TITLE: DetNet: A Backbone network for Object Detection
AUTHOR: Xuepeng Shi, Shiguang Shan, Meina Kan, Shuzhe Wu, Xilin Chen
ASSOCIATION: Tsinghua University, Face++
FROM: arXiv:1804.06215
CONTRIBUTION
- The inherent drawbacks of traditional ImageNet pre-trained model for fine-tunning recent object detectors is analyzed.
- A novel backbone, called DetNet, is proposed, which is specifically designed for object detection task by maintaining the spatial resolution and enlarging the receptive field.
METHOD
Motivation
There are two problems using the classification backbone for object detection tasks. (i) Recent detectors, e.g., FPN, involve extra stages compared with the backbone network for ImageNet classification in order to detect objects with various sizes. (ii) Traditional backbone produces higher receptive field based on large downsampling factor, which is beneficial to the visual classification. However, the spatial resolution is compromised which will fail to accurately localize the large objects and recognize the small objects.
To sumarize, there are 3 main problems to use current pre-trained models, including
- The number of network stages is different. It means that extra layers for object detection compared to classification has not been pretrained.
- Weak visibility of large objects. It is because The feature map with strong semantic information has large strides respect to input image, which is harmful for the object localization.
- Invisibility of small objects. The information from the small objects will be easily weaken as the spatial resolution of the feature maps is decreased and the large context information is integrated.
To address these problems, DetNet has following characteristics. (i) The number of stages is directly designed for Object Detection. (ii) Even though more stages are involved, high spatial resolution of the feature maps is mainted, while keeping large receptive field using dilated convolution.
DetNet Design
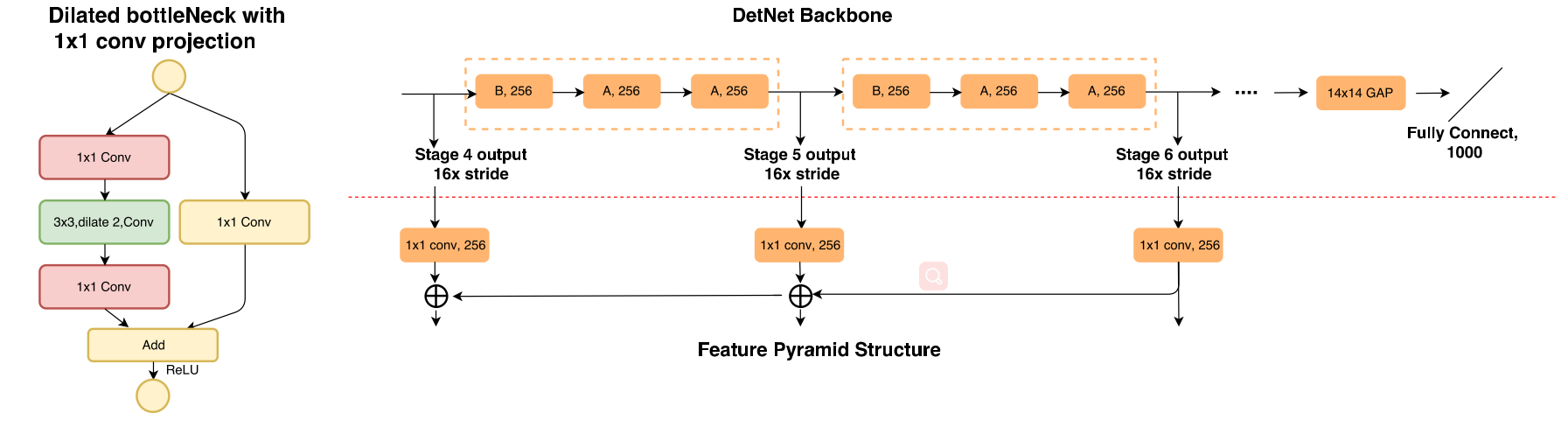
The main architecture of DetNet is designed based on ResNet-50. The first 4 stages are kept same with ResNet-50. The main differences are illustrated as follows:
- The extra stages are merged into the backbone which will be later utilized for object detection as in FPN. Meanwhile, the spatial resolution is fixed as 16x downsampling even after stage 4.
- Since the spatial size is fixed after stage 4, in order to introduce a new stage, a dilated bottleneck with 1×1 1 × 1 convolution projection is utilized in the begining of the each stage. The dilation convolution efficiently enlarge the receptive field.
- Since dilated convolution is still time consuming, stage 5 and stage 6 keep the same channels as stage 4 (256 input channels for bottleneck block). This is different from traditional backbone design, which will double channels in a later stage.
The following figure shows the dialted bottleneck with 1×1 1 × 1 conv projection and the architecture of DetNet.
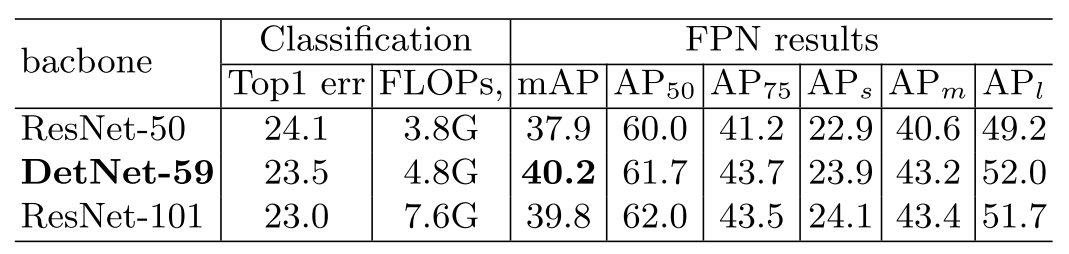
PERFORMANCE








 本文提出了一种新型的骨干网络DetNet,该网络针对对象检测任务进行了优化,通过维持高空间分辨率并扩大感受野来解决传统预训练模型在对象检测上的固有问题。DetNet在ResNet-50的基础上进行改进,保持了前四阶段的设计,并通过扩张卷积引入了额外的阶段,同时确保特征图的空间分辨率固定为16倍下采样。
本文提出了一种新型的骨干网络DetNet,该网络针对对象检测任务进行了优化,通过维持高空间分辨率并扩大感受野来解决传统预训练模型在对象检测上的固有问题。DetNet在ResNet-50的基础上进行改进,保持了前四阶段的设计,并通过扩张卷积引入了额外的阶段,同时确保特征图的空间分辨率固定为16倍下采样。
















 6262
6262

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








