一. Vuex简介
1.1 Vuex是什么
官方解释:
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式 + 库。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
其实vuex就是把组件共享状态抽取出来以一个全局单例模式管理,把共享的数据函数放进vuex中,任何组件都可以进行使用。
每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库)。“store”基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)。Vuex 和单纯的全局对象有以下两点不同:
-
Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
-
你不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit) mutation。这样使得我们可以方便地跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够实现一些工具帮助我们更好地了解我们的应用。
1.2 什么情况下使用Vuex
Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,并附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。
如果不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。一个简单的 store 模式就足够所需了。但是,如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,就需要考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择。
1.3 Vuex核心概念
- state 状态 存储vuex的基本数据
- getters 类似单个组件的计算属性
- mutation 里面定义提交更新数据的方法,必须是同步的(如果需要异步使用action)。每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型 (type) 和一个 回调函数 (handler)。
- commit传递的时候可以传递参数(参数被称为载荷(payload))
- action 与mutation的功能基本相同
不同点:Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态; Action 可以包含任意异步操作
- module 对vuex进行模块化,可以让每一个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、action、getters,使得结构更清晰,方便管理。
二. Vuex的存值取值
创建store模块,分别维护state/actions/mutations/getters
state.js (状态,即要全局读写的数据)
export default{
wxName:'派大星'
}mutations.js
一定要记住,Mutation 必须是同步函数。为什么呢?异步方法,我们不知道什么时候状态会发生改变,所以也就无法追踪了
