学习视频:b站黑马java教程
tomcat
spring-boot工程内嵌了tomcat服务器

-
所有请求经过
DispatcherServlet(实现servlet接口的类)(核心控制器/前端控制器)处理,再通过DispatcherServlet转发给各个controller。 -
最后通过DispatcherServlet给浏览器响应数据
-
他会将浏览器的http请求鞋带的数据,比如header,body等封装到
HttpServletRequest对象中,相当于nest的@Request() req;获取请求对象。 -
然后通过
HttpServletResponse设置相应数据,DispatcherServlet会根据响应数据,封装好http响应头,响应给浏览器。相当于nest的@Response() res; -
BS架构 浏览器/服务器模式 用户只要有浏览器就行
-
CS架构 客户端/服务器,比如qq,网盘等
获取请求参数
query参数
原始方式,从HttpServletrequest中取出并且转换数据
@RequestMapping("/hello") //相当于nest的@Get("/hello"),处理哪个请求
public String hello(HttpServletRequest req){
// 获取query参数
String name = req.getParameter("name");
String age = req.getParameter("age");
return "your name is" + name + "; and you age is" + age;
}
springboot方式
// 请求处理类
@RestController //注解,用来标记这个类是请求处理类,相当于nest的@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello") //相当于nest的@Get("/hello"),处理哪个请求
