前面我们学习到了多线程的一些概念,现在跟着我一起学习多线程的常用的方法吧
1.获得线程的各种属性
1.1获得线程对象
Thread.currentThread()
1.2获得当前执行的方法名
Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getMethodName()
1.3获得线程对象名
线程对象.getName()
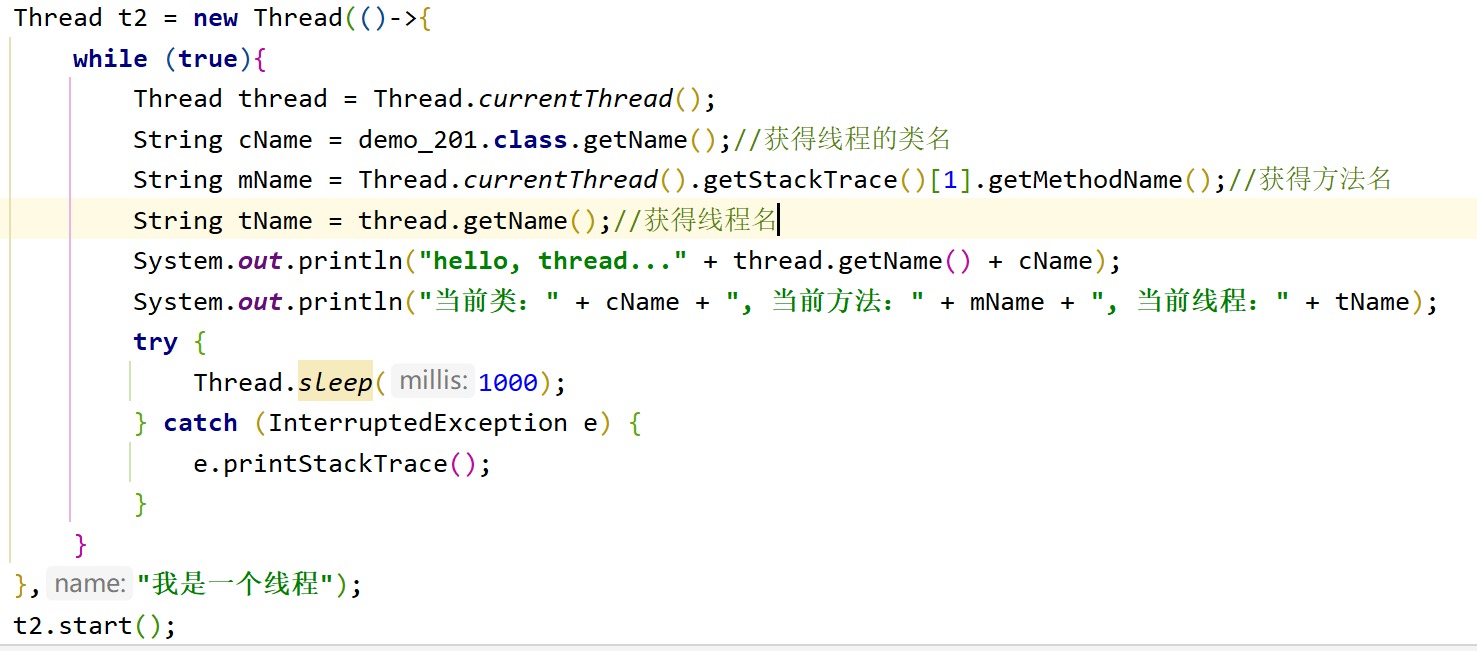

通过类 + 方法 + 线程名的写法能构成线程的日志,在工作中更好的找到问题所在
2.得到线程的各种状态



3.后台线程
线程名.setDaemor(true);
设置成后台线程之后,当执行到main就会结束
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
System.out.println("thread....");
}
});
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
System.out.println("线程是否存活" + thread.isAlive());
System.out.println("main.....");
}