如果我们需要异步操作,Mutations就不能满足我们需求了,这时候我们就需要Actions了
export default{
// state指的是state.js文件中导出的对象
// payload就是vue文件传递过来的参数
setWxName:(state,payload)=>{
state.wxName = payload.wxName
}
}
getters.js (获取数据并渲染)
export default{
getWxName:(state)=>{
return state.wxName;
}
}
在store/index.js文件中新建vuex的store实例,并注册上面引入的各大模块
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import state from './state'
import getters from './getters'
import actions from './actions'
import mutations from './mutations'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations
})
export default store
在main.js中导入并使用store实例
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
//开发环境下才会引入mockjs
// process.env.MOCK && require('@/mock')
// 新添加1
import ElementUI from 'element-ui'
// 新添加2,避免后期打包样式不同,要放在import App from './App';之前
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
// 新添加3
Vue.use(ElementUI)
Vue.config.productionTip = false
import axios from '@/api/http'
import VueAxios from 'vue-axios'
Vue.use(VueAxios,axios)
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
data(){
return {
Bus:new Vue()
}
},
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
LeftNav.vue
<el-submenu index="idx_999" key="key_999">
<template slot="title">
<span>Vuex管理</span>
</template>
<el-menu-item index="/vuex/page01" key="key_99901">
<span>测试页面1</span>
</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="/vuex/page02" key="key_99902">
<span>测试页面2 </span>
