stack
stack是一种容器适配器,专门用在具有后进先出操作的上下文环境中,其只能从容器的一端进行元素的插入与提取操作。
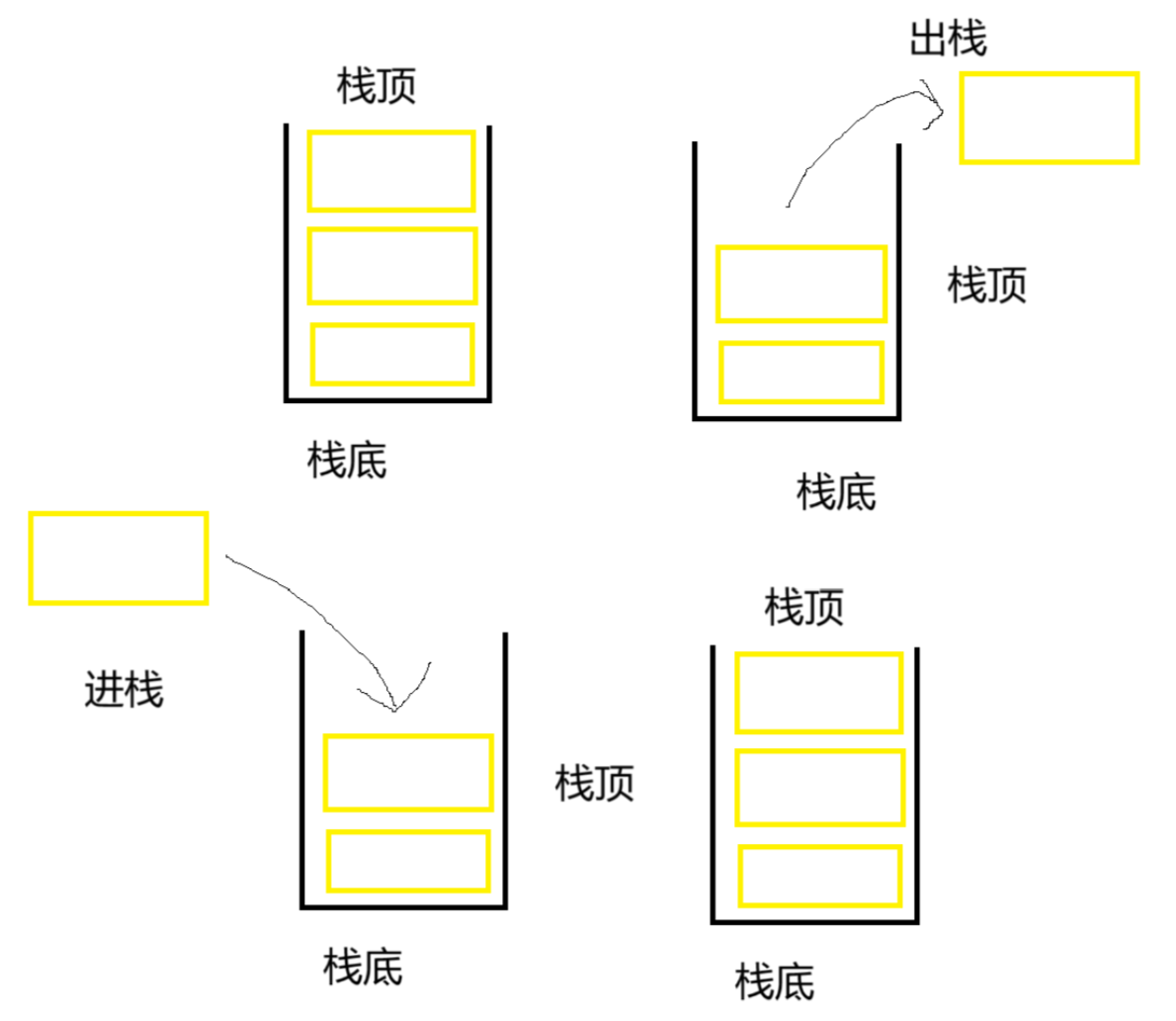
stack的定义方式
//使用内置类型
stack<int> st1;
//使用特定的适配器定义栈。
stack<list<int>> st2;
stack<vector<int>> st3;注意: 如果没有为stack指定特定的底层容器,默认情况下使用deque。
stack使用接口总览
| 成员函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| empty | 判断栈是否为空 |
| size | 返回栈中存储数据个数 |
| top | 取栈顶数据 |
| push | 把数据存放入栈 |
| pop | 数据出栈 |
| swap | 交换两个栈中的数据 |
示例:
int main()
{
//使用内置类型
stack<int> st;
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
st.push(4);
cout << st.size();//4
cout << endl;
while (!st.empty())
{
cout << st.top() << " ";
st.pop();
}//4 3 2 1
}queue
队列是一种容器适配器,专门用在具有先进先出操作的上下文环境中,其只能从容器的一端插入元素,另一端提取元素。

queue的定义方式
//默认类型
queue<int> qu;
//自定义类型
queue<vector<int>> qu1;
queue<list<int>> qu2;注意: 如果没有为queue指定特定的底层容器,默认情况下使用deque。
queue使用接口总览
| 成员函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| empty | 判断队列是否为空 |
| size | 返回队列中有效元素个数 |
| front | 获取队头数据 |
| back | 获取队尾数据 |
| push | 从队尾入队列 |
| pop | 从对头出队列 |
| swap | 交换两个队列中的数据 |
示例:
int main()
{
//使用内置类型
queue<int> qu;
qu.push(1);
qu.push(2);
qu.push(3);
qu.push(4);
cout << qu.size();//4
cout << endl;
while (!qu.empty())
{
cout << qu.front() << " ";
qu.pop();
}//1 2 3 4
}stack和queue的模拟实现都比较简单,这里就一起进行实现了。
stack、queue底层实现
Container 容器适配器
在C++标准库中,stack(栈)和queue(队列)是容器适配器(Container Adapters)。它们不是独立的容器,而是基于其他底层容器实现的。容器适配器提供了一种特定的接口,使得我们可以使用底层容器的功能,但只暴露特定的操作
当我们去C++标准库中搜索stack或者queue时会发现它们的模板参数有两个,第一个是stack和queue当中所存储的元素类型,而另一个就是指定使用的容器类型。


所以Container是什么呢,就是stack和queue的底层容器
| 容器适配器 | 可选底层容器 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| stack |
| 平衡的插入/删除性能 |
|
| 连续内存,尾部操作高效 | |
|
| 任意位置插入/删除高效 | |
| queue |
| 平衡的头部/尾部操作 |
|
| 高效的头部删除 |
stack的模拟实现
namespace lzg
{
template<class T, class Container =std::deque<T>>
class stack
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_back();
}
T& top()
{
return _con.back();
}
const T& top() const
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
void swap(stack<T, Container>& st)
{
_con.swap(st._con);
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}
同理queue的模拟实现也是类似操作
namespace lzg
{
template<class T, class Container = std::deque<T>>
class queue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_front();
}
T& front()
{
return _con.front();
}
const T& front() const
{
return _con.front();
}
T& back()
{
return _con.back();
}
const T& back() const
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
void swap(queue<T, Container>& q)
{
_con.swap(q._con);
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}
 C++ STL中stack和queue的使用与底层实现
C++ STL中stack和queue的使用与底层实现






















 1423
1423

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








