1.内容简介:
本篇继续分析Android Binder机制相关源代码,主要从Native(c++)层到driver层的相关组件已经代码调用流程。
前面的几篇,可以移步至:
1). Android系统源码分析-进程间通信机制binder(一):守护进程servicemanager
2) . Android系统源码分析-进程间通信机制binder(二):binder内存映射
3) . Android系统源码分析-进程间通信机制binder(三):从framework层到Native层
2.Native Binder架构:
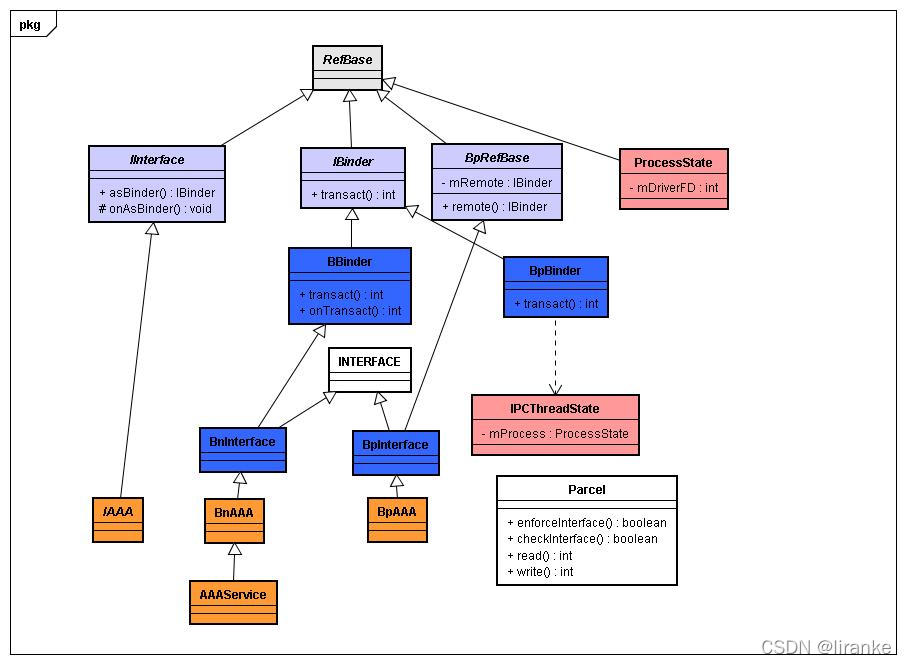
在Android系统源码分析-进程间通信机制binder(三):从framework层到Native层一文中,已经分析了整个Binder架构,以及Binder在framework层的相关组件。现在,来看一下在native层的相关组件,如图:
代码位置:
头文件目录:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/,
具体实现的cpp文件目录:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/ 。
其中,
1)IInterface(在IInterface.h头文件中):该类是一个虚基类(可以看作是java中的接口,但又不完全一样,因为C++中的虚基类和java中的接口有相同点但又有不同电),用户必须继承该类,并且实现onAsBinder函数。它的声明如下:
class IInterface : public virtual RefBase
{
public:
IInterface();
sp<IBinder> asBinder();
sp<const IBinder> asBinder() const;
protected:
virtual ~IInterface();
virtual IBinder* onAsBinder() = 0;
};可以看到,onAsBinder() = 0; 的返回知识IBinder的指针,而且,virtual关键字表示需要子类必须重写该方法。
2)BnInterface(在IInterface.h头文件中):是一个模版类,而且是BBinder的子类,需要重写BBinder的onTransact方法;同时,BnInterface还继承了INTERFACE。在C++中,一个累可以继承自多个父类。
3)BpInterface(在IInterface.h头文件中):是一个模版类,而且是BpRefBase的子类,需要重写BpRefBase的remote方法,而且BpRefBase中还有IBinder类型的数据乘员mRemote,它指向的就是服务的实现方;同时,BpInterface还继承了INTERFACE。
BnInterface和BpInterface的声明如下:
template<typename INTERFACE>
class BnInterface : public INTERFACE, public BBinder
{
public:
virtual sp<IInterface> queryLocalInterface(const String16& _descriptor);
virtual const String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const;
protected:
virtual IBinder* onAsBinder();
};
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
template<typename INTERFACE>
class BpInterface : public INTERFACE, public BpRefBase
{
public:
BpInterface(const sp<IBinder>& remote);
protected:
virtual IBinder* onAsBinder();
};4)IBinder(IBinder.h):它是BBinder和BpBinder的父类,是一个虚基类,提供transact函数供子类实现;
class IBinder : public virtual RefBase
{
......