</el-menu-item>page01.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>测试页面1</h1>
<p>改变state中的值</p>
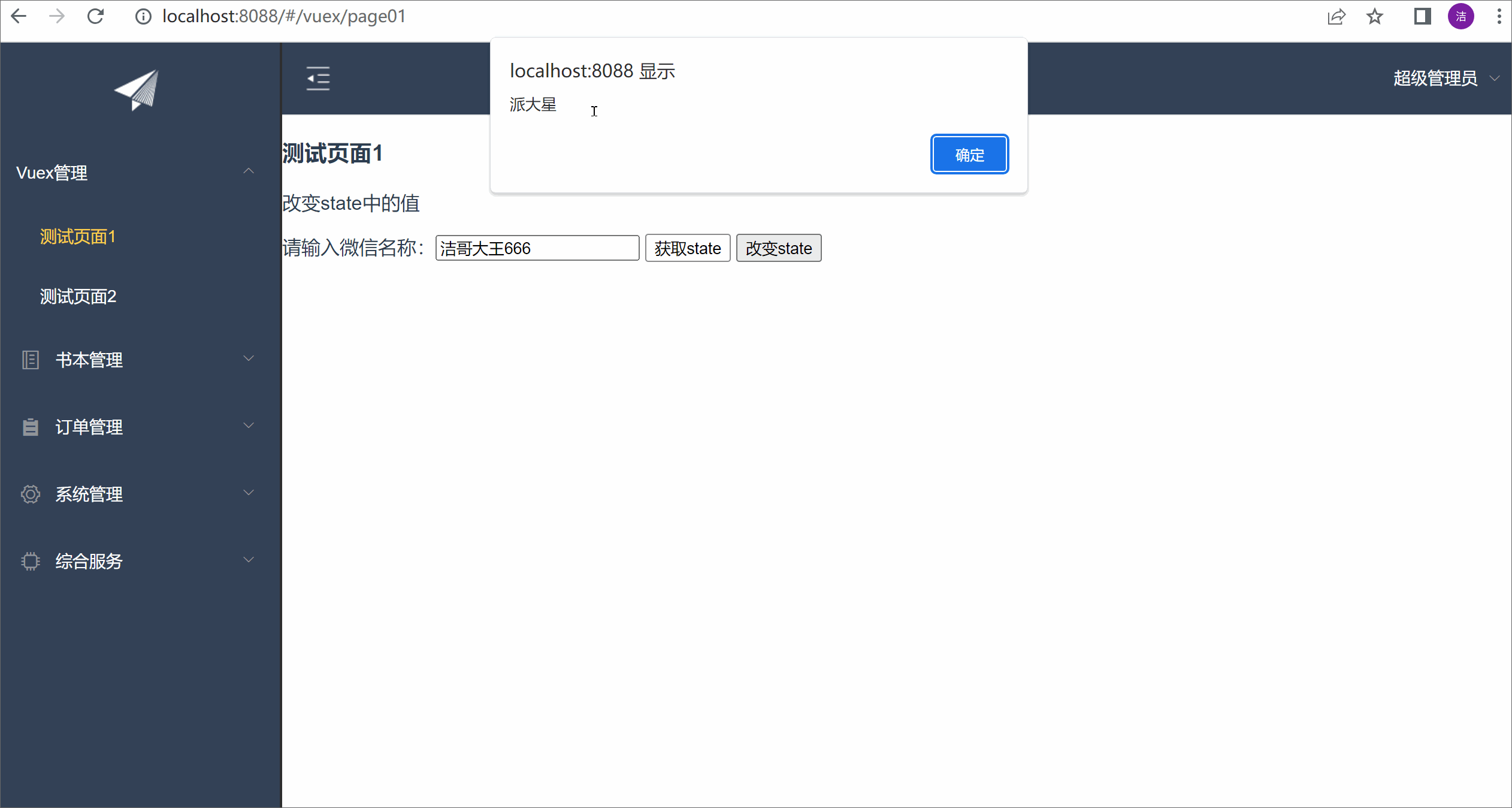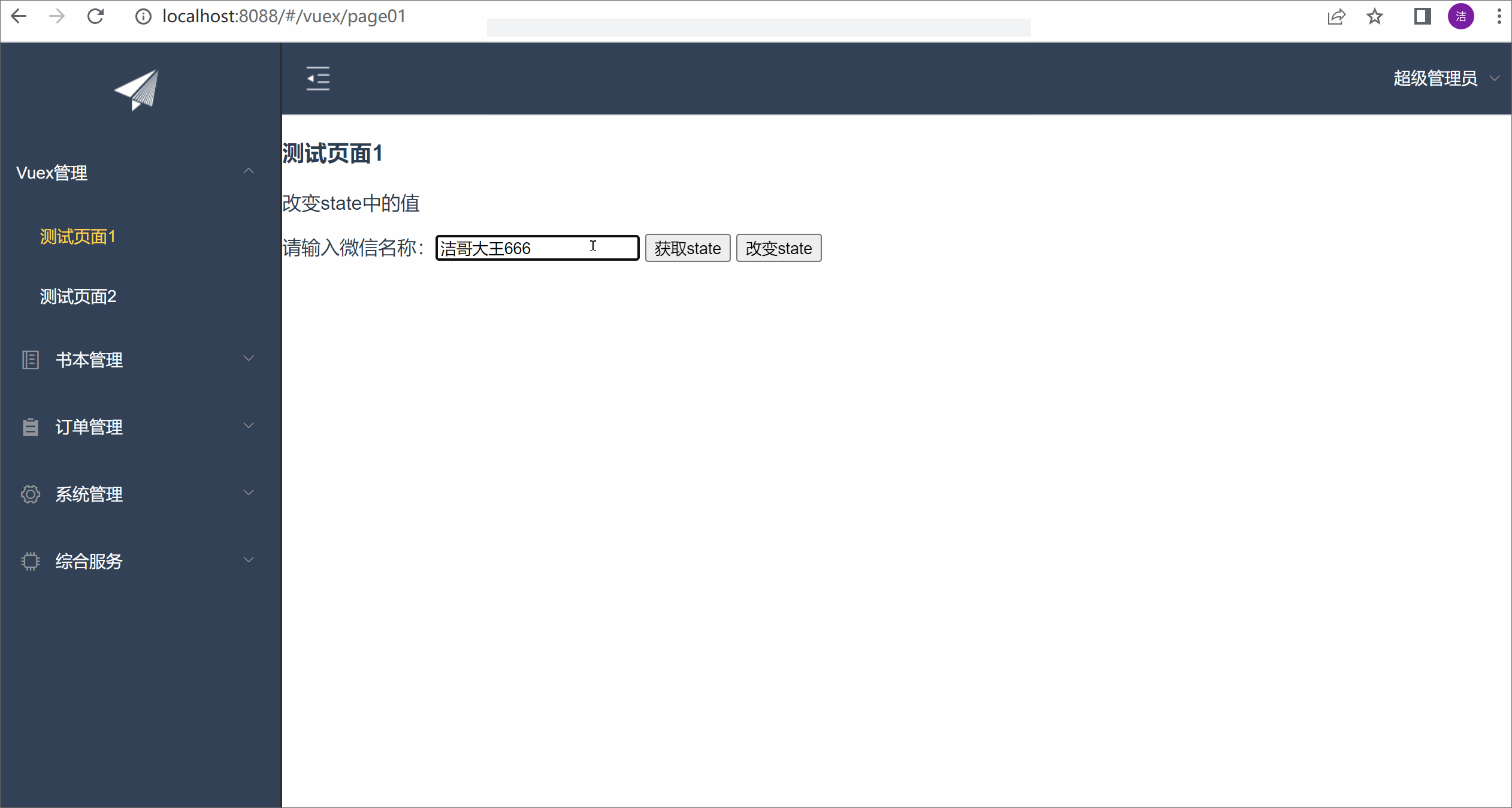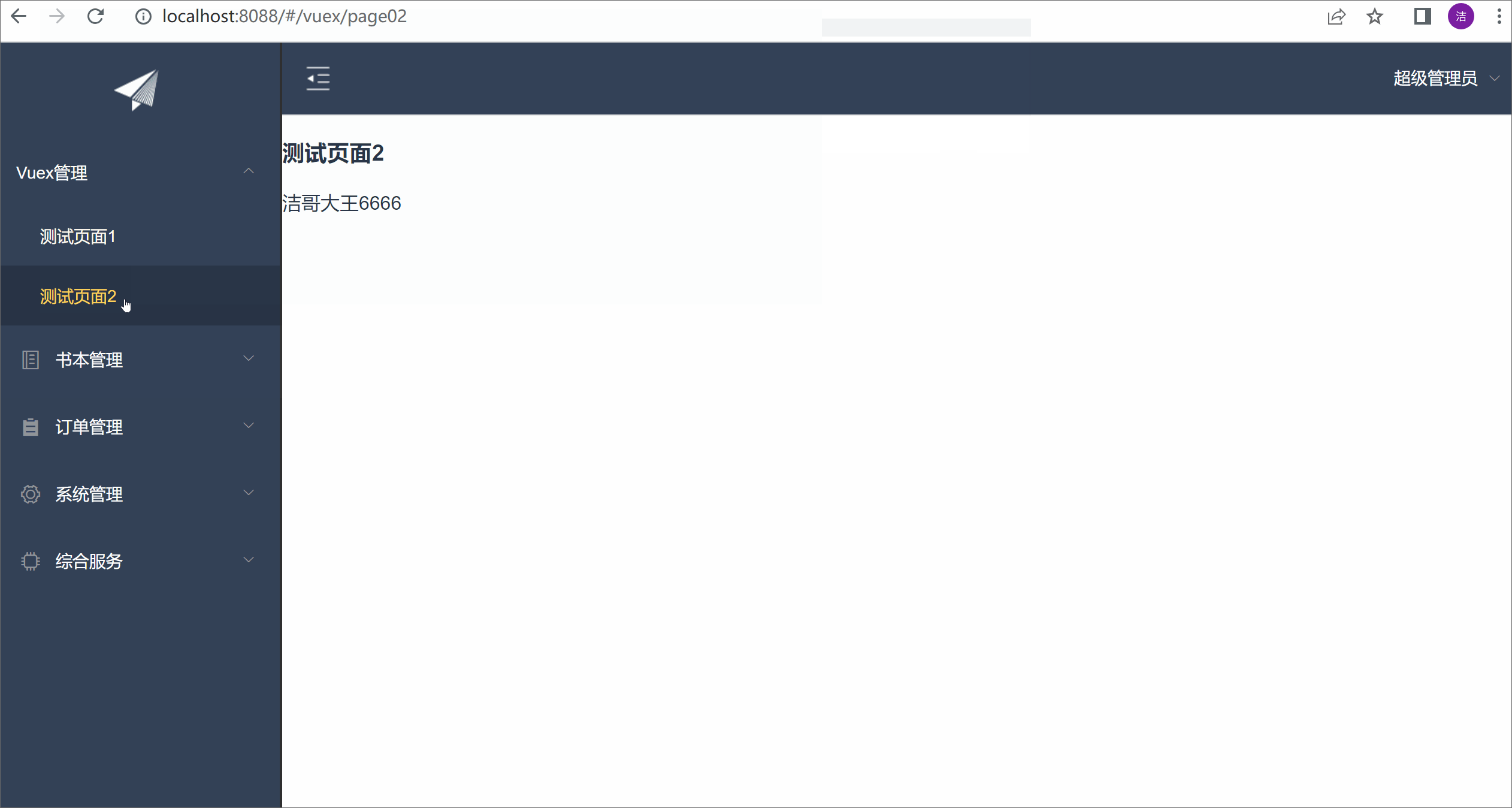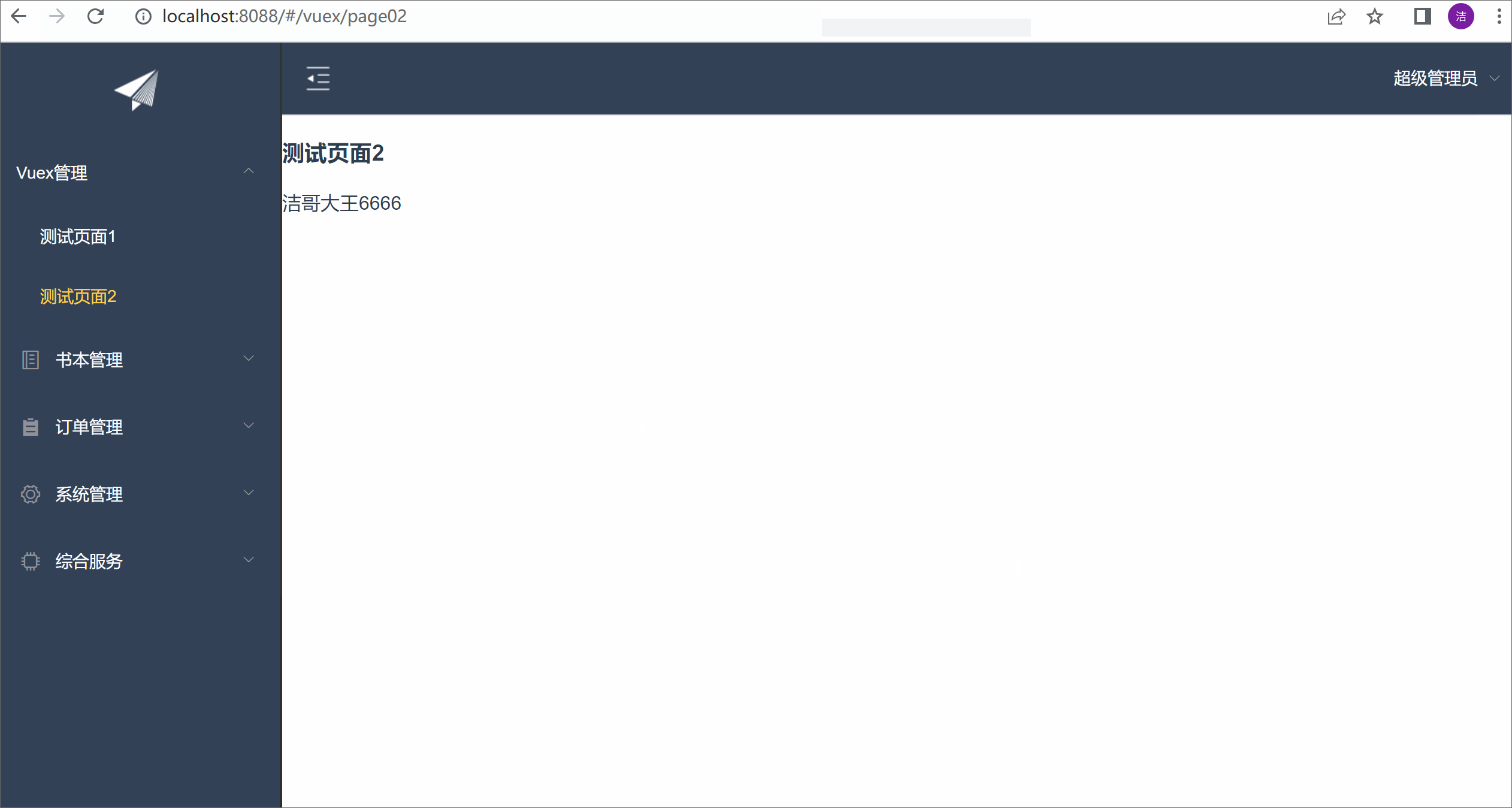
请输入微信名称:<input v-model="msg">
<button @click="fun1">获取state</button>
<button @click="fun2">改变state</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data() {
return {
msg:'洁哥大王666'
}
},
methods:{
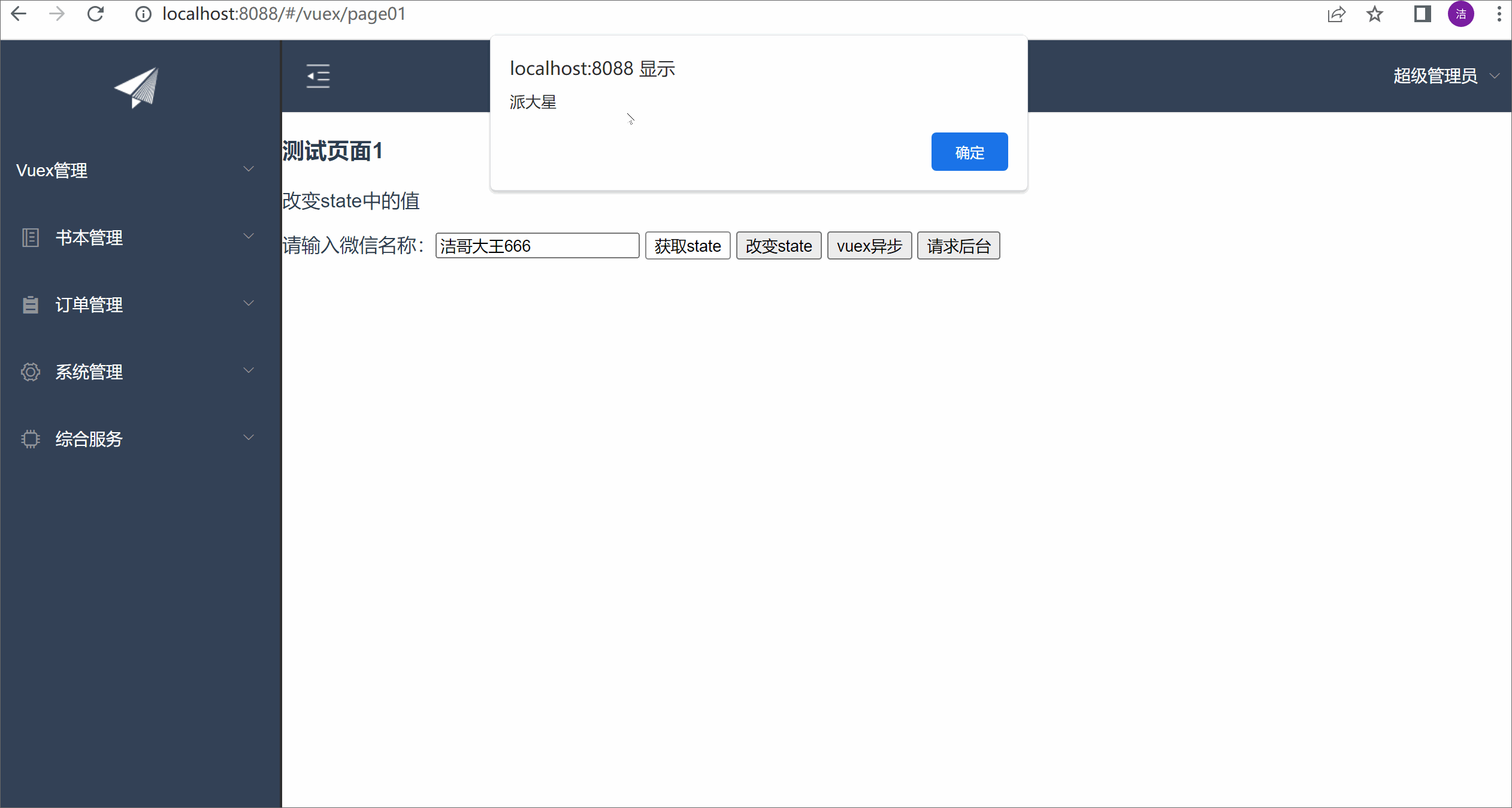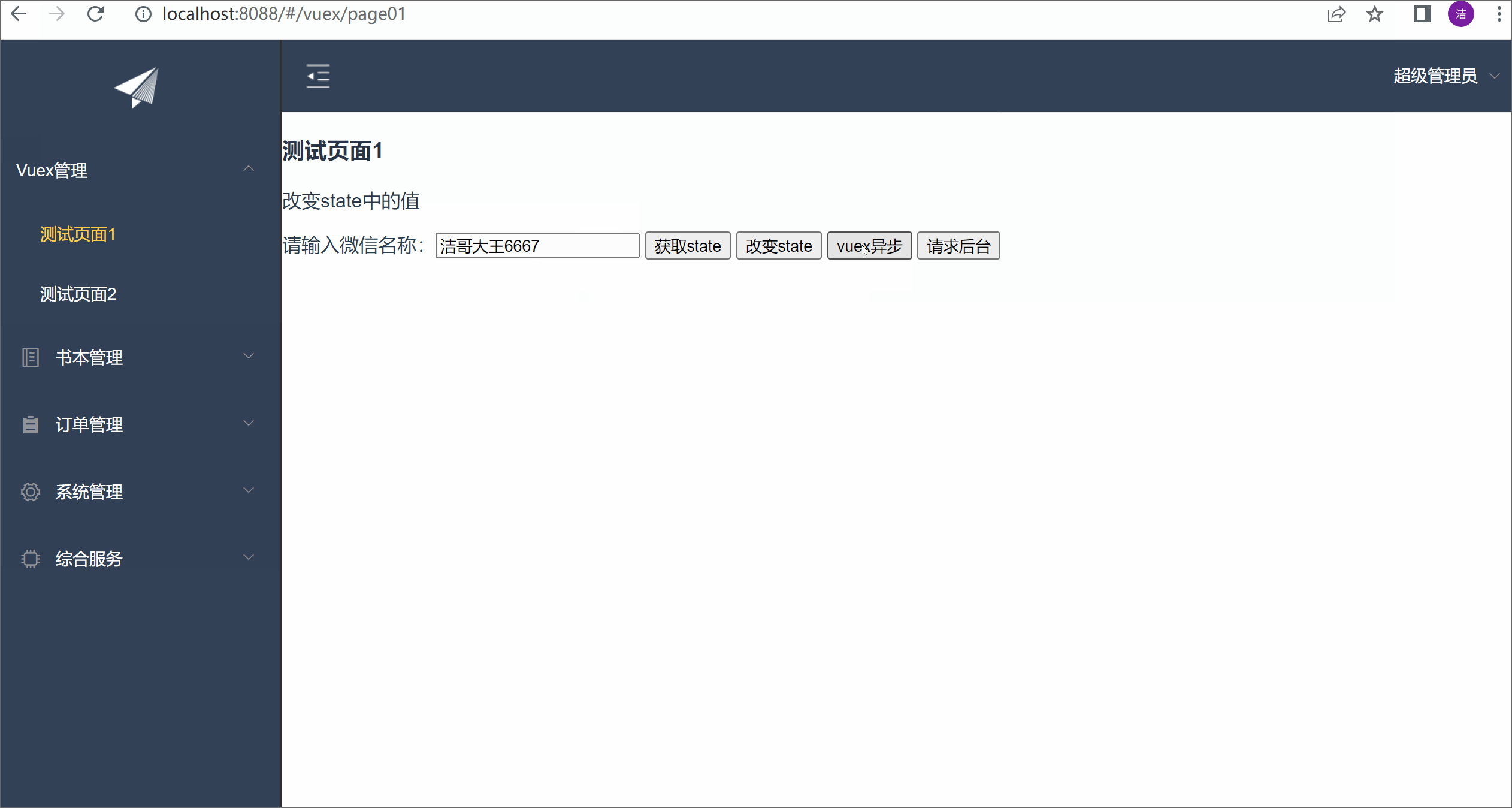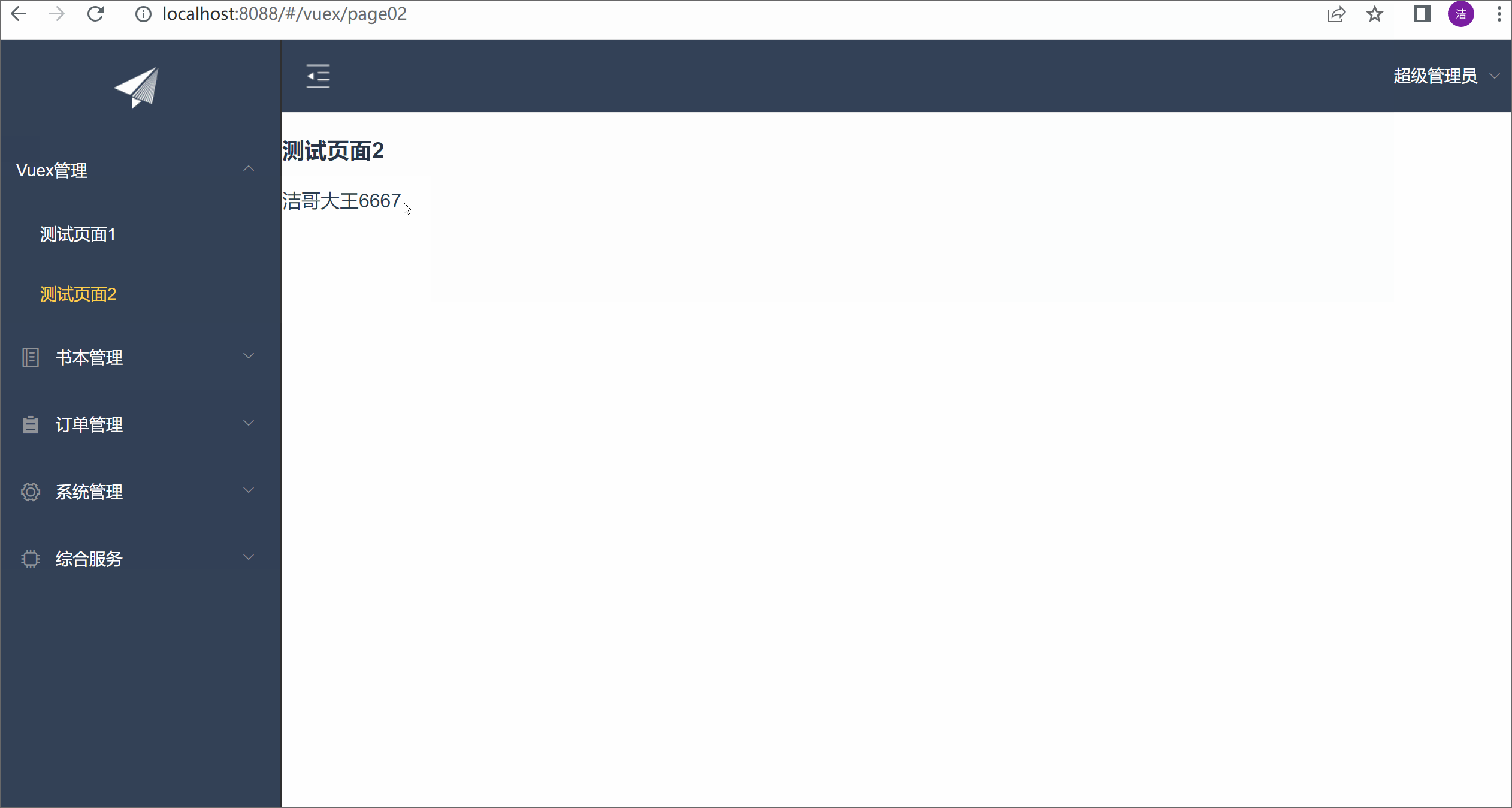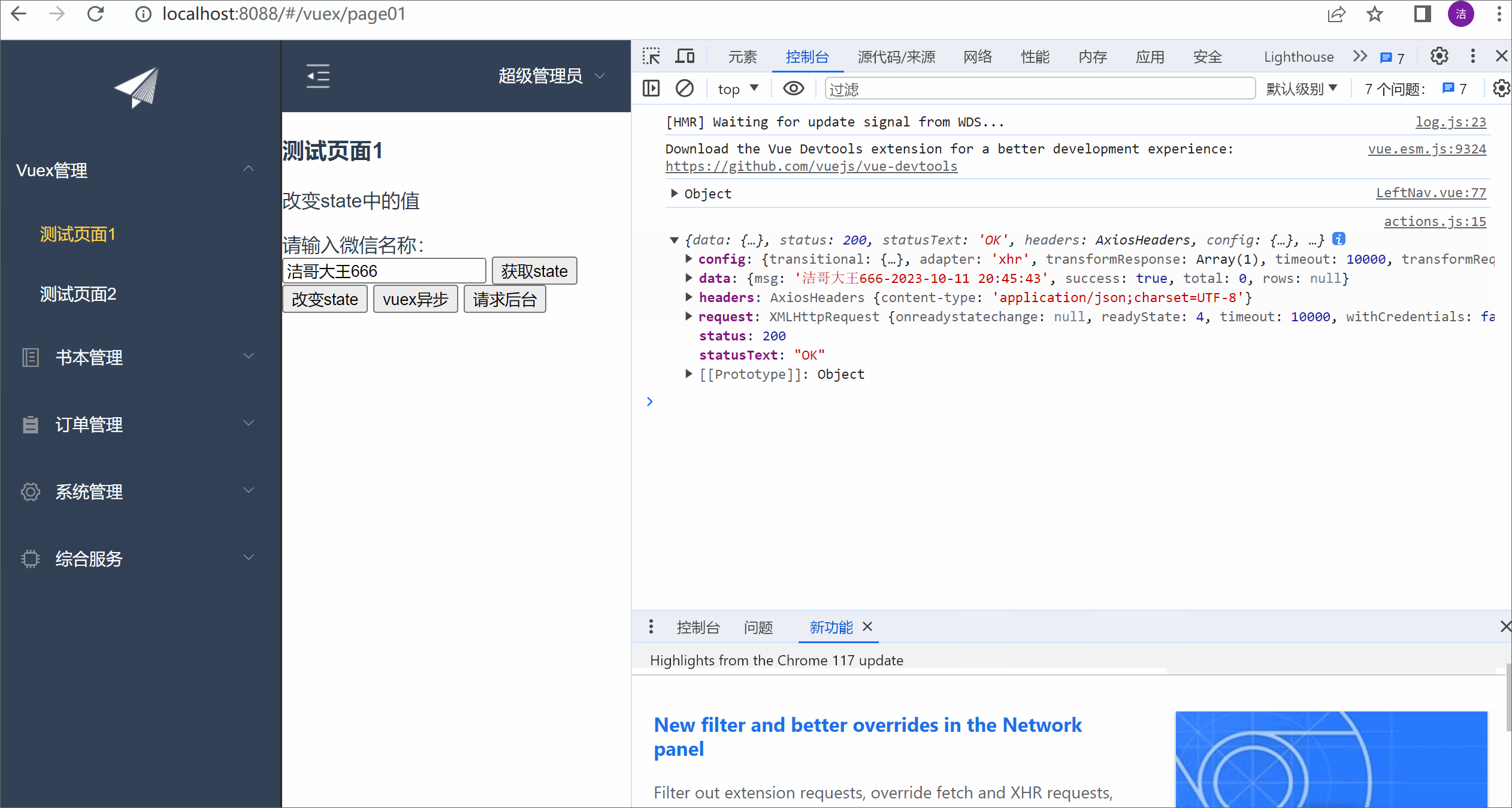
fun1(){
let wxName = this.$store.state.wxName;
alert(wxName);
},
fun2(){
this.$store.commit('setWxName',{
wxName:this.msg
