剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:
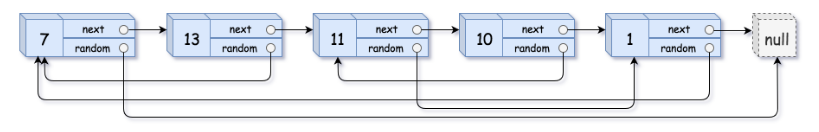
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
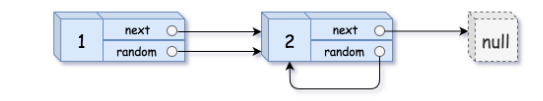
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
思路:
假定以下链表。randon指向给出全部情况。指向别人,指向自己,指向NULL。
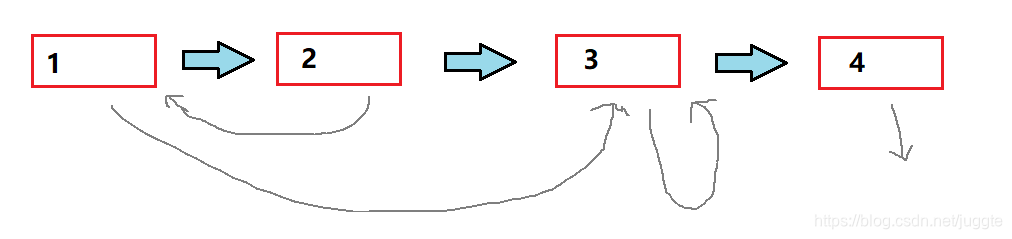
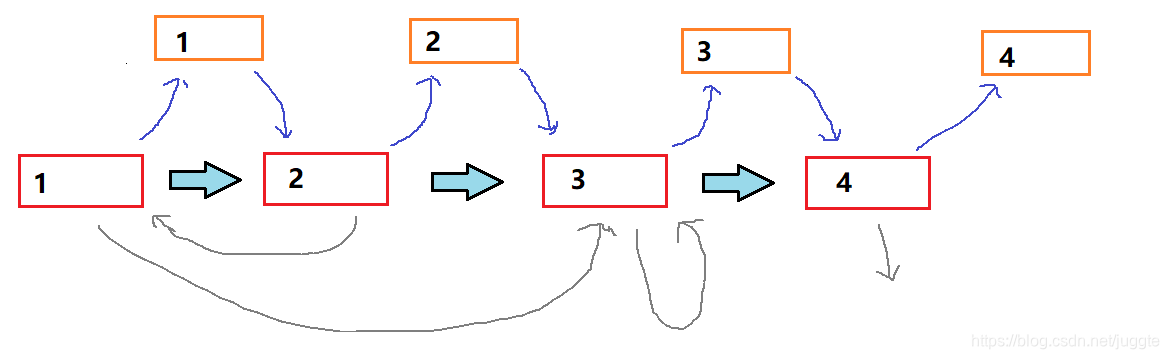
在每个节点后插入一个copy节点。
代码示例:
Node* cur =head;
while(cur)
{
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = cur->val;
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
cur = newNode->next;
}
通过观察发现,每一个copy节点的random都是它上一个节点的random指向的下一个节点。
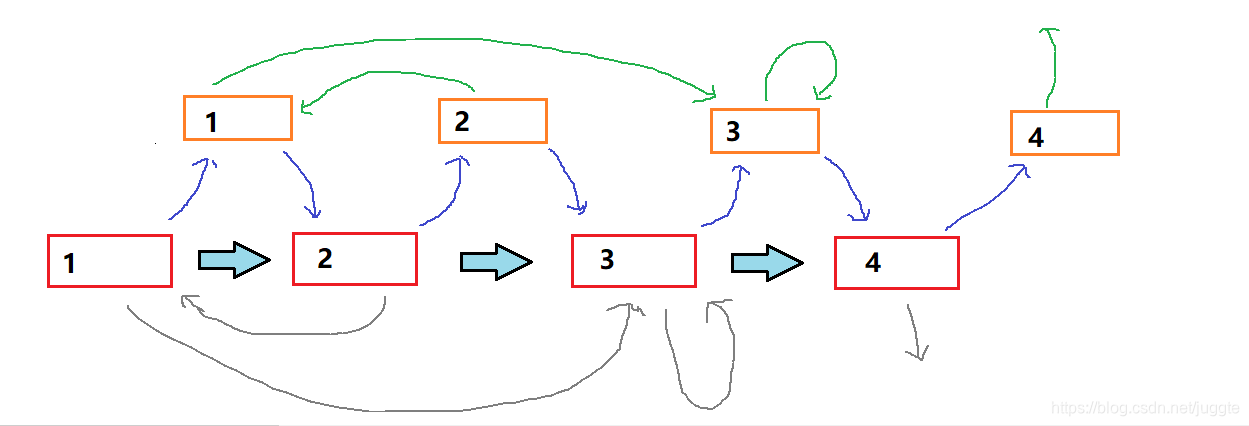
代码示例:
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* newNode = cur->next;
if(cur->random)//注意random指向NULL,
newNode->random = cur->random->next;
else
newNode->random = NULL;
cur = newNode->next;
}
最后,分割两个链表。
//分割链表。
//保留copy链表的头
Node* copyhead = head->next;
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* newNode = cur->next;
Node* next = newNode->next;
if(next)//注意空指针访问
newNode->next = next->next;
else
newNode->next =NULL;
cur->next = next;
cur =next;
}
总体代码示例:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == NULL)
return head;
Node* cur =head;
//1,添加copy节点
while(cur)
{
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = cur->val;
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
cur = newNode->next;
}
//2.复制random
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* newNode = cur->next;
if(cur->random)
newNode->random = cur->random->next;
else
newNode->random = NULL;
cur = newNode->next;
}
//3.分割链表。
Node* copyhead = head->next;
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* newNode = cur->next;
Node* next = newNode->next;
if(next)
newNode->next = next->next;
else
newNode->next =NULL;
cur->next = next;
cur =next;
}
return copyhead;
}




 本文详细介绍了如何复制带有额外random指针的复杂链表。通过在原链表中每个节点后插入副本节点的方式,解决了random指针的复制难题,并提供了完整的代码实现。
本文详细介绍了如何复制带有额外random指针的复杂链表。通过在原链表中每个节点后插入副本节点的方式,解决了random指针的复制难题,并提供了完整的代码实现。

















 2303
2303

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










