一、示例,我们从最简单的GET命令开始。
RBucket<Object> t = redissonClient.getBucket("syncTradeUid_idOff");
int idOff = (int)t.get();
二、springboot的Redission自动配置
@Order(value = 4001)
@ConditionalOnProperty("redisson.password")
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({RedissonProperties.class})
public class RedissonAutoConfiguration {
public RedissonAutoConfiguration() {
System.out.println("==========================redis 初始化成功=======================");
}
@Autowired
private RedissonProperties redissonProperties;
@Bean(name = "redissonClient")
@ConditionalOnProperty(name="redisson.address")
RedissonClient redissonSingle() {
Config config = new Config();
config.setCodec(new FastJsonCodec());
SingleServerConfig serverConfig = config.useSingleServer()
.setAddress(redissonProperties.getAddress())
.setTimeout(redissonProperties.getTimeout())
.setConnectionPoolSize(redissonProperties.getConnectionPoolSize())
.setConnectionMinimumIdleSize(redissonProperties.getConnectionMinimumIdleSize());
if(!StrUtil.isEmpty(redissonProperties.getPassword())) {
serverConfig.setPassword(redissonProperties.getPassword());
}
return Redisson.create(config);
}
/**
* 哨兵模式自动装配
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "redissonClient")
@ConditionalOnProperty(name="redisson.masterName")
RedissonClient redissonSentinel() {
Config config = new Config();
config.setCodec(new FastJsonCodec());
SentinelServersConfig serverConfig = config.useSentinelServers().addSentinelAddress(redissonProperties.getSentinelAddresses())
.setMasterName(redissonProperties.getMasterName())
.setTimeout(redissonProperties.getTimeout())
.setMasterConnectionPoolSize(redissonProperties.getMasterConnectionPoolSize())
.setSlaveConnectionPoolSize(redissonProperties.getSlaveConnectionPoolSize())
.setReadMode(ReadMode.SLAVE);
if(!StrUtil.isEmpty(redissonProperties.getPassword())) {
serverConfig.setPassword(redissonProperties.getPassword());
}
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
application.properites
#单机
redisson.address = redis://127.0.0.1:6379
redisson.password =
#哨兵
#redisson.masterName=BF-20190319DBXF
#redisson.schema=redis://
#redisson.sentinelAddresses=redis://127.0.0.1:26379,redis://127.0.0.1:26479,redis://127.0.0.1:26579
#redisson.password=三、REDISSION自动配置初始化流程
1.从Redisson.create(config)创建redission对象开始。Redission继承于
RedissonClient

2. 创建连接管理器对象
org.redisson.config.ConfigSupport
public static ConnectionManager createConnectionManager(Config configCopy) {
UUID id = UUID.randomUUID();
if (configCopy.getMasterSlaveServersConfig() != null) {
validate(configCopy.getMasterSlaveServersConfig());
return new MasterSlaveConnectionManager(configCopy.getMasterSlaveServersConfig(), configCopy, id);
} else if (configCopy.getSingleServerConfig() != null) {
validate(configCopy.getSingleServerConfig());
return new SingleConnectionManager(configCopy.getSingleServerConfig(), configCopy, id);
} else if (configCopy.getSentinelServersConfig() != null) {
validate(configCopy.getSentinelServersConfig());
return new SentinelConnectionManager(configCopy.getSentinelServersConfig(), configCopy, id);
} else if (configCopy.getClusterServersConfig() != null) {
validate(configCopy.getClusterServersConfig());
return new ClusterConnectionManager(configCopy.getClusterServersConfig(), configCopy, id);
} else if (configCopy.getReplicatedServersConfig() != null) {
validate(configCopy.getReplicatedServersConfig());
return new ReplicatedConnectionManager(configCopy.getReplicatedServersConfig(), configCopy, id);
} else if (configCopy.getConnectionManager() != null) {
return configCopy.getConnectionManager();
}else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("server(s) address(es) not defined!");
}
}3.先看下MasterSlaveEntry->setupMasterEntry,这里会创建RedisClient,以及连接REDIS服务器。
org.redisson.connection.MasterSlaveEntry
public RFuture<RedisClient> setupMasterEntry(RedisURI address) {
RedisClient client = connectionManager.createClient(NodeType.MASTER, address, sslHostname);
return setupMasterEntry(client);
}
4.创建RedisClient,这里面单机也是使用主从管理器,即是只有主没有从。统一起来。
org.redisson.connection.MasterSlaveConnectionManager
@Override
public RedisClient createClient(NodeType type, RedisURI address, int timeout, int commandTimeout, String sslHostname) {
RedisClientConfig redisConfig = createRedisConfig(type, address, timeout, commandTimeout, sslHostname);
return RedisClient.create(redisConfig);
}
5.在RedisClient会创建NEETY的bootstrap,channel,handler.