virtual status_t transact( uint32_t code,
const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply,
uint32_t flags = 0) = 0;
......
}5)BBinder(Binder.h):IBinder的子类,必须实现transact函数,它代表着本地对象;
6)BpBinder(BpBinder.h):IBinder的子类,必须实现transact函数,它代表着远程对象;
7)ProcessState和IPCProcessState:用于提供Binder进程间通信的管理,包括和Binder驱动的交互。
8)Parcel:是java到Native层的数据结构;在Binder进程间通信时,需要进行传递的数据就封装在Parcel实例中。
9)INTERFACE: 是类模版的指代。在C++中,用template<class T>来声明一个类模版。所以,这里的INTERFACE其实相当于template<class T>中的T。具体是哪个类,答案就是T的子类。在Android Binder Native机制中,INTERFACE就是实现Binder服务接口的基类。
Binder库的编译:
Binder库最终会编译成一个动态链接库:libbinder.so,供其他进程链接使用。
对应的Android.mk编译文件:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/Android.mk,如下:
# Copyright (C) 2009 The Android Open Source Project
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# we have the common sources, plus some device-specific stuff
sources := \
Binder.cpp \
BpBinder.cpp \
IInterface.cpp \
IMemory.cpp \
IPCThreadState.cpp \
IPermissionController.cpp \
IServiceManager.cpp \
MemoryDealer.cpp \
MemoryBase.cpp \
MemoryHeapBase.cpp \
Parcel.cpp \
PermissionCache.cpp \
ProcessState.cpp \
Static.cpp
LOCAL_PATH:= $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_LDLIBS += -lpthread
LOCAL_MODULE := libbinder
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := liblog libcutils libutils
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(sources)
include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_LDLIBS += -lpthread
LOCAL_MODULE := libbinder
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(sources)
include $(BUILD_STATIC_LIBRARY)
3.Native Binder代码分析:
在介绍完各个组件功能后,来看一下这些组件的代码执行流程。
IPCThreadState负责了与驱动通信的细节处理,它也是初始化Native binder的入口,所以,从这个类入手进行分析。
在 Android系统源码分析-进程间通信机制binder(三):从framework层到Native层 一文中的最后,分析到IPCThreadState这个类。
接着IPCThreadState这个入口继续分析:
IPCThreadState的初始化:
IPCThreadState::IPCThreadState()
: mProcess(ProcessState::self()),
mMyThreadId(androidGetTid()),
mStrictModePolicy(0),
mLastTransactionBinderFlags(0)
{
pthread_setspecific(gTLS, this);
clearCaller();
mOrigCallingUid = mCallingUid;
mIn.setDataCapacity(256);
mOut.setDataCapacity(256);
}ProcessState采用单利模式(Singleton),在一个进程中,只会存在一个实例。通过ProcessState::self()函数来获取这个实例,从而调用到ProcessState的构造函数。ProcessState的构造函数,如下:
ProcessState::ProcessState()
: mDriverFD(open_driver())
, mVMStart(MAP_FAILED)
, mManagesContexts(false)
, mBinderContextCheckFunc(NULL)
, mBinderContextUserData(NULL)
, mThreadPoolStarted(false)
, mThreadPoolSeq(1)
{
if (mDriverFD >= 0) {
// XXX Ideally, there should be a specific define for whether we
// have mmap (or whether we could possibly have the kernel module
// availabla).
