英文原文:
https://research.colfax-intl.com/cutlass-tutorial-wgmma-hopper/
翻译文:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ysvE4PBiKkljwFfBQAN1Jw
创建TiledMMA
TiledMMA tiled_mma = make_tiled_mma(SM90_64x64x16_F16F16F16_SS{}, Layout<Shape<_2,_1,_1>>{});
dim3 dimBlock(cute::size(tiled_mma));
定义了一个 WGMMA 操作,其中 warp 组 1 和 2 分别计算输出瓦片的上半部分和下半部分,沿M模式划分(现在假设bM是 128
的倍数)。此外,size(tiled_mma)将等于 256(2 warp groups => 2 * 4 * 32 threads)。
构建共享内存布局tile_to_shape
如果A, B是MN_major的
auto bM = Int<128>{};
auto bN = Int<128>{};
auto bK = Int< 64>{};
auto bP = Int< 3>{}; // Pipeline
auto sA = cute::tile_to_shape(GMMA::Layout_MN_SW128_Atom<T>{}, cute::make_shape(bM, bK, bP));
auto sB = cute::tile_to_shape(GMMA::Layout_MN_SW128_Atom<T>{}, cute::make_shape(bN, bK, bP));
sA或sB:
Sw<3,4,3> o smem_ptr[16b](unset) o ((_64,_2),(_8,_8),_3):((_1,_512),(_64,_1024),_8192)
((_64,_2),(_8,_8)):((_1,_512),(_64,_1024))的layout形状(加粗维度为图中红字维度,斜体维度为图中绿字维度)
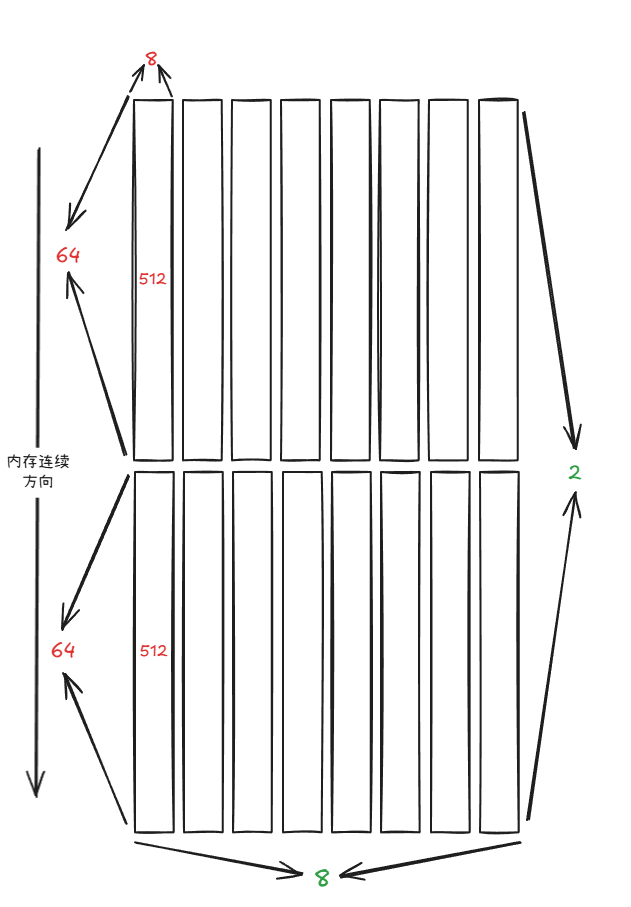
如果A,B是K-major的
auto sA = cute::tile_to_shape(GMMA::Layout_K_SW128_Atom<T>{},cute::make_shape(bM,bK,bP));
auto sB = cute::tile_to_shape(GMMA::Layout_K_SW128_Atom<T>{},cute::make_shape(bN,bK,bP));
那么sA, sB则为:
Sw<3,4,3> o smem_ptr[16b](unset) o (_128,_64,_3):(_64,_1,_8192)
// ((_8,_16),(_64,_1),_3):((_64,_512),(_1,_0),_8192) => (_128,_64,_3):(_64,_1,_8192))
((_8,_16),(_64,_1))😦(_64,_512),(_1,_0))的layout形状为:
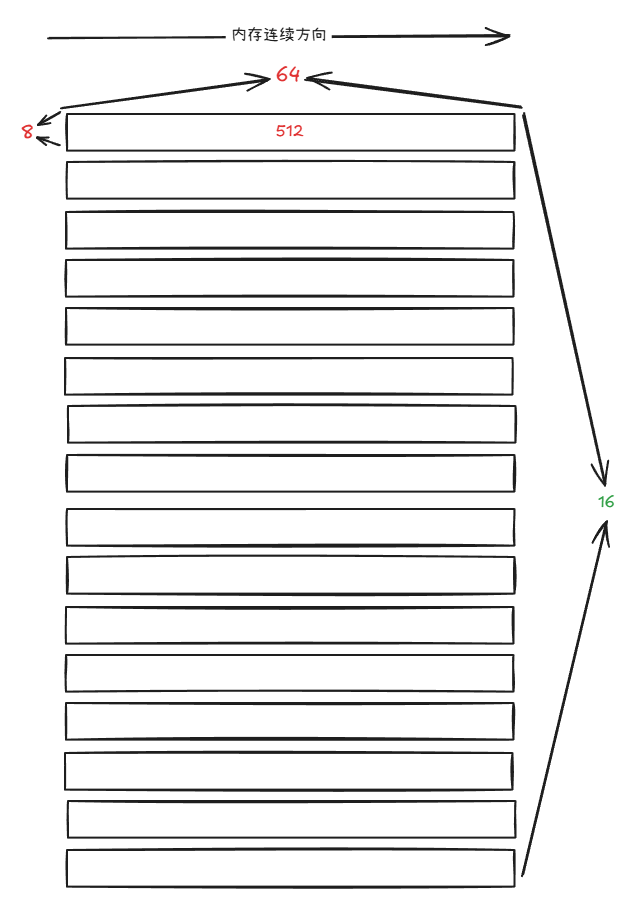
64乘以sizeof(half_t)等于128字节,这是swizzle模式的名称。这是设计:由于核心矩阵的工作方式,我们总是在连续方向上安排布局原子的长度以等于swizzle字节数-对于无swizzle,可以是16,或者32、64或128之一。
GMMA::Layout_MN_INTER_Atom<T>
GMMA::Layout_MN_SW32_Atom<T>
GMMA::Layout_MN_SW64_Atom<T>
GMMA::Layout_MN_SW128_Atom<T>
GMMA::Layout_K_INTER_Atom<T> // 无交错。隐含 16 字节边界。
GMMA::Layout_K_SW32_Atom<T> // 32 字节交错:交错 2 个连续的 16 字节段。
GMMA::Layout_K_SW64_Atom<T> // 交错 4 个连续的 16 字节段。
GMMA::Layout_K_SW128_Atom<T> // 交错 8 个连续的 16 字节段。
MMA thread layout
ThrMMA thr_mma = tiled_mma.get_thread_slice(threadIdx.x); // 0 ~ 127 thread
Tensor tCsA = thr_mma.partition_A(sA); // (MMA,MMA_M,MMA_K,PIPE)
