Runnable、实现Callable)、线程生命周期、常用方法、线程安全问题(同步代码块、同步方法、Lock接口)、线程池的工作原理及创建,以及Callable与线程池的结合使用。通过实例展示了如何解决线程安全问题,如死锁和线程通信,还介绍了并发集合(CopyOnWriteArrayList、CopyOnWriteArraySet)以及阻塞队列 BlockingQueue。最后,文章讲解了线程池的ExecutorService和ThreadPoolExecutor,强调了线程池在管理线程资源中的重要性。
















 3083
3083

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








