先看看W3C中对position值的描述:
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| absolute | 生成绝对定位的元素,相对于 static 定位以外的第一个父元素进行定位。 元素的位置通过 "left", "top", "right" 以及 "bottom" 属性进行规定。 |
| fixed | 生成绝对定位的元素,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。 元素的位置通过 "left", "top", "right" 以及 "bottom" 属性进行规定。 |
| relative | 生成相对定位的元素,相对于其正常位置进行定位。 因此,"left:20" 会向元素的 LEFT 位置添加 20 像素。 |
| static | 默认值。没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中(忽略 top, bottom, left, right 或者 z-index 声明)。 |
| inherit | 规定应该从父元素继承 position 属性的值。 |
1.absolute
根据上述定义,我们编写一段测试代码,有一个div(father),内部嵌套三个div(d1,d2,d3),还有一个div(sFather),内部嵌套d4的div,d3、d4、d5为absolute定位,sFather为relative(即非static),其余未指定的为static,代码如下:
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> *{ padding:0; margin:0; } #father{ width:400px; height:400px; border:1px #000 solid; box-sizing:border-box; } #d1{ width:100px; height:100px; border:1px #000 solid; box-sizing:border-box; background-color:rgba(0,0,0,0.3); } #d2{ width:200px; height:200px; background-color:rgba(0,0,0,0.5); border:1px #000 solid; box-sizing:border-box; } #d3{ width:100px; height:100px; position:absolute; top:50px; left:50px; background-color:rgba(0,255,0,0.5); border:1px #000 solid; box-sizing:border-box; } #d4{ width:100px; height:100px; position:absolute; top:50px; left:50px; background-color:rgba(255,0,0,0.5); border:1px #000 solid; box-sizing:border-box; } #sFather{ position:relative; width:300px; height:300px; border:1px #000 solid; box-sizing:border-box; } #d5{ width:100px; height:100px; position:absolute; top:200px; left:200px; background-color:rgba(0,0,255,0.5); border:1px #000 solid; box-sizing:border-box; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="father"> <div id="d1">d1</div> <div id="d2">d2</div> <div id="d3">d3</div> </div> <div id="sFather"> <div id="d4">d4</div> </div> <div id="d5">d5</div> </body>
运行结果如下:
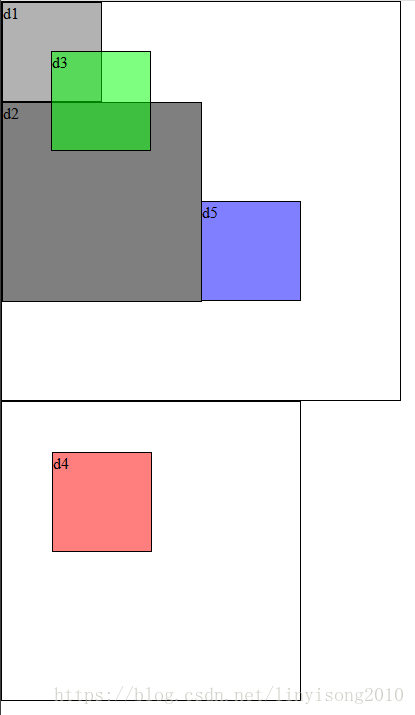
如图可知,d3、d4、d5的第一个非static定位的父元素分别为:body,sFather,body;
故而
d3位置是body的上50px、左50px,
d4位置是sFather的上50px、左50px,
d5位置是body的上200px、左200px;
在我们平时使用absolute定位时,会存在只要absolute定位,就是可以调整相对于body的定位位置,这个是容易出错的一点。
2.fixed
fixed定位,是相对浏览器窗口的定位,脱离文档流,很容易理解,很多手机购物网站的头部就是采用这种定位,代码如下:
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="maximum-scale=1.0,minimum-scale=1.0,user-scalable=0,width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0"/> <title>Title</title> <style> *{ padding:0; margin:0; } #t1{ position:fixed; width:375px; height:20px; background-image:linear-gradient(to right,#01cbcc,#fe01ff); } #d2{ width:375px; height:1000px; background-color:#9F9F9F; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="t1"></div> <div id="d2"> <h1>我是头部内容</h1> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> <li>4</li> <li>5</li> <li>6</li> <li>7</li> <li>8</li> </div> </body>
效果如下:

可以看到,无论窗口如何上下滚动,fixed定位的t1,总是在窗口的顶部
3.relative
relative是相对于其正常位置进行定位,不脱离文档流
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> #d1{ width: 300px; height:10px; border:1px #000 solid; } #d2{ position:relative; width: 30px; height:30px; border:1px #000 solid; top:10px; left:50px; } #d3{ width: 300px; height:10px; border:1px #000 solid; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="d1">d1</div> <div id="d2">d2</div> <div id="d3">d3</div> </body>

这个就不用解释了,很简单,父子元素使用定位时,父元素是absolute,子元素还是可以使用relative进行相对定位,相对是父元素的位置。
自学记录用,有错误之处还请不吝赐教。








 本文详细解析了CSS中的三种定位方式:absolute、fixed及relative的特点及应用。通过实例代码演示了每种定位方式的效果,并强调了它们相对于不同元素进行定位的具体表现。
本文详细解析了CSS中的三种定位方式:absolute、fixed及relative的特点及应用。通过实例代码演示了每种定位方式的效果,并强调了它们相对于不同元素进行定位的具体表现。
















 2857
2857

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