Tensor tCsB = thr_mma.partition_B(sB); // (MMA,MMA_N,MMA_K,PIPE)
Tensor tCgC = thr_mma.partition_C(gC); // (MMA,MMA_M,MMA_N)
A, B矩阵thread layout
tCsA,tCsB的layout为
tCsA: Sw<3,4,3>_smem_ptr[16b](0x7f8800000400) o ((_64,(_8,_2)),_2,_4,_3):((_1,(_64,_1024)),_512,_2048,_8192)
tCsB: Sw<3,4,3>_smem_ptr[16b](0x7f880000c400) o ((_64,(_8,_2)),_2,_4,_3):((_1,(_64,_1024)),_512,_2048,_8192)
tCsA描述的不是共享内存中的A在thread层级的layout,而是整个A在共享内存中的重组layout。
MMA(_64,(_8,_2)): 是MMA Atom的MxK形状,如图(ptx中wgmma的A矩阵在寄存器的layout)K方向每8列重复pattern(64 * 8 * 2),其对应stride分别为:1,64, M * 8 = 128 * 8 = 1024(参看前面sA的图);
实际中共享内存中的数据并未拷贝到寄存器中,只是把一个64位的共享内存的layout信息存在寄存器中供wgmma使用
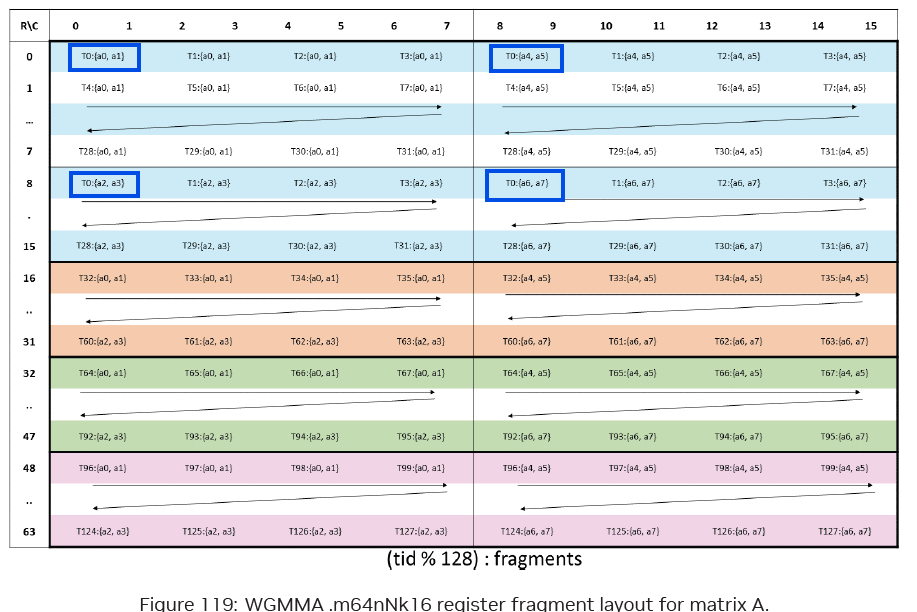
MMA_M(2)和MMA_K(4)是它在sA的M和K模式上平铺的范围(因此MMA_M= bM/64 = 2和MMA_K= bK/16 = 4)。
整个A的大小为MxK = 128 * 64, (128, 64) / (64, (8, 2)) =>(2, 4) ,依照sA的layout,对应的stride为: (512, 2048)
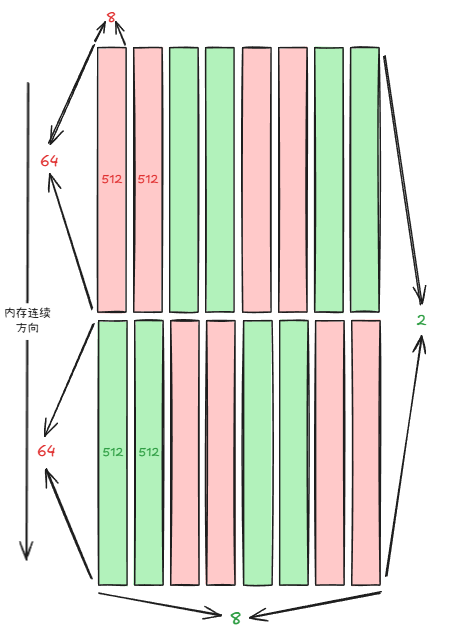
PIPE(3)是stage数。
每个线程的fragment为:
// Allocate "fragments"
Tensor tCrA = thr_mma.make_fragment_A(tCsA);
Tensor tCrB = thr_mma.make_fragment_B(tCsB);
tCrA: GMMA::DescriptorIterator o (_1,_2,_4,_3):(_0,_64,_256,_1024)
tCrB: GMMA::DescriptorIterator o (_1,_2,_4,_3):(_0,_64,_256,_1024)
tCrA中,(2, 4, 3)同tCsA,其对应stride为(单位为thread):(64, 128 * 2 = 256, 128 * 2 * 4 = 1024)
C矩阵 thread layout
C的thread layout:
Tensor tCrC = thr_mma.make_fragment_C(tCgC); // (MMA,MMA_M,MMA_N)
例如thread0的layout为:
tCgC: gmem_ptr[16b](0x7f877a780000) o ((_2,_2,_8),_2,_2):((512,_8,4096),_64,32768)
tCrC: ptr[16b](0x7feee1fffbe0) o ((_2,_2,_8),_2,_2):((_1,_2,_4),_32,_64)
C矩阵的thread layout和A,B不同,描述的是一个thread承包的一个slice的layout,其中:
tCgC是epilogue里拷贝到global memory中的目标layout;
tCrC是计算时寄存器中的一个slice的layout;
MMA = ATOM_MxATOM_N = 64 * 64, MMA_M = MMA_N = 2,与tCsA和tCsB相同
即C最终矩阵大小为 MxN = 128 * 128, (128, 128) / (64, 64) = (2, 2)。
文章中并没有给大矩阵的各个步长,但根据这个地方推测计算一下:从tCgC的layout中的MMA_N=2这一维度看, 由stride为32768可知,大矩阵的M_stride为 32768/64 = 512,
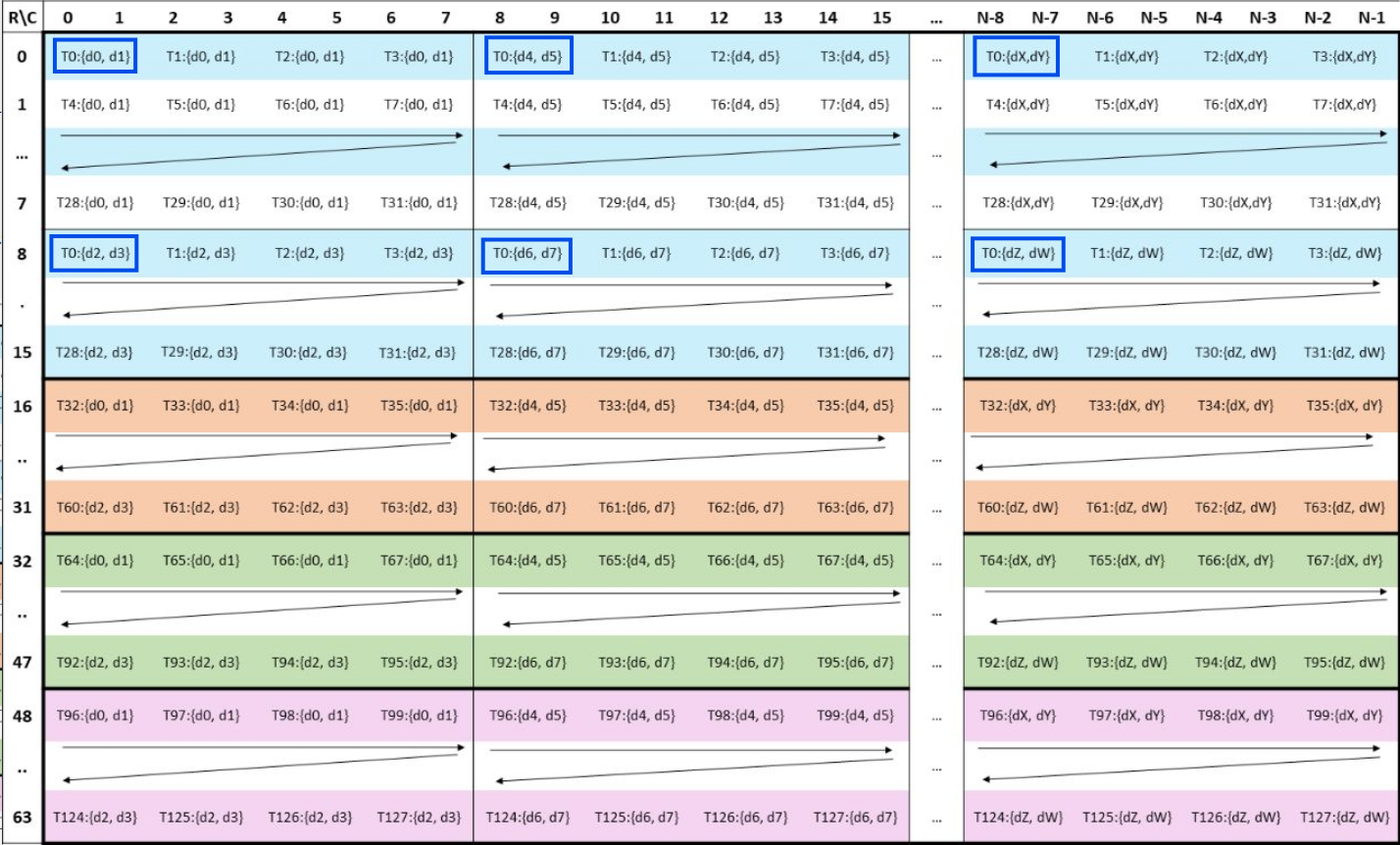
每个线程持有(2,2,8)形状的 32个值,
如图(PTX中wgmma C矩阵的寄存器layout) 蓝色框内为T0所持有的数据,总共2 * 2 * 8=32个值,其中stride依次为(单位为thread):
