Handler的工作流程
我们先从消息的发送和接收切入,也就是handler的工作流程。

如何往MessageQueue中放数据queue.enqueueMessage()
首先MessageQueue是数据结构是一个优先级队列

如何重MessageQueue中取数据呢?
通过Looper.loop()方法从MessageQueue中循环的取,queue.next。

从图中可以看出,当队列中没有message时,nextPollTimeoutMillis=-1,looper会一直休眠;那么当我们往队列中放入message时queue.enqueuemessage(),looper是不是应该起来干活了?
这时在会调用queue.enqueuemessage()中的nativeWake(mPtr),把looper唤醒,起来干活了。
这里就涉及到休眠和唤醒:nativePollOnce/NativeWake
Message next(){
for(;;){
...
// 阻塞
nativePollOnce();
...
}
}
//android_os_MessageQueue.cpp
static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativePollOnce(){
NativeMessage * nativeMessageQueue = reinterpter_cast<NativeMessageQueue*>(ptr);
nativeMessageQueue->poolOnce();
}
void NativeMessageQueue::poolOnce(){
...
mLooer->pollOnce(timeoutMillis)
...
}
//Looper.cpp
int Looper:pollOnce(timeoutMillis){
...
result = pollInner(timeoutMillis)
}
int Looper::pollInner(timeoutMillis){
...
// 就是这里利用epoll_wait(),进行阻塞等待,这里timeoutMillis表示阻塞时间
int eventCount = epoll_wait(timeoutMillis)
...
awake();
...
}
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg,long when){
...
//将消息放到队头
if(needWake){
// 唤醒
natieWake(mPtr);
}
}
// android_os_MessageQueue.cpp
static void android_os_MessageQueue(){
NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = reinterpret_cast< NativeMessageQueue *>(ptr);
nativeMessageQueue
}
void NativeMessageQueue::wake(){
mLooper->wake();
}
void Looper::wake(){
...
//往mWakeEventFd中 write 1,用以唤醒looper
ssize_t mWrite = TEMP_FAILURE_READY(write(mWakeEventFd,...))
}epoll是lINUX内核中的一种可扩展IO时间处理机制,大量应用程序请求时能够获得较好的性能。通俗点说:epoll会把哪个流发生了怎样的I/O时间通知我们,这样就避免了,如果有很多刘都没有数据,我们都要去循环遍历,浪费CPU。
Looper和线程是怎么样关联的呢?
public static void prepare() {
prepare(true);
}
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}通过代码发现是通过prepare()方法ThreadLocal关联的,ThreadLocal就不再讲了,这样就保证了一个线程对应一个自己的Looper
public Handler(@NonNull Looper looper, @Nullable Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = looper;
mQueue = looper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}通过handler的构造方法得知,一个Looper对应一个自己的MessageQueue。

