目录
二分查找
def binary_search(data,target,low,high):
if low > high:
return False
else:
mid = (low+high)//2
if target == data[mid]:
return True
elif target < data[mid]:
return binary_search(date,target,low,mid-1)
else:
return binary_search(data,target,mid+1,high)public static boolean binarySearch(int[] data,int target, int low,int high){
if (low>high)
return false;
else {
int mid = (low+high)/2;
if (target == data[mid])
return true;
else if (target<data[mid])
return binarySearch(data,target,low,mid-1);
else
return binarySearch(data,target,mid+1,high);
}
}阶乘函数

def factorial(n):
if n == 0:
return 1
else:
return n*factorial(n-1) public static int factorial(int n) throws IllegalArgumentException{
if (n<0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
else if (n==0)
return 1;
else
return n*factorial(n-1);
}画尺子

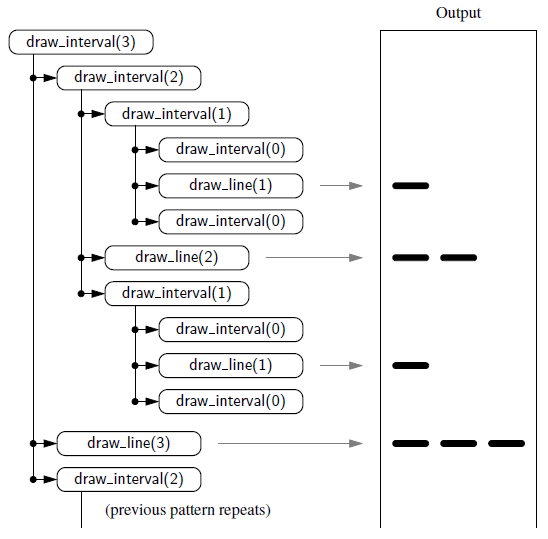
def draw_line(tick_length,tick_label=''):
'''根据长度tick_length画出刻度线'''
line = '-' * tick_length
if tick_label:
line += ' ' + tick_label
print(line)
def draw_interval(center_length):
'''在上一个等级区间内,插入一个下一个等级刻度线'''
if center_length >0: #当长度下降到0时停止。
draw_interval(center_length-1) # recursively draw top ticks
draw_line(center_length) # draw center tick
draw_interval(center_length-1) # recursively draw bottom ticks
def draw_ruler(num_inches, major_length):
draw_line(major_length,'0')
for j in range(1,num_inches+1):
draw_interval(major_length-1) #按等级绘制内刻度线
draw_line(major_length,str(j)) #负责最外围刻度线以及号码;
if __name__ == '__main__':
draw_ruler(4,3)public class drawRuler {
/** Draws an English ruler for the given number of inches and major tick length. */
public static void drawRuler(int nInches,int majorLength){
drawLine(majorLength,0);
for (int j=1;j<=nInches;j++){
drawInterval(majorLength - 1);
drawLine(majorLength,j);
}
}
private static void drawInterval(int cetralLength){
if (cetralLength >=1){
drawInterval(cetralLength - 1);
drawLine(cetralLength);
drawInterval(cetralLength - 1);
}
}
private static void drawLine(int tickLength, int tickLabel){
for (int j=0;j<tickLabel;j++)
System.out.print("-");
if (tickLabel>=0)
System.out.print("\n");
}
/** Draws a line with the given tick length (but no label). */
private static void drawLine(int tickLength){
drawLine(tickLength,-1);
}
}
文件系统
现代操作系统以递归方式定义文件系统目录(也称为“文件夹”)。即一个文件系统由一个顶层目录组成,这个目录的内容由文件和其他目录组成,这些目录又可以包含文件和其他目录等。 我们将计算嵌套在特定目录中的所有文件和目录的总磁盘使用量。

Algorithm DiskUsage( path):
Input: A string designating a path to a file-system entry
Output: The cumulative disk space used by that entry and any nested entries
total = size( path) {immediate disk space used by the entry}
if path represents a directory then
for each child entry stored within directory path do
total = total + DiskUsage( child) {recursive call}
return total
Python’s os Module
| os.path.getsize(path) | 返回由字符串path(例如/user/rt/courses)标识的文件或目录的即时磁盘使用情况(以字节为单位)。 |
| os.path.isdir(path) | 如果字符串path指定的是目录,则返回true;否则返回false |
| os.listdir(path) | 返回字符串列表,这些字符串是由字符串路径指定的目录中所有条目的名称。在我们的示例文件系统中,如果参数为/user/rt/courses,则返回列表[cs016,cs252]。 |
| os.path.join(path, filename) | 使用适当的操作系统分隔符组合路径字符串和文件名字符串(例如,UNIX/Linux系统的/character和Windows的\character)。返回表示文件完整路径的字符串。 |
import os
def disk_usage(path):
"""Return the number of bytes used by a file/folder and any descendents"""
total = os.path.getsize(path)
if os.path.isdir(path):
for filename in os.listdir(path):
childpath = os.path.join(path,filename)
total += disk_usage(childpath)
print('{0:<7}'.format(total),path)
return totalThe java.io.File Class
| new File(pathString) or new File(parentFile, childString) | 可以通过将完整路径作为字符串提供或提供表示目录的现有文件实例和指定该目录中子条目名称的字符串来构造新的文件实例。 |
| file.length() | 返回由文件实例(例如/user/rt/courses)表示的操作系统条目的即时磁盘使用情况(以字节为单位)。 |
| file.isDirectory( ) | 如果文件实例表示目录,则返回true;否则返回false。 |
| file.list( ) | 返回指定给定目录中所有项的名称的字符串数组。在我们的示例文件系统中,如果我们对与path/user/rt/courses/cs016关联的文件调用此方法,它将返回一个包含以下内容的数组:“grades”、“homeworks”、“programs”。 |
import java.io.File;
public class diskUsage {
/**
* Calculates the total disk usage (in bytes) of the portion of the file system rooted
* at the given path, while printing a summary akin to the standard 'du' Unix tool.
*/
public static long diskUsage(File root){
long total = root.length();
if (root.isDirectory()){
for (String childname:root.list()){
File child = new File(root,childname);
total += diskUsage(child);
}
}
System.out.println(total+"\t"+root);
return total;
}
}





















 770
770

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