d0 -> d1: M_stride, 即512, d0 -> d2: 8, d0 -> d4: M_stride * 8 = 4096;
而tCrC中stride部分,d0 -> d1是1,d0->d2是2,d0->d4是4,这应该是指一个thread内寄存器/元素的偏移量;
又ATOM_N=64,下图中dX = 28, dY = 29, dZ = 30, dW = 31, 一个ATOM_MxATOM_N中每个thread用32个寄存器,一个thread中总共32个元素,则在MxN=128*128的C矩阵大小中,(2,2)对应的stride为:(32,64);
WGMMA
cute::warpgroup_arrive(); // -> wgmma.fence
// (V,M,K) x (V,N,K) => (V,M,N)
cute::gemm(tiled_mma, tCrA(_,_,_,read_pipe), tCrB(_,_,_,read_pipe), tCrC); // -> wgmma.mma_sync
cute::warpgroup_commit_batch(); // -> wgmma.commit_group
cute::warpgroup_wait<0>(); // -> wgmma.wait_group
wgmma.fence
在wgmma.mma_async指令前必须用wgmma.fence指令来确保寄存器以及共享内存已经完成写入;
对于涉及寄存器wgmma.mma_sync来说,fence指令确保mma_sync指令前所有的读写都已完成,除非前指令也是mma_sync并使用同一个D,这种情况下不需要fence;
对于涉及共享内存的wgmma.mma_sync来说,如果前面是一般代理的读写共享内存的操作,则需要fence.proxy.async;但如果是TMA操作,则不需要fence.proxy.async。
本例中的A,B都是TMA操作因此不需要fence。
wgmma.mma_sync
//
CUTE_HOST_DEVICE static void
fma(uint64_t const& desc_a,
uint64_t const& desc_b,
uint32_t& d00, uint32_t& d01, uint32_t& d02, uint32_t& d03,
uint32_t& d04, uint32_t& d05, uint32_t& d06, uint32_t& d07,
uint32_t& d08, uint32_t& d09, uint32_t& d10, uint32_t& d11,
uint32_t& d12, uint32_t& d13, uint32_t& d14, uint32_t& d15,
GMMA::ScaleOut const scale_D = GMMA::ScaleOut::One)
{
#if defined(CUTE_ARCH_MMA_SM90A_ENABLED)
asm volatile(
"{\n"
".reg .pred p;\n"
"setp.ne.b32 p, %18, 0;\n"
"wgmma.mma_async.sync.aligned.m64n64k16.f16.f16.f16 "
"{%0, %1, %2, %3, %4, %5, %6, %7, "
" %8, %9, %10, %11, %12, %13, %14, %15}," // d
" %16," // a-desc
" %17," // b-desc
" p, %19, %20, %21, %22;\n" // scale-D, scale-A, scale-B, trans-A, trans-B
"}\n"
: "+r"(d00), "+r"(d01), "+r"(d02), "+r"(d03),
"+r"(d04), "+r"(d05), "+r"(d06), "+r"(d07),
"+r"(d08), "+r"(d09), "+r"(d10), "+r"(d11),
"+r"(d12), "+r"(d13), "+r"(d14), "+r"(d15)
: "l"(desc_a),
"l"(desc_b),
"r"(int32_t(scale_D)),
"n"(int32_t(scaleA)),
"n"(int32_t(scaleB)),
"n"(int32_t(tnspA)),
"n"(int32_t(tnspB)));
#else
CUTE_INVALID_CONTROL_PATH(
"Attempting to use SM90_64x64x16_F16F16F16_SS "
"without CUTE_ARCH_MMA_SM90A_ENABLED");
#endif
}