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
page02.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>测试页面2</h1>
{{wxName}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data() {
return {
msg:'洁哥大王666'
}
},
computed:{
wxName(){
// return this.$store.state.wxName;
return this.$store.getters.getWxName;
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
测试效果:
三. Vuex的异步请求
同步:一个时间点只做一件事情,做完后再做下一件事
异步:一个时间点可以同时做多件事情
actions.js
export default{
// context指的是vuex的上下文
setWxNameAsync:(context,payload)=>{
setTimeout(function() {
context.commit('setWxName',payload);
}, 10000);
},
setWxNameAjax:(context,payload)=>{
let _this = payload._this
let url = _this.axios.urls.VUEX_AJAX;
let params = {
resturantName:payload.wxName
}
_this.axios.post(url, params).then(r => {
console.log(r);
}).catch(e => {
})
}
}
Action类似于 mutation,不同在于:
1.Action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态
2.Action可以包含任意异步操作
3.Action的回调函数接收一个 context 上下文参数,注意,这个参数可不一般,它与 store 实例有着相同的方法和属性
但是他们并不是同一个实例,context 包含:
1. state、2. rootState、3. getters、4. mutations、5. actions 五个属性
所以在这里可以使用 context.commit 来提交一个 mutation,或者通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters。
page01.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>测试页面1</h1>
<p>改变state中的值</p>
请输入微信名称:<input v-model="msg">
<button @click="fun1">获取state</button>
<button @click="fun2">改变state</button>
<button @click="fun3">vuex异步</button>
<button @click="fun4">请求后台</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data() {
return {
msg:'洁哥大王666'
}
},
methods:{
fun1(){
let wxName = this.$store.state.wxName;
alert(wxName);
},
fun2(){
this.$store.commit('setWxName',{
wxName:this.msg
})
},
fun3(){
this.$store.dispatch('setWxNameAsync',{
wxName:this.msg
})
},
fun4(){
this.$store.dispatch('setWxNameAjax',{
wxName:this.msg,
_this:this
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
测试效果:




 本文详细介绍了Vuex在Vue.js中的应用,包括其作为状态管理模式的原理、何时选择使用、核心概念如state、mutation、action和module的用法,以及如何处理异步操作和数据的存取。通过实例演示了Vuex在实际项目中的使用和测试效果。
本文详细介绍了Vuex在Vue.js中的应用,包括其作为状态管理模式的原理、何时选择使用、核心概念如state、mutation、action和module的用法,以及如何处理异步操作和数据的存取。通过实例演示了Vuex在实际项目中的使用和测试效果。

















 3488
3488

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