前台线程可以阻止进程的退出,后台线程不可以阻止进程的推出
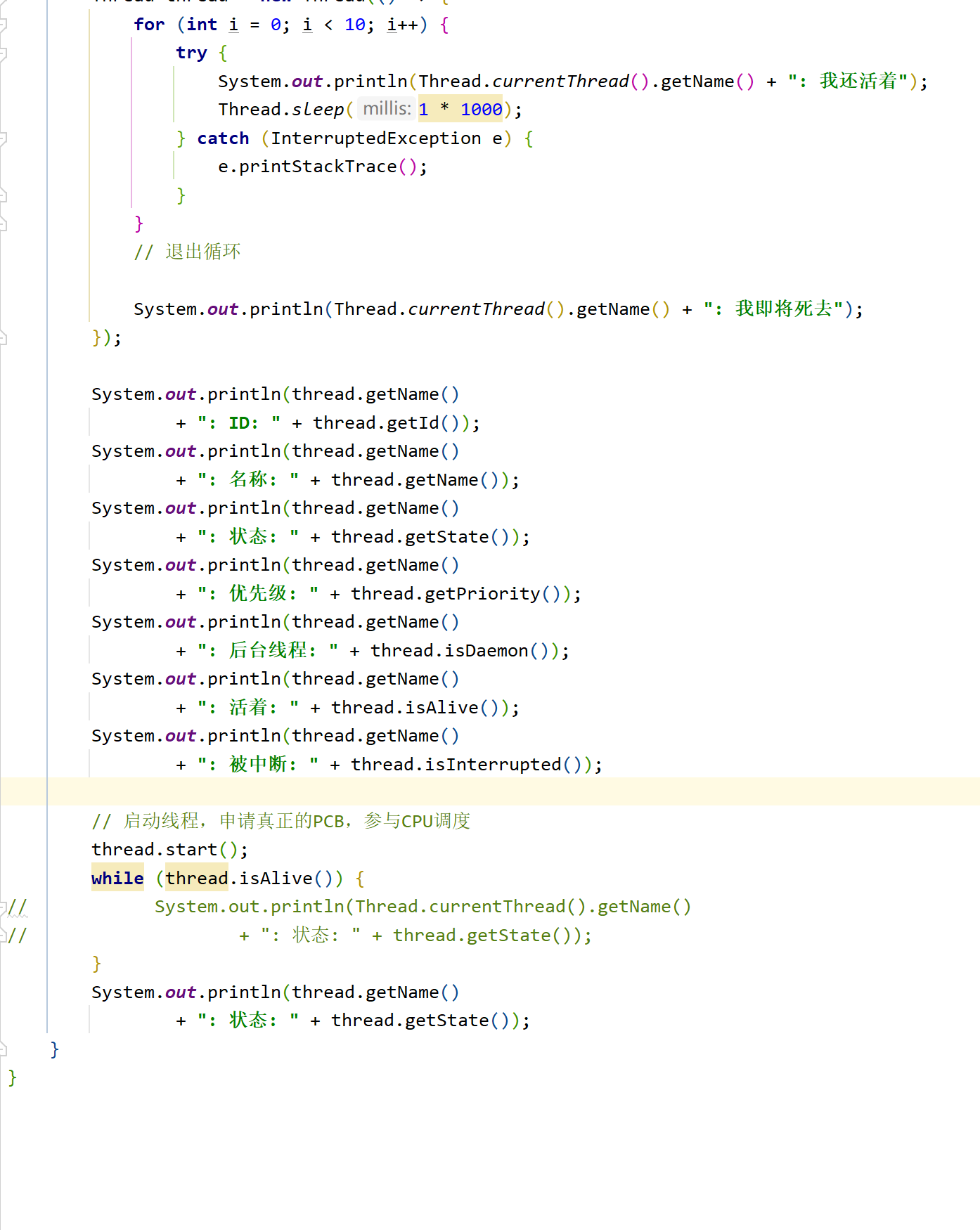
4.线程是否存活
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread th = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("hello thread.....");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println("启动前线程是否存活" + th.isAlive());
th.start();
System.out.println("启动后线程是否存活" + th.isAlive());
th.join();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("线程结束后是否存活" + th.isAlive());
}
5.线程中断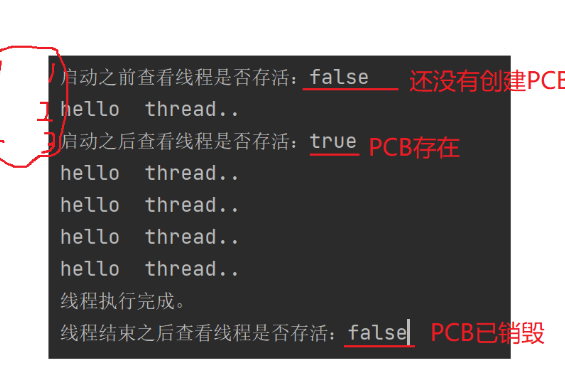
方法一:设置全局变量,通过更改全局变量来改变线程内循环的变量来中断
static boolean iQuit = false;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread th = new Thread(()->{
while(!iQuit){
System.out.println("hello ,thread...");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程退出。。。");
});
th.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
iQuit = true;
}

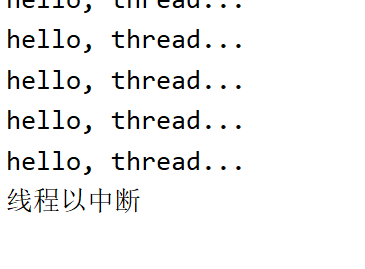
方法二:通过编译器内置的函数,循环内写
!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()
然后在结尾可以对变量进行更改
线程名.interrupt();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread th = new Thread(()->{
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("hello, thread...");
// try {
// Thread.sleep(100);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// System.out.println("休眠被中断");
// break;
// }
}
System.out.println("线程以中断");
});
th.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
th.interrupt();
}
当中断过程中如果有sleep的话,会报错然后将sleep中断,然后继续进行线程,这时就需要在异常处手动退出即可
未手动退出时
手动退出时
6.线程等待-join()方法
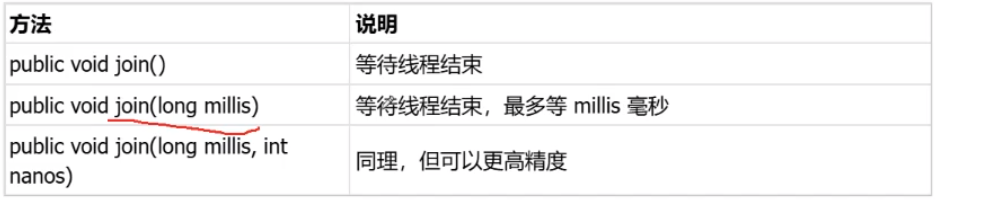
等待线程走完后才能进行下一步
 多线程常用方法介绍
多线程常用方法介绍




















 2788
2788

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