wgmma.mma_sync完成一个D = A * B + D的矩阵乘加,其中参数:
d0-15: 结果D矩阵的寄存器,其数量为D_m * D_n * sizeof(f16) / (4(byte/thread) * 32(thread) * 4(warp))= 64 * 64 * 2 / (4 * 32 * 4) = 16;
a-desc和b-desc: 为上文提到的"一个64位的共享内存的layout信息"
具体查看:https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/parallel-thread-execution/index.html#asynchronous-warpgroup-level-matrix-shared-memory-layout-matrix-descriptor
scale-D:取值范围0或1;取0则指令效果化为:D = A * B;
scale-A和scale-B: 取值范围-1或1;取-1为矩阵数值取反;
trans-A和trans-B: 取值范围0或1;A和B分别按row-major和col-major存储(K-major),如果需要转置,需指定trans-A或trans-B为1(仅支持.f16,bf16的共享内存中的A,B);
wgmma.commit_group
创建wgmma-group并将前面所有的wgmma.mma_sync操作提交到这个group中;
wgmma.wait_group
等待wgmma.mma_sync指令的完成,其参数N为剩余进行中的mma_sync数量;如果N为0,则等待所有的mma_sync指令完成。
Matrix Descriptor
wgmma.mma_sync中的a-desc和b-desc参数,是64位:
参看PTX:
https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/parallel-thread-execution/index.html#shared-memory-matrix-layout
| 位数 | 描述 | 详细描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 13–0 | Matrix start address | |
| 29–16 | Leading dimension byte offset | K-Major: No-Swizzling: the offset from the first column to the second columns of the 8x2 tile in the 128-bit element type normalized matrix. Swizzled layouts: not used, assumed to be 1. MN-Major: Interleave: offset from the first 8 columns to the next 8 columns. Swizzled layouts: offset from the first (swizzle-byte-size/16) rows to the next (swizzle-byte-size/16) rows. |
| 45–32 | Stride dimension byte offset | K-Major: The offset from the first 8 rows to the next 8 rows. MN-Major: Interleave: offset from the first row to the next row; Swizzled layout: offset from the first 8 columns to the next 8 columns |
| 48-46 | Constant | Fixed constant value of 0b001 |
| 51–49 | Matrix base offset | base_offset = (pattern_start_addr >> 0x7) & 0x7, alignment for each swizzle mode; 0 if pattern_start_addr is 1024 bytes aligned for 128B swizzle, 512 bytes aligned for 64B and 256 bytes aligned for 32B |
| 52 | Constant | Fixed constant value of 0xb0 |