org.redisson.client.RedisClient
private Bootstrap createBootstrap(RedisClientConfig config, Type type) {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.resolver(config.getResolverGroup())
.channel(config.getSocketChannelClass())
.group(config.getGroup());
bootstrap.handler(new RedisChannelInitializer(bootstrap, config, this, channels, type));
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, config.getConnectTimeout());
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, config.isKeepAlive());
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, config.isTcpNoDelay());
config.getNettyHook().afterBoostrapInitialization(bootstrap);
return bootstrap;
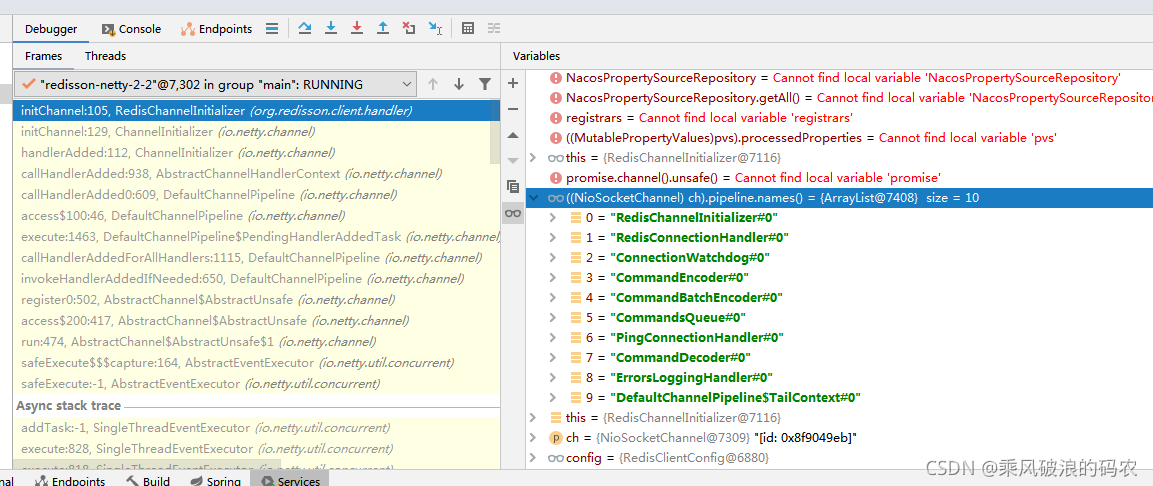
}6.我们再看下RedisChannelInitializer,有添加哪些inBounder,outBounder
org.redisson.client.handler.RedisChannelInitializer
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
initSsl(config, ch);
if (type == Type.PLAIN) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new RedisConnectionHandler(redisClient));
} else {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new RedisPubSubConnectionHandler(redisClient));
}
ch.pipeline().addLast(
connectionWatchdog,
CommandEncoder.INSTANCE,
CommandBatchEncoder.INSTANCE,
new CommandsQueue());
if (pingConnectionHandler != null) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(pingConnectionHandler);
}
if (type == Type.PLAIN) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new CommandDecoder(config.getAddress().getScheme()));
} else {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new CommandPubSubDecoder(config));
}
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ErrorsLoggingHandler());
config.getNettyHook().afterChannelInitialization(ch);
} 
7.创建好RedisClient后,开始连接REDIS服务器。这里首先异步解析地址,解析成功后,在添加到写连接池时会创建和添加连接,在创建连接时会去连接REDIS服务器。
org.redisson.connection. MasterSlaveEntry
private RFuture<RedisClient> setupMasterEntry(RedisClient client) {
RPromise<RedisClient> result = new RedissonPromise<RedisClient>();
result.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
client.shutdownAsync();
}
});
RFuture<InetSocketAddress> addrFuture = client.resolveAddr();
addrFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
result.tryFailure(e);
return;
}
masterEntry = new ClientConnectionsEntry(
client,
config.getMasterConnectionMinimumIdleSize(),
config.getMasterConnectionPoolSize(),
config.getSubscriptionConnectionMinimumIdleSize(),
config.getSubscriptionConnectionPoolSize(),
connectionManager,
NodeType.MASTER);
int counter = 1;
if (config.getSubscriptionMode() == SubscriptionMode.MASTER) {
counter++;
}
CountableListener<RedisClient> listener = new CountableListener<>(result, client, counter);
RFuture<Void> writeFuture = writeConnectionPool.add(masterEntry);
writeFuture.onComplete(listener);
});
return result;
}8.查看连接REDIS服务器过程
org.redisson.connection.pool.ConnectionPool.