@RequestMapping("/hello") //相当于nest的@Get("/hello"),处理哪个请求
public String hello(@RequestParam(name="name", required=false) String userName, String age){
return "your name is" + userName + "; and you age is" + age;
}
}
简单参数直接作为方法参数写入即可,命名需要一样(不一样需要用@ReueqstParam(name=“name”)去重命名)。相当于nest的@Query() query快速获取参数。
对应Post请求,如果是x-www-form-urlencoded的方式,也是上述这种方式即可
小结

实体参数
如果简单参数太多,一个一个些不切实际,定义POJO接收即可。
package com.example.demo.pojo;
public class UserProps {
private String name;
private String age;
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public String getAge(){
return this.age;
}
}
定义一个实体对象,pojo类,
@RequestMapping("/hello") //相当于nest的@Get("/hello"),处理哪个请求
public String hello(UserProps user){
return "your name is" + user.getName() + "; and you age is" + user.getAge();
}
直接创建了一个实例,然后调用定义好的方法去获取。结果一样。
如果是复杂的,比如
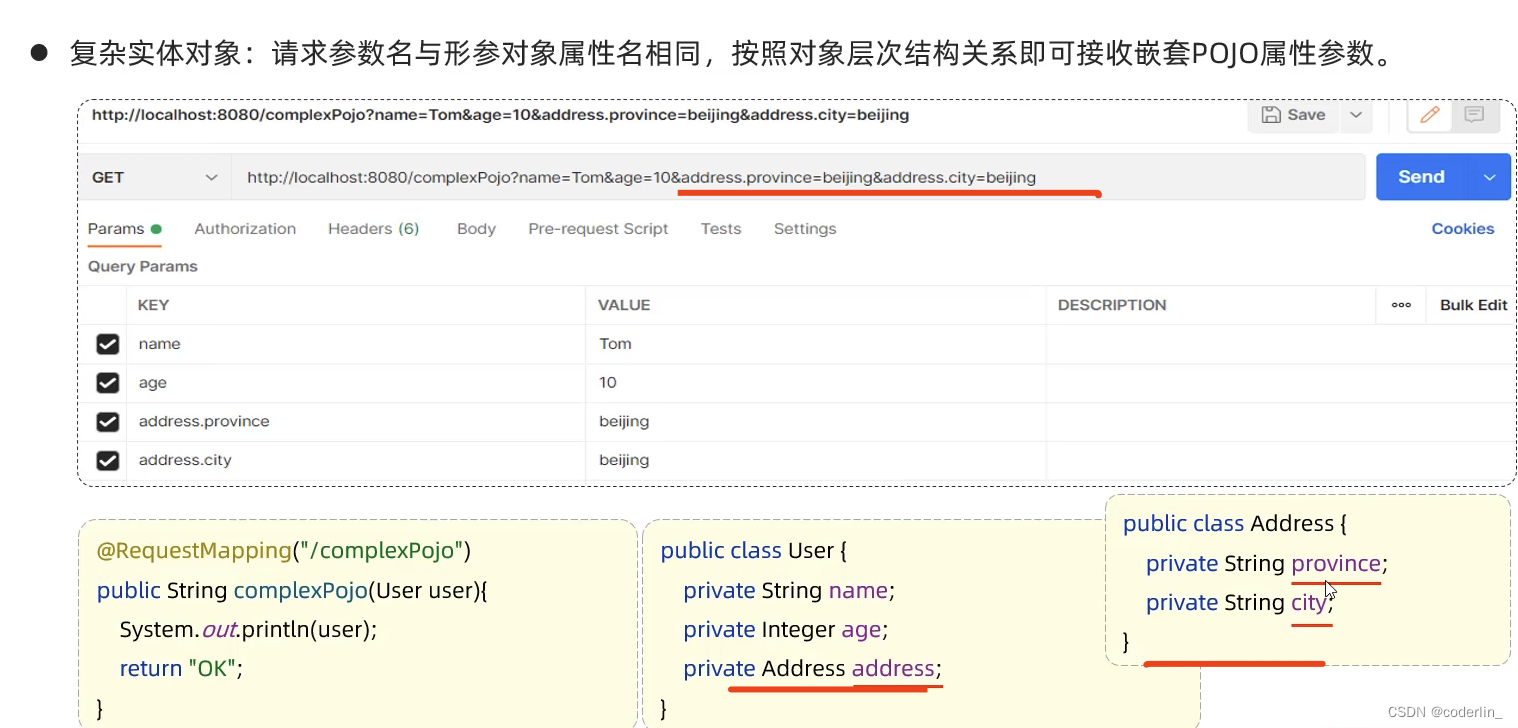
用得较少。
数组集合参数

用得较少。
日期参数

用得较少,大多都是通过post封装json。
JSON参数

package com.example.demo.pojo;
public class AddressProps {
public String province;
public String city;
public String get(String field){
switch (field){
case "city": {
return this.city;
}
case "province":
default: {
return this.province;
}
}
}
}
package com.example.demo.pojo;
public class UserJsonProps {
public String name;
public String age;
public AddressProps address;
}
@RequestMapping("/json")
public String json(@RequestBody UserJsonProps user){
System.out.println(user.age);
System.out.println(user.name);
System.out.println(user.address.city + user.address.province);
return "ok";
};
使用@RequestBody标识,类似于nest的@Body() body;
Params 参数
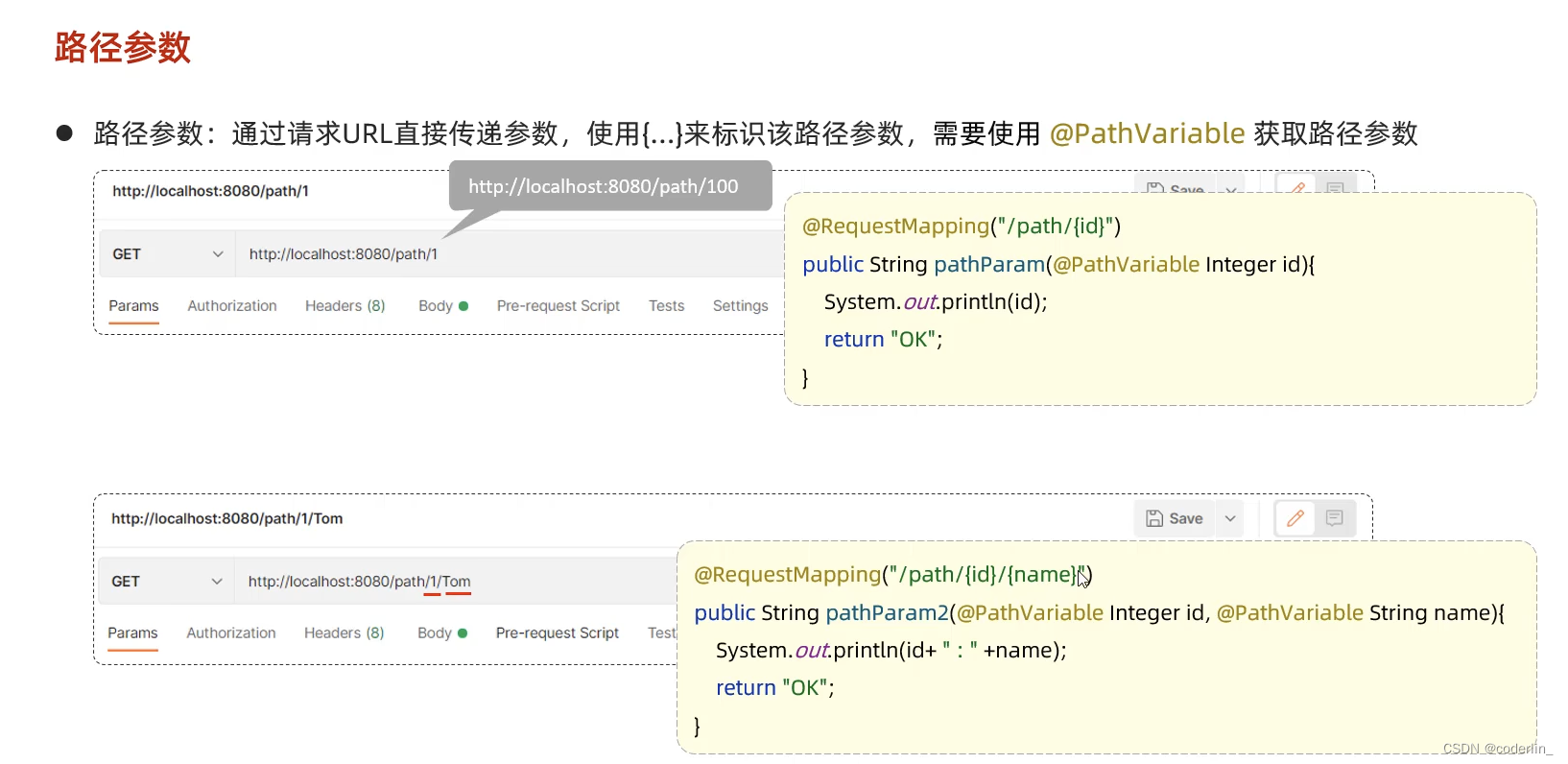
@RequestMapping指定路径的时候就加上变量定义,然后通过@pathVariable去获取对应的变量。多个就写多个。