| 53-60 | Constant | Fixed constant value of 0xb00000000 |
| 63-61 | swizzling mode | 0. No swizzling 1. 128-Byte with 32B atomic swizzling 2. 128-Byte swizzling 4. 64-Byte swizzling 6. 32-Byte swizzling Note: Values 3, 5 and 7 are invalid |
以128B Swizzling Mode的K-Major为例,矩阵大小8x8,每个元素128bits即16bytes,一行8 * 16 = 128Bytes,即名字中的128B。
如果每个元素32bits,那么矩阵大小即为 8 * (128 / 32) * 8 = 32 * 8, 即一行128B保持不变。
| Swizzling mode | Leading Dimension / Major-ness | Swizzle atom layout (128b element) |
|---|---|---|
| 128B Swizzling Mode | M/N | 8x8 |
| K | 8x8 | |
| 64B Swizzling Mode | M/N | 4x8 |
| K | 8x4 | |
| 32B Swizzling Mode | M/N | 2x8 |
| K | 8x2 | |
| None | M/N | 1x8 |
| K | 8x1 |
// cutlass/include/cute/atom/mma_traits_sm90_gmma.hpp
// M|N-major GMMA layouts in units of bits
using Layout_MN_INTER_Atom_Bits = ComposedLayout<Swizzle<0,4,3>, smem_ptr_flag, Layout<Shape< _128,_8>,Stride<_1, _128>>>;
using Layout_MN_SW32_Atom_Bits = ComposedLayout<Swizzle<1,4,3>, smem_ptr_flag, Layout<Shape< _256,_8>,Stride<_1, _256>>>;
using Layout_MN_SW64_Atom_Bits = ComposedLayout<Swizzle<2,4,3>, smem_ptr_flag, Layout<Shape< _512,_8>,Stride<_1, _512>>>;
using Layout_MN_SW128_Atom_Bits = ComposedLayout<Swizzle<3,4,3>, smem_ptr_flag, Layout<Shape<_1024,_8>,Stride<_1,_1024>>>;
// K-major GMMA layouts in units of bits
using Layout_K_INTER_Atom_Bits = ComposedLayout<Swizzle<0,4,3>, smem_ptr_flag, Layout<Shape<_8, _128>,Stride< _128,_1>>>;
using Layout_K_SW32_Atom_Bits = ComposedLayout<Swizzle<1,4,3>, smem_ptr_flag, Layout<Shape<_8, _256>,Stride< _256,_1>>>;
using Layout_K_SW64_Atom_Bits = ComposedLayout<Swizzle<2,4,3>, smem_ptr_flag, Layout<Shape<_8, _512>,Stride< _512,_1>>>;
using Layout_K_SW128_Atom_Bits = ComposedLayout<Swizzle<3,4,3>, smem_ptr_flag, Layout<Shape<_8,_1024>,Stride<_1024,_1>>>;
// cutlass/include/cute/swizzle.hpp
// A generic Swizzle functor
/* 0bxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxYYYxxxxxxxZZZxxxx
* ^--^ MBase is the number of least-sig bits to keep constant
* ^-^ ^-^ BBits is the number of bits in the mask