private void initConnections(ClientConnectionsEntry entry, RPromise<Void> initPromise, boolean checkFreezed) {
int minimumIdleSize = getMinimumIdleSize(entry);
if (minimumIdleSize == 0 || (checkFreezed && entry.isFreezed())) {
initPromise.trySuccess(null);
return;
}
AtomicInteger initializedConnections = new AtomicInteger(minimumIdleSize);
int startAmount = Math.min(10, minimumIdleSize);
AtomicInteger requests = new AtomicInteger(startAmount);
for (int i = 0; i < startAmount; i++) {
createConnection(checkFreezed, requests, entry, initPromise, minimumIdleSize, initializedConnections);
}
}
在这里可以看到会初始化10个客户端连接到连接池。
9.从连接池去申请创建连接
ConnectionPool
private void createConnection(boolean checkFreezed, AtomicInteger requests, ClientConnectionsEntry entry, RPromise<Void> initPromise,
int minimumIdleSize, AtomicInteger initializedConnections) {
acquireConnection(entry, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
RPromise<T> promise = new RedissonPromise<T>();
createConnection(entry, promise);
promise.onComplete((conn, e) -> {
});
}
});
}10.最终创建连接是在RedisClient.connectAsync这个异步连接方法中。
public RFuture<RedisConnection> connectAsync() {
final RPromise<RedisConnection> f = new RedissonPromise<RedisConnection>();
RFuture<InetSocketAddress> addrFuture = resolveAddr();
addrFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
f.tryFailure(e);
return;
}
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(res);
});
return f;
}
11.在连接成功后,RedisConnectionHandler.channelRegistered方法中创建连接对象。
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
if (connection == null) {
connection = createConnection(ctx);
}
super.channelRegistered(ctx);
}
12.在这里对channel赋值,保存。这里每个channel里面会有一个RedisConnection的属性。
RedisConnection
public void updateChannel(Channel channel) {
this.channel = channel;
channel.attr(CONNECTION).set(this);
}13.在连接成功后发送PING心跳命令
BaseConnectionHandler
@Override
public void channelActive(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
List<RFuture<Object>> futures = new ArrayList<RFuture<Object>>();
RedisClientConfig config = redisClient.getConfig();
if (config.getPassword() != null) {
RFuture<Object> future;
if (config.getUsername() != null) {
future = connection.async(RedisCommands.AUTH, config.getUsername(), config.getPassword());
} else {
future = connection.async(RedisCommands.AUTH, config.getPassword());
}
futures.add(future);
}futures.add(future);
}
if (config.getPingConnectionInterval() > 0) {
RFuture<Object> future = connection.async(RedisCommands.PING);
futures.add(future);
}
final AtomicBoolean retry = new AtomicBoolean();
final AtomicInteger commandsCounter = new AtomicInteger(futures.size());
for (RFuture<Object> future : futures) {
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
if (e instanceof RedisLoadingException) {
if (retry.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
ctx.executor().schedule(() -> {
channelActive(ctx);
}, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
return;
}
connection.closeAsync();
connectionPromise.tryFailure(e);
return;
}
if (commandsCounter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