#if !defined(HAVE_WIN32_IPC)
// mmap the binder, providing a chunk of virtual address space to receive transactions.
mVMStart = mmap(0, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0);
if (mVMStart == MAP_FAILED) {
// *sigh*
ALOGE("Using /dev/binder failed: unable to mmap transaction memory.\n");
close(mDriverFD);
mDriverFD = -1;
}
#else
mDriverFD = -1;
#endif
}
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mDriverFD < 0, "Binder driver could not be opened. Terminating.");
}首先,open_driver():
static int open_driver()
{
int fd = open("/dev/binder", O_RDWR);
if (fd >= 0) {
fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
int vers;
status_t result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_VERSION, &vers);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to obtain version failed: %s", strerror(errno));
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
if (result != 0 || vers != BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION) {
ALOGE("Binder driver protocol does not match user space protocol!");
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
size_t maxThreads = 15;
result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS, &maxThreads);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to set max threads failed: %s", strerror(errno));
}
} else {
ALOGW("Opening '/dev/binder' failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
return fd;
}分析:open_driver的主要作用:
1)打开binder驱动设备文件“/dev/binder”;
2)检测版本号;
3)设置最大线程数。
都是通过ioctl系统调用完成的。
然后,mVMStart = mmap(0, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0);
IPCThreadState类中的关键几个方法说明如下:
transact: 供代理类Proxy发送数据到驱动,并读取返回结果;
sendReply: 供Server端写回请求的返回结果;
waitForResponse: 发送请求后等待响应结果;
talkWithDriver: 通过ioctl BINDER_WRITE_READ来与驱动通信;
writeTransactionData: 写入一次事务的数据;
executeCommand: 处理binder_driver_return_protocol协议命令;
freeBuffer: 通过BC_FREE_BUFFER命令释放Buffer。
线程管理:
再来分析一下ProcessState中对线程的管理,看一下setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount的实现:
status_t ProcessState::setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(size_t maxThreads) {
status_t result = NO_ERROR;
if (ioctl(mDriverFD, BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS, &maxThreads) == -1) {
result = -errno;
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to set max threads failed: %s", strerror(-result));
}
return result;
}DEFAULT_MAX_BINDER_THREADS就是Binder服务支持的最大线程数。
驱动在运行过程中,会根据需要,并在没有超过上限的情况下,通过BR_SPAWN_LOOPER命令通知进程创建线程:
status_t IPCThreadState::executeCommand(int32_t cmd)
{
BBinder* obj;
RefBase::weakref_type* refs;
status_t result = NO_ERROR;
switch (cmd) {
case BR_ERROR:
result = mIn.readInt32();
break;
case BR_OK:
break;
case BR_ACQUIRE:
......
case BR_TRANSACTION:
......
case BR_SPAWN_LOOPER:
mProcess->spawnPooledThread(false);
break;
default:
printf("*** BAD COMMAND %d received from Binder driver\n", cmd);
result = UNKNOWN_ERROR;
break;
}
if (result != NO_ERROR) {
mLastError = result;
}
return result;
}ProcessState::spawnPooledThread的实现:
void ProcessState::spawnPooledThread(bool isMain)
{
if (mThreadPoolStarted) {
int32_t s = android_atomic_add(1, &mThreadPoolSeq);
char buf[16];
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "Binder_%X", s);
ALOGV("Spawning new pooled thread, name=%s\n", buf);
sp<Thread> t = new PoolThread(isMain);
t->run(buf);
}
}PoolThread的声明:(代码位于ProcessState.cpp文件中)
class PoolThread : public Thread
{
public:
PoolThread(bool isMain)
: mIsMain(isMain)
{
}
protected:
virtual bool threadLoop()
{
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool(mIsMain);
return false;
}
const bool mIsMain;
};joinThreadPool就将创建的线程添加到线程池里。
这样,一个线程的初始化就完成了。






















 9737
9737

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