* ^---------^ SShift is the distance to shift the YYY mask
* (pos shifts YYY to the right, neg shifts YYY to the left)
*
* e.g. Given
* 0bxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxYYxxxxxxxxxZZxxx
* the result is
* 0bxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxYYxxxxxxxxxAAxxx where AA = ZZ xor YY
*/
// take 128B swizzle mode as example: Swizzle<3,4,3>
template <int BBits, int MBase, int SShift = BBits>
struct Swizzle
{
static constexpr int num_bits = BBits; // 3
static constexpr int num_base = MBase; // 4
static constexpr int num_shft = SShift; // 3
static_assert(num_base >= 0, "MBase must be positive.");
static_assert(num_bits >= 0, "BBits must be positive.");
static_assert(abs(num_shft) >= num_bits, "abs(SShift) must be more than BBits.");
// using 'int' type here to avoid unintentially casting to unsigned... unsure.
using bit_msk = cute::constant<int, (1 << num_bits) - 1>; // (1 << 3) - 1 = 0b111
using yyy_msk = cute::constant<int, bit_msk{} << (num_base + max(0,num_shft))>; // 0b111 << (4 + 3) = 0b1110000000
using zzz_msk = cute::constant<int, bit_msk{} << (num_base - min(0,num_shft))>; // 0b111 << (4 - 0) = 0b1110000
using msk_sft = cute::constant<int, num_shft>; // 3
static constexpr uint32_t swizzle_code = uint32_t(yyy_msk{} | zzz_msk{}); // 0b1111110000
template <class Offset>
CUTE_HOST_DEVICE constexpr static
auto
apply(Offset const& offset)
{
return offset ^ shiftr(offset & yyy_msk{}, msk_sft{}); // ZZZ ^= YYY
}
template <class Offset>
CUTE_HOST_DEVICE constexpr
auto
operator()(Offset const& offset) const
{
return apply(offset);
}
template <int B, int M, int S>
CUTE_HOST_DEVICE constexpr
auto
operator==(Swizzle<B,M,S> const&) const
{
return B == BBits && M == MBase && S == SShift;
}
};
// Canonical layout: ((8,m),(T,2k)):((8T,SBO),(1,T))
// T = 128 / sizeof-elements-in-bits, represents scale factor which normalizes matrix element types to 128-bits.
// m represents the number of repeating patterns across rows.
// k represents the number of repeating patterns across columns.