小结
- query参数,可以通过
HttpServletrequest得到req,然后通过req.getParamter获取值@也可以通过springboot封装好的,直接通过方法参数的形式获取,变量名称不一样的话需要使用@RequestParam去重命名。 - 实体对象,但query很多的时候,可以封装pojo类来创建一个实例,然后通过实例获取值
- 数据集合和日期通过query的比较少,一般通过json请求
- json格式的数据,通过@RequestJson,封装pojo类获取
- params格式的数据,通过@ReqeusetMapping指定url的时候就制定变量(跟nest类似),然后通过@PathVariable定义方法参数变量获取数据。
设置响应数据
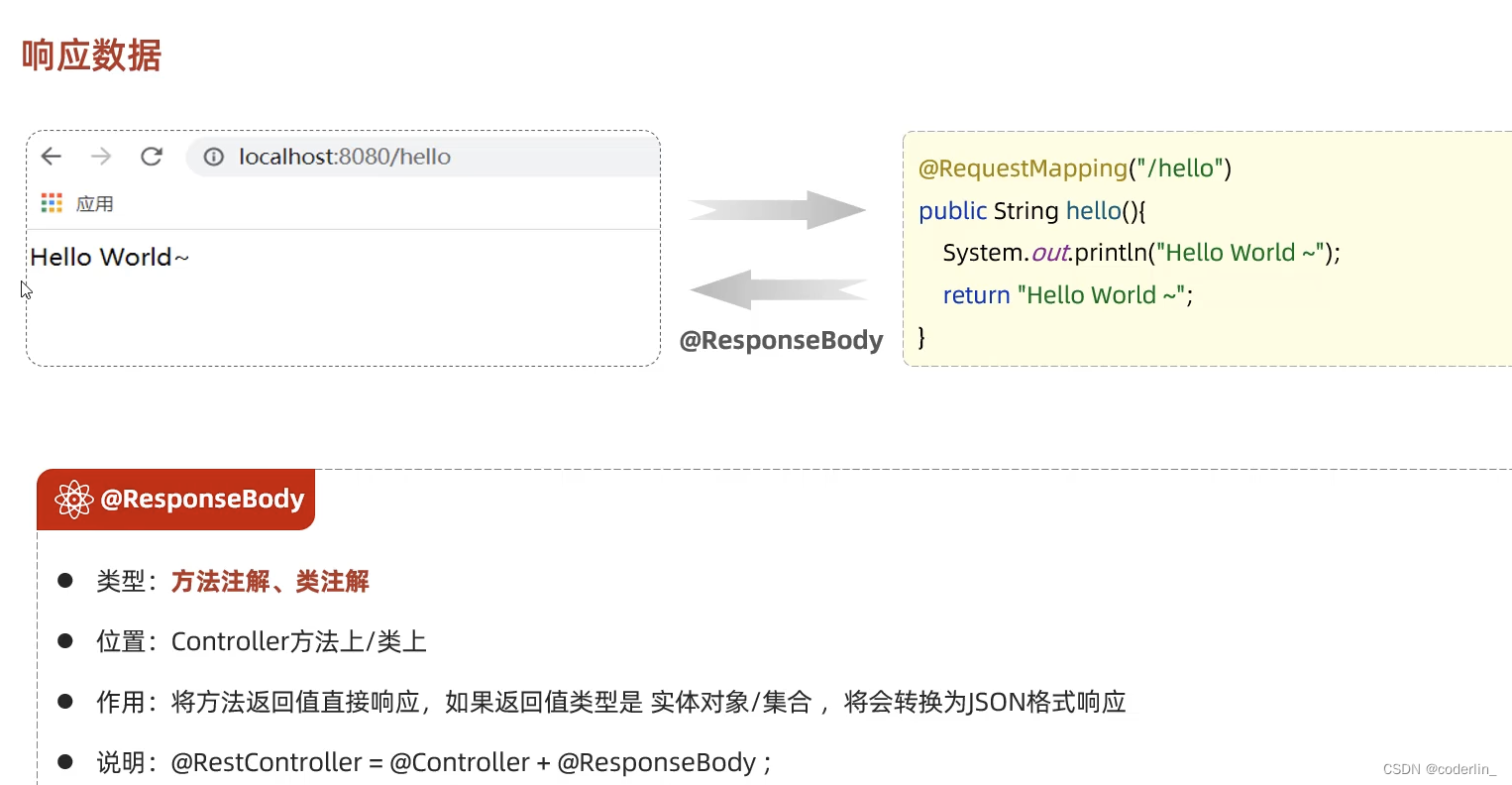
@RestController注解的定义。
@Target({
ElementType.TYPE}) //类型,TYPE表示作用在类或者接口
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //运行时间, runtime的时候运行
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Controller.class
)
String value() default "";
}
上述将HelloController标记为@RestController,@RestController是@Controller和@ResponseBody的集合,因为作用在类上,所以该类的所有方法的返回值都会作为响应传给客户端。
统一响应内容
类似于nest的拦截器,统一响应格式。








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










