Description
ztr loves lucky numbers. Everybody knows that positive integers are lucky if their decimal representation doesn't contain digits other than 4 and 7. For example, numbers 47, 744, 4 are lucky and 5, 17, 467 are not.
Lucky number is super lucky if it's decimal representation contains equal amount of digits 4 and 7. For example, numbers 47, 7744, 474477 are super lucky and 4, 744, 467 are not.
One day ztr came across a positive integer n. Help him to find the least super lucky number which is not less than n.
Lucky number is super lucky if it's decimal representation contains equal amount of digits 4 and 7. For example, numbers 47, 7744, 474477 are super lucky and 4, 744, 467 are not.
One day ztr came across a positive integer n. Help him to find the least super lucky number which is not less than n.
Input
There are T








 cases
cases
For each cases:
The only line contains a positive integer







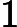

 . This number doesn't have leading zeroes.
. This number doesn't have leading zeroes.








 cases
cases
For each cases:
The only line contains a positive integer








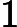

 . This number doesn't have leading zeroes.
. This number doesn't have leading zeroes.
Output
For each cases
Output the answer
Output the answer
Sample Input
2
4500
47
Sample Output
4747
47
分析:
好强大的全排列函数,当然也需要一个良好的分析能力,;
做了几次bestcoder的题,发现一个现象,总爱出一种题型,这好像是一种数学题吧,题意很简单,但是你如果按照它的思路写就一定会超时,就需要去认真分析题目,找到其中的规律,才能达到AC;
题意:ztr喜欢幸运数但有要求:
只包含4和7,且4和7的数量一样。比如47474477是,而47444677,4747447都不是,现在要找到不小于n的幸运数
通过分析可知,如果n是奇数位,那么比它大离它最近的幸运数一定就是最小的由4和7组成的n+1位数,
比如54000,答案一定是444777;
如果是偶数,就由4和7组成的n位数全排列得到,如果此数大于最大的n位幸运数,答案就是最小的n+2位幸运数;比如4800,答案是7447;而8400,答案是444777
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,m,i,j;
char a[20],b[20]; //a数组存储输入数据,b数组存储幸运数
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n--)
{
scanf("%s",a);
int s=strlen(a);
if(s%2==1) //s&1==1,如果s为奇数,答案必须是偶数位
{
for(i=0; i<=s/2; i++) //一定是最小的s+1位幸运数
printf("4");
for(i=0; i<=s/2; i++)
printf("7");
printf("\n");
}
else
{
for(i=0; i<s/2; i++) //首先初始化最小的s位幸运数
b[i]='4';
for(i=s/2; i<s; i++)
b[i]='7';
j=0;
do//全排列找到最近的幸运数
{
if(strcmp(a,b)<=0) //如果b>=a,就输出b数组
{
for(i=0; i<s; i++)
printf("%c",b[i]);
printf("\n");
j=1; //标记为1,说明已经找到
break;
}
}
while(next_permutation(b,b+s));
if(j==0) //如果没有找到,说明a大于了最大的s位幸运数
{
for(i=0; i<=s/2; i++) //就需要输出最小的s+2位幸运数
printf("4");
for(i=0; i<=s/2; i++)
printf("7");
printf("\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