// for fp16, T = 128 / 16 = 8
using Layout_K_SW128_Atom_Bits = ComposedLayout<Swizzle<3,4,3>, smem_ptr_flag, Layout<Shape<_8,_1024>,Stride<_1024,_1>>>;
在这个swizzle的结构中,BBits = 3, MBase = 4, SShift = 3, 按照Swizzle代码注释中的说明解读:
/* 0bxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxYYYZZZxxxx
* ^--^ MBase = 4, the number of least-sig bits to keep constant
* ^-^^-^ BBits = 3, the number of bits in the mask
* ^-^ SShift = 3, the distance to shift the YYY mask
* (pos shifts YYY to the right, neg shifts YYY to the left)
* =>
* given 0bxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxAAABBBxxxx, result is:
* 0bxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxAAARRRxxxx, where RRR = AAA ^ BBB, i.e. 6-4 bits are modified
公式是:addr = idx << 4, swizzle_addr = addr ^ ( (addr & (0b111 << 7)) >> 3), , swizzle_idx = swizzle_addr >> 4, 计算(这个地方有兴趣的可以让大模型算算😈)可得到8x8大小的矩阵中每个元素的新位置如图:
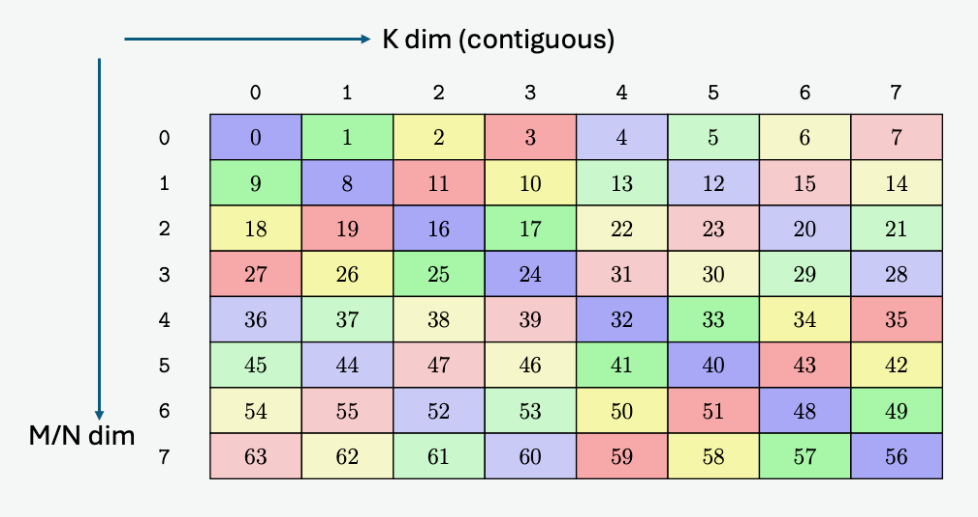
Matrix smem layout
Core Matrix
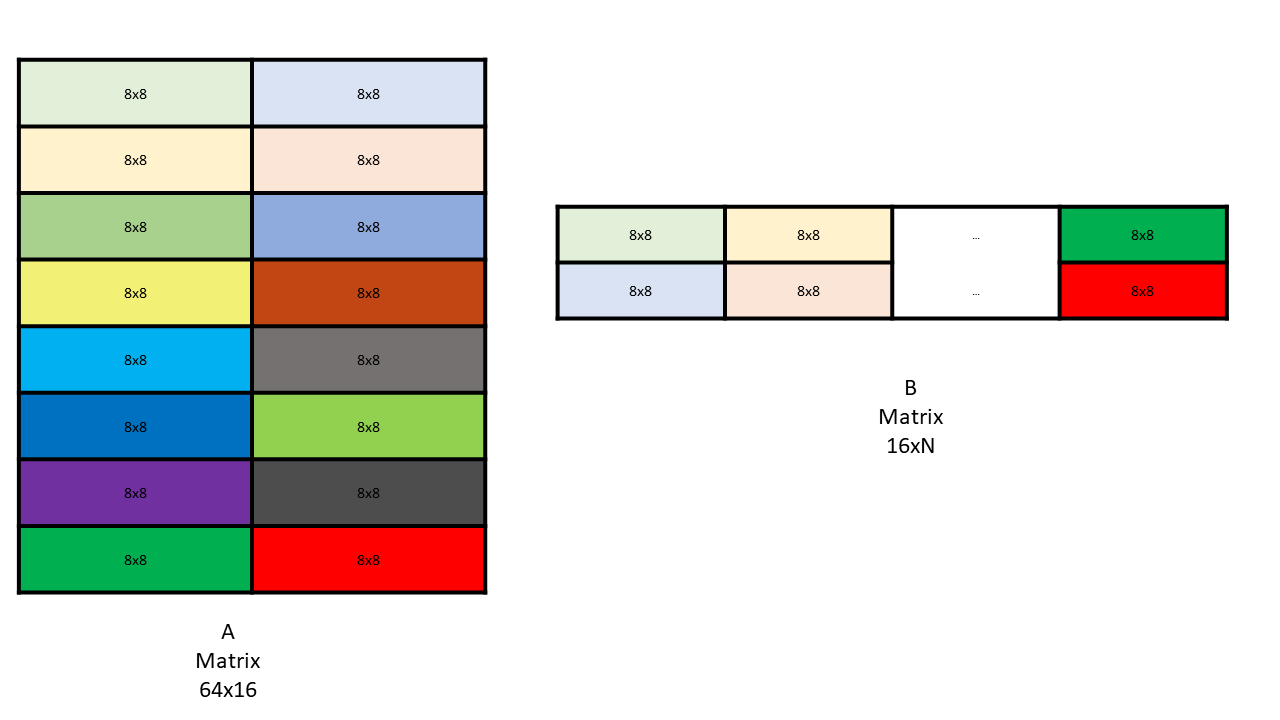