connectionPromise.trySuccess(connection);
}
});
}
}
四、发送命令过程。
1.首先从RedissionBucket的set方法
,这里面的 commandExecutor来源于connectionManager中的命令执行器。
2.然后进行入到RedisExecutor中的execute方法,去异步执行命令。这里首先从连接池获取连接,然后在异步连接成功后,发送命令。
public void execute() {
codec = getCodec(codec);
RFuture<RedisConnection> connectionFuture = getConnection();
connectionFuture.onComplete((connection, e) -> {
sendCommand(attemptPromise, connection);
writeFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
checkWriteFuture(writeFuture, attemptPromise, connection);
}
});
releaseConnection(attemptPromise, connectionFuture);
});
}
3.获取连接是从连接池中获取。根据读写模式从连接管理器中选择可用连接返回。
RedisExecutor
protected RFuture<RedisConnection> getConnection() {
if (readOnlyMode) {
connectionFuture = connectionManager.connectionReadOp(source, command);
} else {
connectionFuture = connectionManager.connectionWriteOp(source, command);
}
return connectionFuture;
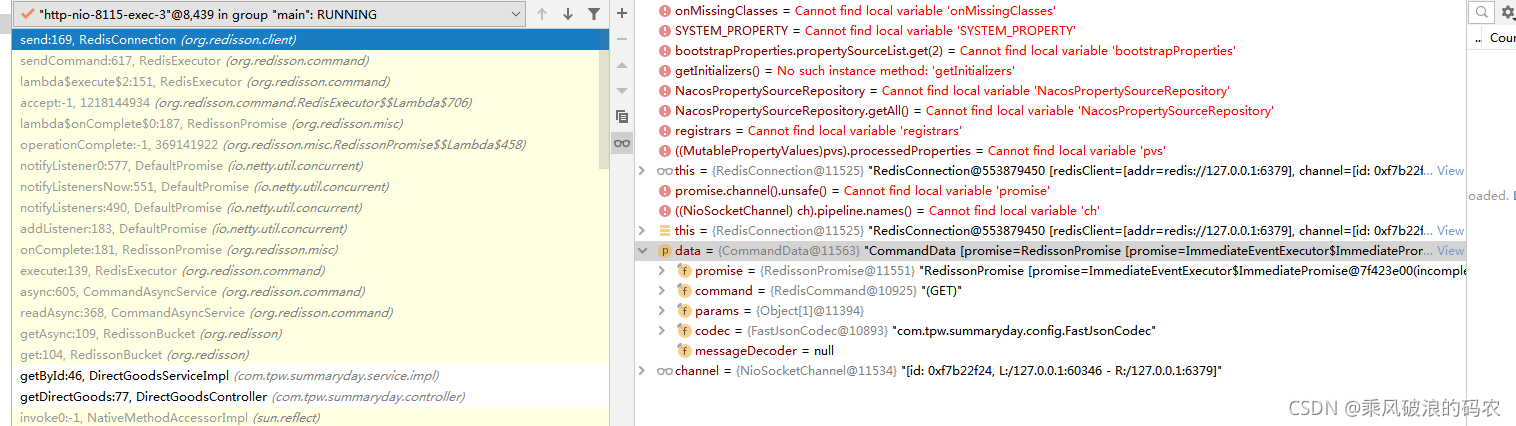
}3.接着调用RedisConnection的send向channel写入数据。
RedisConnection
public <T, R> ChannelFuture send(CommandData<T, R> data) {
return channel.writeAndFlush(data);
}
4.netty的inBoundHandler中有一个CommandsQueue,为一个命令同步队列,同一时刻一个连接只有一个命令在执行,执行完后,再执行下一个命令。
org.redisson.client.handler.CommandsQueue
private void sendData(Channel ch) {
QueueCommandHolder command = queue.peek();
if (command != null && command.trySend()) {
QueueCommand data = command.getCommand();
List<CommandData<Object, Object>> pubSubOps = data.getPubSubOperations();
if (!pubSubOps.isEmpty()) {
for (CommandData<Object, Object> cd : pubSubOps) {
for (Object channel : cd.getParams()) {
ch.pipeline().get(CommandPubSubDecoder.class).addPubSubCommand((ChannelName) channel, cd);
}
}
} else {
ch.attr(CURRENT_COMMAND).set(data);
}
command.getChannelPromise().addListener(listener);
ch.writeAndFlush(data, command.getChannelPromise());
}
} 

五、接收数据回调过程。
1.接收inhandler, 在收到数据后,从attr中的current_command属性中取出数据。
CommandDecoder
@Override
protected final void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
QueueCommand data = ctx.channel().attr(CommandsQueue.CURRENT_COMMAND).get();
if (state() == null) {
state(new State());
}
if (data == null) {
while (in.writerIndex() > in.readerIndex()) {
int endIndex = skipCommand(in);
try {
decode(ctx, in, data);
} catch (Exception e) {
in.readerIndex(endIndex);
throw e;
}
}
} else {
int endIndex = 0;
if (!(data instanceof CommandsData)) {
endIndex = skipCommand(in);
}
try {
decode(ctx, in, data);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!(data instanceof CommandsData)) {
in.readerIndex(endIndex);
}
throw e;
}
}
}
2.根据相应的PROMISE设置回调数据。
CommandDecoder
protected void completeResponse(CommandData<Object, Object> data, Object result) {
if (data != null) {
data.getPromise().trySuccess(result);
}
}
3.在等待异步PROMISE结果。
CommandAsyncService
@Override
public <V> V get(RFuture<V> future) {
try {
future.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
if (future.isSuccess()) {
return future.getNow();
}
throw convertException(future);
}
























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








