BFS
注意:当边权都为1时,可以用BFS求最短路
queue <= 初始状态
while(queue 不空)
{
t <= 队头
队头出队
扩展t
}
例题:走迷宫

-
每次从一点向四处扩,扩展要求必须满足该点符合题意且从未走过(可以保证是最短路)
-
注意记录到起点的距离(移动次数)
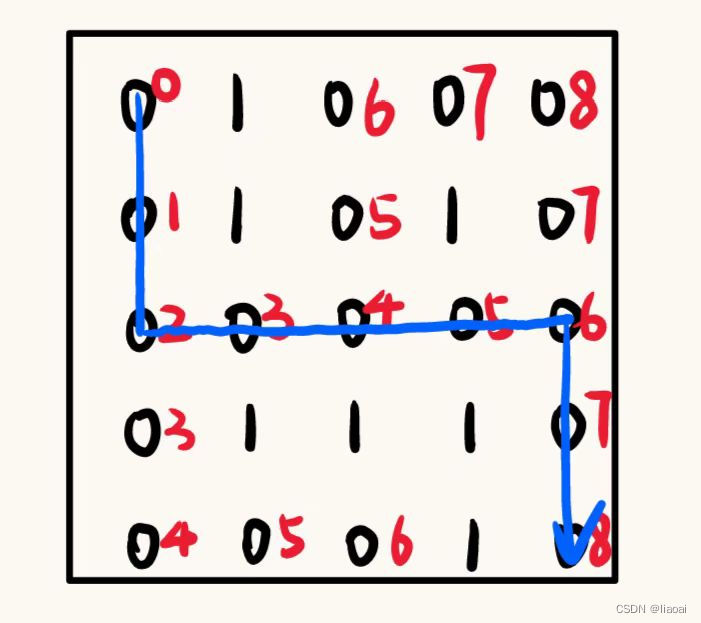
模拟样例:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 110;
//g存地图,d存到起点的距离
int g[N][N],d[N][N];
int n,m;
int bfs()
{
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
queue<PII> q;
//从(0,0)开始,queue <= 初始状态
d[0][0] = 0;
q.push({0,0});
int dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
while(q.size())
{
//t <= 队头
PII t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
//扩展下一点的下标
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
//要求该点从未经过(d[x][y] == -1)
if(x < n && x >= 0 && y < m && y >= 0 && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1)
{
q.push({x,y});
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1; //记录距离
}
}
}
return d[n-1][m-1];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)
cin >> g[i][j];
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