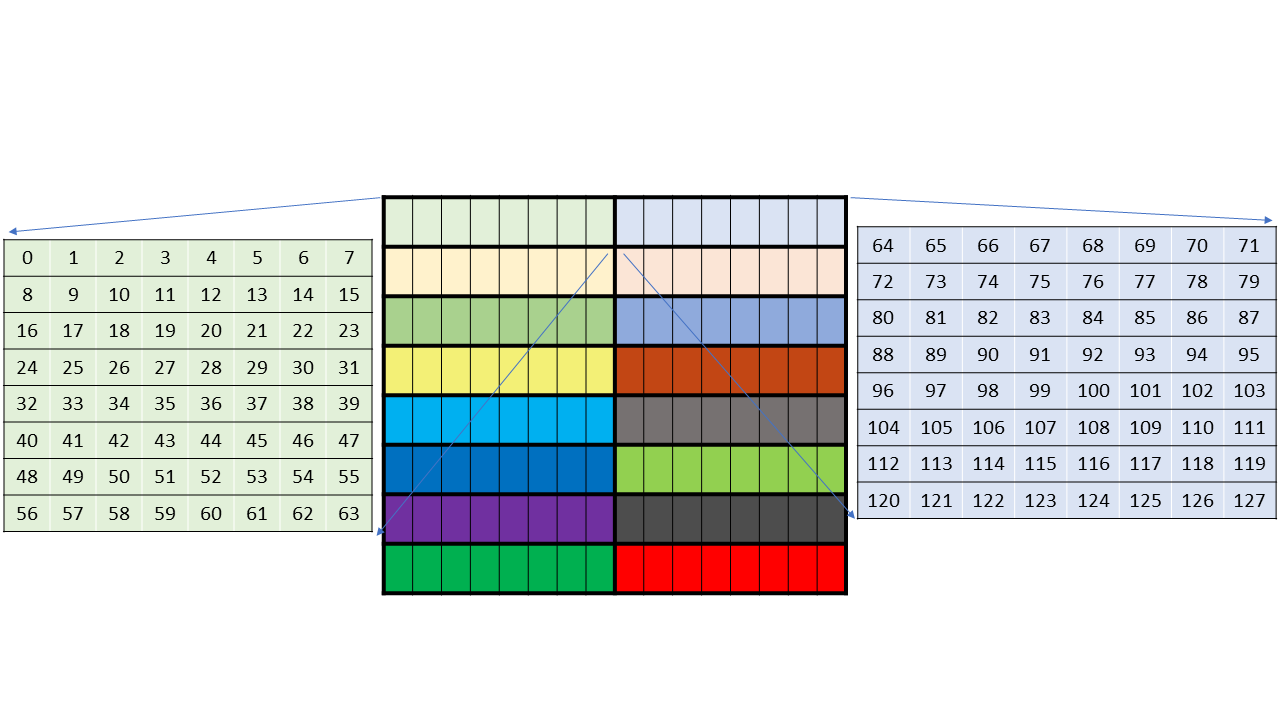
矩阵在共享内存中被分为更小的core矩阵,core矩阵大小为8x(16/sizeof(elem)),其中16 / sizeof(elem)为内存连续方向的大小,可能是行或列。
对于指令wgmma.mma_async.sync.aligned.m64n64k16.f16.f16.f16来说,core矩阵大小为8x8,
矩阵A大小为64x16,总共分为(64 / 8) x (16 / 8) = 8x2 个core矩阵;
矩阵B大小为16x64,总共分为(16 / 8) x (64 / 8) = 2x8个core矩阵;
以下两张图出自PTX8.5,左看右看实在是理解无能,最新的PTX8.7里已经没有这两张图了,然后PTX8.7里新增了上面128B-Swizzle那一套图,另外还举例了几张no-swizzle,32B-swizzle的图,也是理解无能。
A矩阵No-Swizzle
A矩阵128B-Swizzle
NV自己人表示也看不懂PTX里的图,还是以代码为准吧
https://github.com/NVIDIA/cutlass/issues/1396
auto bM = cute::Int<16>{};
auto bN = cute::Int<16>{};
auto bK = cute::Int<128>{};
auto sAk = cute::tile_to_shape(cute::GMMA::Layout_K_SW128_Atom<TA>{}, cute::make_shape(bM,bK));
auto sBk = cute::tile_to_shape(cute::GMMA::Layout_K_SW128_Atom<TB>{}, cute::make_shape(bN,bK));
print_latex(sAk); // % Layout: Sw<3,3,3> o _0 o ((_8,_2),(_64,_2)):((_64,_512),(_1,_1024))
结果还是符合预期的:





















 385
385

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








