分词
# coding:utf-8
import nltk
import re
import string
from nltk.corpus import brown
from nltk.book import *
from nltk.tokenize import WordPunctTokenizer
# print(brown.words())
# print(len(brown.sents())) # 句子数
# print(len(brown.words())) # 单词数
def filter_punctuation(words):
new_words = [];
illegal_char = string.punctuation + '【·!…()—:“”?《》、;】'
pattern=re.compile('[%s]' % re.escape(illegal_char))
for word in words:
new_word = pattern.sub(u'', word)
if not new_word == u'':
new_words.append(new_word)
return new_words
'''英文文本处理'''
'''词性标注'''
text_en = open(u'./data/text_en.txt',encoding='utf-8-sig',errors='ignore').read()
# text_cn = open(u'./data/text_cn.txt',encoding='utf-8',errors='ignore').read()
text="Don't hesitate to ask questions. Be positive."
# 文本切分成语句
# from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize
# print(sent_tokenize(text))
# 大批量切分
# tokenizer=nltk.data.load('tokenizers/punkt/english.pickle')
# print(tokenizer.tokenize(text))
# 分词1
words=nltk.word_tokenize(text_en)
print(words[0:20])
# 分词2, 分离标点
# tokenizer=WordPunctTokenizer()
# words = tokenizer.tokenize(text)
# print(words)
['The', 'Project', 'Gutenberg', 'EBook', 'of', 'Pride', 'and', 'Prejudice', ',', 'by', 'Jane', 'Austen', 'Chapter', '1', 'It', 'is', 'a', 'truth', 'universally', 'acknowledged']
提取词干
from nltk.stem import LancasterStemmer
stemmerlan=LancasterStemmer()
words = [stemmerlan.stem(x) for x in words]
print(words[0:20])
['the', 'project', 'gutenberg', 'ebook', 'of', 'prid', 'and', 'prejud', ',', 'by', 'jan', 'aust', 'chapt', '1', 'it', 'is', 'a', 'tru', 'univers', 'acknowledg']
去除停用词和标点
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stops=set(stopwords.words('english'))
words = [word for word in words if word.lower() not in stops]
words = filter_punctuation(words)
print(words[0:20])
['project', 'gutenberg', 'ebook', 'prid', 'prejud', 'jan', 'aust', 'chapt', '1', 'tru', 'univers', 'acknowledg', 'singl', 'man', 'possess', 'good', 'fortun', 'must', 'want', 'wif']
低频词过滤
from nltk.probability import *
fdist = FreqDist(words)
words = [word for word in words if fdist[word] > 5]
print(words[0:20])
['prid', 'prejud', 'jan', 'chapt', 'tru', 'univers', 'acknowledg', 'singl', 'man', 'possess', 'good', 'fortun', 'must', 'want', 'wif', 'howev', 'littl', 'known', 'feel', 'view']
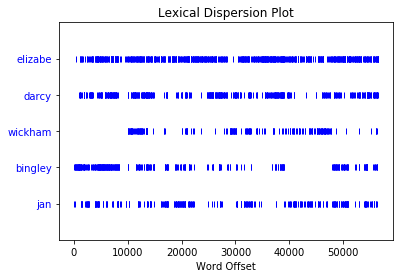
绘制位置图
from nltk.text import *
Text.dispersion_plot(words, [stemmerlan.stem(x) for x in ["Elizabeth", "Darcy", "Wickham", "Bingley", "Jane"]])
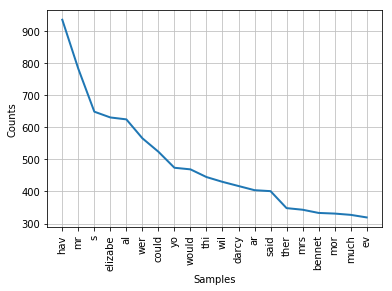
绘制频率分布图
fdist.plot(20)
词汇标注
the lawyer questioned the witness about the revolver
import nltk
sentence = "the lawyer questioned the witness about the revolver"
words = nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)
tags = nltk.pos_tag(words)
print(tags)
[('the', 'DT'), ('lawyer', 'NN'), ('questioned', 'VBD'), ('the', 'DT'), ('witness', 'NN'), ('about', 'IN'), ('the', 'DT'), ('revolver', 'NN')]
得到句法树
sentence = "the boy saw the dog with a rod"
grammar = nltk.CFG.fromstring("""
S -> NP VP
VP -> VBD NP | VBD NP PP
PP -> IN NP
NP -> DT NN | DT NN PP
DT -> "the" | "a"
NN -> "boy" | "dog" | "rod"
VBD -> "saw"
IN -> "with"
""")
words = nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)
rd_parser = nltk.RecursiveDescentParser(grammar)
for tree in rd_parser.parse(words):
print(tree)
(S
(NP (DT the) (NN boy))
(VP
(VBD saw)
(NP (DT the) (NN dog) (PP (IN with) (NP (DT a) (NN rod))))))
(S
(NP (DT the) (NN boy))
(VP
(VBD saw)
(NP (DT the) (NN dog))
(PP (IN with) (NP (DT a) (NN rod)))))





 本文详细介绍了一种处理英文文本的方法,包括分词、词干提取、去除停用词、低频词过滤等步骤,同时展示了如何使用NLTK库进行词性标注、绘制词频分布图和位置图,以及构建句法树。
本文详细介绍了一种处理英文文本的方法,包括分词、词干提取、去除停用词、低频词过滤等步骤,同时展示了如何使用NLTK库进行词性标注、绘制词频分布图和位置图,以及构建句法树。

















 350
350

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










