直接在子线程中调用一下代码:
Director::getInstance()->getScheduler()->performFunctionInCocosThread([&, this]
{
// 运行在主线程中
log("performFunctionInCocosThread");
});需要注意的是,因为这段代码运行在主线程中,你无法知道具体运行的时间,有可能线程已经运行完毕退出了,这部分代码还没有执行完毕。所以需要自己把控。
使用:
HelloWorldScene.h
#ifndef __HELLOWORLD_SCENE_H__
#define __HELLOWORLD_SCENE_H__
#include "cocos2d.h"
class HelloWorld : public cocos2d::Scene
{
public:
static cocos2d::Scene* createScene();
virtual bool init();
void menuCloseCallback(cocos2d::Ref* pSender);
// 线程调用的方法
void runThread();
CREATE_FUNC(HelloWorld);
};
#endif // __HELLOWORLD_SCENE_H__HelloWorldScene.cpp
#include "HelloWorldScene.h"
#include "SimpleAudioEngine.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
Scene* HelloWorld::createScene()
{
return HelloWorld::create();
}
Label* label;
bool HelloWorld::init()
{
if (!Scene::init())
{
return false;
}
auto visibleSize = Director::getInstance()->getVisibleSize();
// 文字标签
label = Label::createWithSystemFont("1111111", "Arial", 25);
label->setPosition(Vec2(visibleSize.width/2, visibleSize.height/2));
this->addChild(label);
// 开启线程
thread t1(&HelloWorld::runThread,this);
t1.detach();
return true;
}
// 线程调用的方法
void HelloWorld::runThread() {
// 子线程中 调用 该方法
Director::getInstance()->getScheduler()->performFunctionInCocosThread([&, this]
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
}
label->setString("22222222222222");
log("mian finish");
});
// 子线程退出
log("thread finish");
}
开启一个线程,线程调用 runThread() 方法。
该方法中,在代用 performFunctionInCocosThread 方法,切换到主线程
打印日志可以看到:
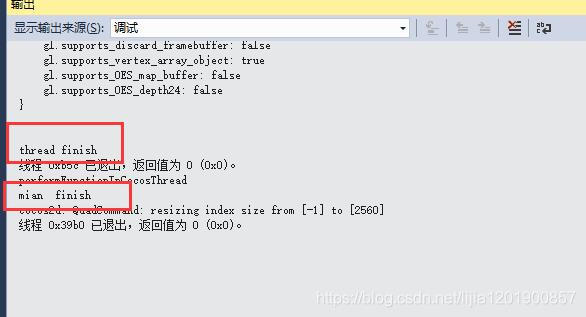
子线程比 performFunctionInCocosThread中的代码先一步结束。
























 2450
2450

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