作为一个阻塞优先级队列MessageQueue,当多个Handler往MessageQueue中添加数据(发消息时,各个Hanlder可能处于不同的线程),那它的内部是如何确保线程安全的?
看源码可以得知,不论是enqueuemessage()还是next()方法,内部有synchronized内置锁,这样就保证了线程安全。
什么是synchronized?请看:深入理解并发编程和归纳总结_醉饮千觞不知愁的博客-优快云博客
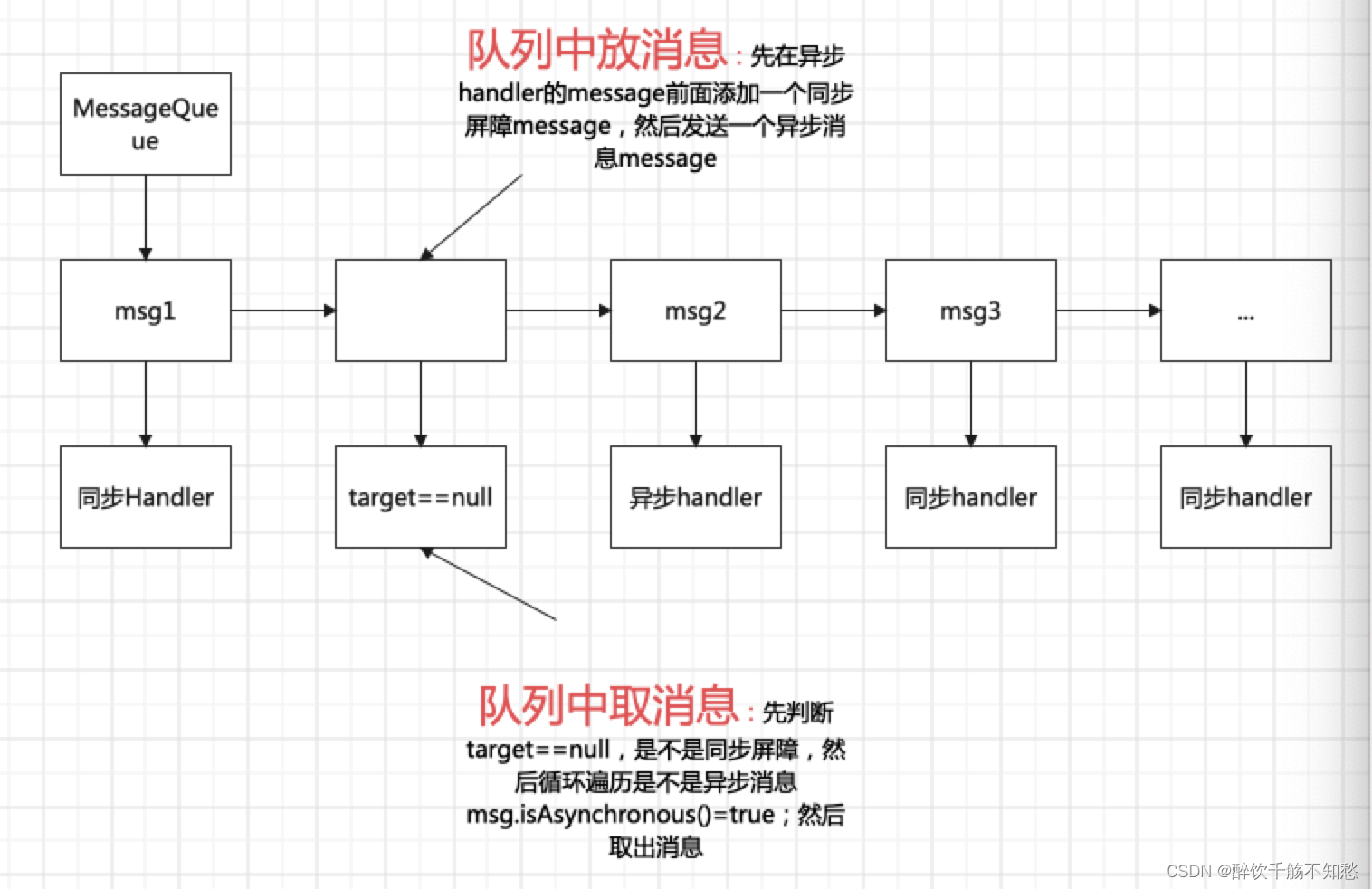
消息机制之同步屏障:
MessageQueue是根据执行时间进行优先级排序的,然后消息保存在队列中,因而消息只能从队列的队头开始取,那么问题来了。万一有一个紧急消息来了怎么办?
比如我们手机的UI刷新机制,也是用的Handler。
MessageQueue中有个postSyncBarrier()方法,给looper的消息队列中发送一个同步屏障。
private int postSyncBarrier(long when) {
// Enqueue a new sync barrier token.
// We don't need to wake the queue because the purpose of a barrier is to stall it.
synchronized (this) {
final int token = mNextBarrierToken++;
final Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.markInUse();
msg.when = when;
msg.arg1 = token;
Message prev = null;
Message p = mMessages;
if (when != 0) {
while (p != null && p.when <= when) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
}
}
if (prev != null) { // invariant: p == prev.next
msg.next = p;
prev.next = msg;
} else {
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
}
return token;
}
}注意上面的message给msg.target赋值,即msg.target==null
下面是ViewRootImpl和 Choreographer的代码:
// UI刷新
void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
// 先给队列中发送一个同步屏障
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
// 然后发送一个异步消息
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
mChoreographer.postCallback->
private void postCallbackDelayedInternal(int callbackType,
Object action, Object token, long delayMillis) {
if (DEBUG_FRAMES) {
Log.d(TAG, "PostCallback: type=" + callbackType
+ ", action=" + action + ", token=" + token
+ ", delayMillis=" + delayMillis);
}
synchronized (mLock) {
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final long dueTime = now + delayMillis;
mCallbackQueues[callbackType].addCallbackLocked(dueTime, action, token);
if (dueTime <= now) {
scheduleFrameLocked(now);
} else {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_DO_SCHEDULE_CALLBACK, action);
msg.arg1 = callbackType;
// 发送一个异步消息
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, dueTime);
}
}
}我们来看next()方法:
synchronized (this) {
// Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message prevMsg = null;
Message msg = mMessages;
if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {
// Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.
do {
prevMsg = msg;
msg = msg.next;
} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());
}上面这段代码是这样的:
假如我们发现了一个消息屏障:if (msg != null && msg.target == null),我们就循环遍历找出
msg.isAsynchronous()=true的异步消息,return给loop中去。
拿到消息后就移出同步屏障。























 758
758

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








