主要工作:提出使用双流方法的**2S-AGCN **模型,改进了ST-GCN
主要内容
文章首先提出ST-GCN的几个问题
- 在动作识别中,骨头的方向和长度是很有用的特征,但ST-GCN的模型没有应用这方面的信息。
- ST-GCN更多是应用预先设定好的、自然状态下的人的骨架结构,对于某些特定场景下的识别并不适用。
- GCN网络不同的层应该是包含着不同级别的信息的,但ST-GCN的每一层的图的拓扑结构是固定的,缺乏灵活性。
对于这三个问题,作者提出2S-AGCN的模型
- 为了提取骨骼的信息,将靠近重心的节点作为源节点,另一端作为目标节点,用源节点指向目标节点的向量来表示骨骼。
除了中心节点,骨骼与节点应该是一一对应的,对于中心节点,作者加入了一个值为0的骨骼与其对应,从而能将这两类数据分别送到对应的模型中,也就是J-stream和B-stream。两路数据经模型输出后,将Softmax得到的结果相加,得到最终的分类结果。
- 将原来ST-GCN中的归一化邻接矩阵A k _{\mathrm{k}} k和参数矩阵M K _{\mathrm{K}} K替换成A k _{\mathrm{k}} k、B k _{\mathrm{k}} k和C k _{\mathrm{k}} k相加。(将相乘换成相加的意义在于:如果邻接矩阵中的值一开始是0,那么做乘法就不能在点之间产生新的连接)
A k _{\mathrm{k}} k表示原来的邻接矩阵;
B k _{\mathrm{k}} k也是一个NxN的邻接矩阵,但B k _{\mathrm{k}} k的参数是可学习的,用来表示两个节点之间是否有连接以及连接的强度。
C k _{\mathrm{k}} k是利用一个normalized embedded Gaussian(等价于softmax层)来构建一基于样本的图,用来决定两个点之间是否能产生连接以及这种连接有多强,对于输入的特征图大小为,首先用两个embedding方程(1x1的卷积)将其embed成,并将其resize成和,然后将生成的两个矩阵相乘得到N×N的相似矩阵。既:
网络架构
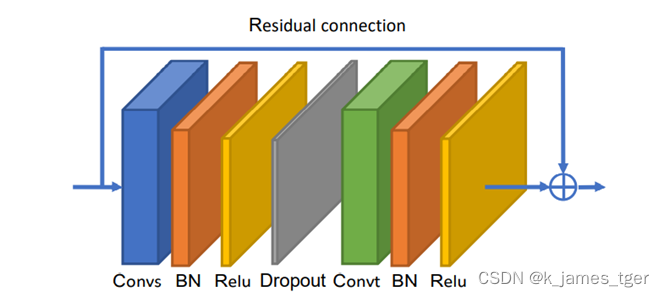
该图表示AGCN的一个模块, AGCN在时间上的卷积与ST-GCN一致。图中的Convs表示空间上的卷积、Convt表示时间上的卷积。
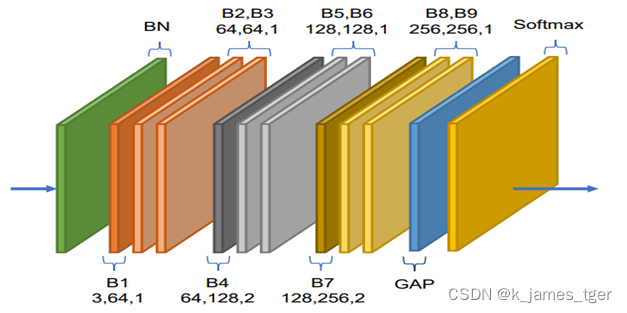
整个AGCN包含9个模块,每个模块的输入输出通道有所不同,GAP为global average pooling 用来代替全连接层,可以减少参数量。
实验
1、为了与ST-GCN直接对比,本文采用了一样的数据集Kinetics和NTU-RGB+D。
2、采用了消融实验,证明三种图A、B、C对正确率的提升均有帮助以及双流的模型优于单流的模型。
3、对不同层的骨架图结构做了可视化,发现更高层的图中包含着更高级的信息,证明了不同的层需要不同的拓扑结构的图。
4、在两个数据集上都达到了最佳水平。




 针对ST-GCN存在的问题,提出2S-AGCN模型,通过双流方法改进动作识别效果。该模型引入可学习的拓扑结构,增强网络灵活性,并通过可视化验证高层级信息的有效性。
针对ST-GCN存在的问题,提出2S-AGCN模型,通过双流方法改进动作识别效果。该模型引入可学习的拓扑结构,增强网络灵活性,并通过可视化验证高层级信息的有效性。

















 3414
3414

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








