1、二分类
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
X, y = mglearn.datasets.make_forge()#导入数据
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 3))#1行2列
for model, ax in zip([LinearSVC(), LogisticRegression()], axes): #模型取=LinearSVC(), LogisticRegression()
clf = model.fit(X, y)
mglearn.plots.plot_2d_separator(clf, X, fill=False, eps=0.5,
ax=ax, alpha=.7)
mglearn.discrete_scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], y, ax=ax)
ax.set_title(clf.__class__.__name__)
ax.set_xlabel("Feature 0")
ax.set_ylabel("Feature 1")
axes[0].legend()

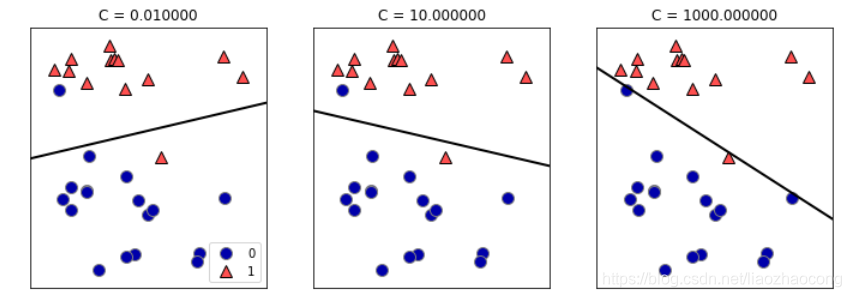
mglearn.plots.plot_linear_svc_regularization()
使用正则化
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
cancer = load_breast_cancer()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
cancer.data, cancer.target, stratify=cancer.target, random_state=42)
logreg = LogisticRegression().fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Training set score: {:.3f}".format(logreg







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








