代码源码:
框架结构
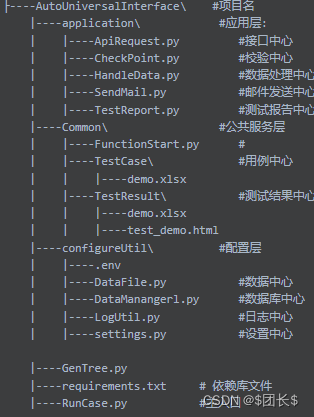
核心代码
excel用例demo

excel数据处理
from configureUtil.LogUtil import getlog
logger = getlog(targetName='HandleData')
import xlrd
from openpyxl import load_workbook,workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Font, colors
import openpyxl
import os
# from Common.FunctionStart import MoveSpace
# from openpyxl import load_workbook
# from openpyxl.reader.excel import load_workbook
# from openpyxl.styles import Color, Font, Alignment
# from openpyxl.styles import colors
'''
1、cope一份用例所保存的excel,当做执行环境保证测试数据清洁。
2、读取excle数据,返回dick形式的结果。
'''
class ExcelHander():
'''
excel操作类,对外提供取excle返回dick结果功能、
新增excel、sheet、
cope excel功能、
写入excel功能等。
'''
def __init__(self,filepath):
self.filepath=filepath
self.wb=xlrd.open_workbook(filepath)#加载excel
self.sheet_names=self.wb.sheet_names()#获取excel所有sheet名集合形如:['test', 'test2', 'test3']
def ExcelDick(self,SheetName):
'''
:param SheetName: excel的sheet名字
:return: 返回读取excel字典类型数据
'''
table = self.wb.sheet_by_name(SheetName)
# 获取总行数
rowNum = table.nrows
# 获取总列数
colNum = table.ncols
if rowNum<=1:
logger.error('总行数小于等于1行')
else:
logger.debug('开始解析excel----excel总行数:%s'%rowNum)
# 获取第一行(表头)
keys = table.row_values(0)
print(keys)
r=[]
j=1
for i in range(rowNum-1):
s={
}
# 从第二行开始
values=table.row_values(j)
print(values)
for x in range(colNum):
s[keys[x]]=values[x]
r.append(s)
j+=1
# logger.debug('返回列名:%s'%r)
ExcelDick={
}
ExcelDick[SheetName]=r
logger.debug('ExcelDick:%s' % ExcelDick)
return ExcelDick #形如ExcelDick{'sheetName':[{列名:values},{列名:values}]}
def sheet_method(self,work_book, add_sheet=[]):
wk = work_book
# rename default sheet
ss_sheet = wk["Sheet"]
# ss_sheet = wk.get_sheet_by_name('Sheet')
ss_sheet.title = add_sheet[0]
for i in range(1, len(add_sheet)):
# add new sheet
wk.create_sheet(add_sheet[i])
# switch to active sheet
# sheet_num = wk.get_sheet_names()
sheet_num = wk.sheetnames
last_sheet = len(sheet_num) - 1
sheet_index = sheet_num.index(sheet_num[last_sheet])
wk.active = sheet_index
def CreateExcel(self,filepath,add_sheet=[]):
'''
:param filepath: excel地址
:return: 无
'''
# 新建一个工作簿
p1=os.path.exists(filepath)#判断是否存在
if p1:
os.remove(filepath)
wb2 = workbook.Workbook()
self.sheet_method(wb2,add_sheet)
logger.debug('新建excle:%s' % filepath)
wb2.save(filepath)
def CopeExcel(self,filepath,newexcelPath,i=0):
'''
:param filepath: 原excel地址
:param newexcelPath: 新excel地址
:param SheetName: 原sheet的名字
:return: 无
'''
# 读取数据
logger.debug('读取数据excle:%s' % filepath)
source = openpyxl.load_workbook(filepath)
target = openpyxl.load_workbook(newexcelPath)
sheets1 = source.sheetnames
sheets2 = target.sheetnames
logger.info('源sheet列表:%s,目标sheet列表:%s'%(sheets1,sheets2))
sheet1 = source[sheets1[i]]
logger.debug('获取sheet:%s' % sheet1)
sheet2 = target[sheets2[i]]
table = self.wb.sheet_by_name(sheets1[i])
# 获取总行数
max_row = table.nrows
# 获取总列数
max_cloumn = table.ncols





 博客围绕Python与Excel展开,包含代码源码、框架结构等内容。有excel用例demo和数据处理,还涉及requests请求封装、检查点函数等,最后有数据处理工厂和发送邮件函数。
博客围绕Python与Excel展开,包含代码源码、框架结构等内容。有excel用例demo和数据处理,还涉及requests请求封装、检查点函数等,最后有数据处理工厂和发送邮件函数。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 1297
1297

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










