28. 实现 strStr()
题目链接
(1)文字讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0028.实现strStr.html#思路
(2)视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1M5411j7Xx/?spm_id_from=333.788&vd_source=bca249a7a739de13f222d238e1152887
(3)题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string/
看到题解之前的想法
不会写,完全忘记了kmp算法的任何内容。
看到题解之后的想法
其实就是kmp,haystack是字符串,needle是模式串。如果needle或者haystack为空,那么返回0;如果模式串没有匹配到,那么返回-1;否则返回匹配到的第一个位置的下标。
kmp的具体方法请看文字讲解,动图很清楚。
对于我自己来说,需要讲一下的就是next数组的两种写法的区别:
(1)next数组都不➖1:
void getNext(int* next, string s){
next[0] = 0;
int j = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++){
while(j > 0 && s[i] != s[j]){
j = next[j-1];
}
if(s[i] == s[j]){
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
}
检测到s[i] != s[j]的时候,j应该回退到next[j-1]。
- 因为next数组的含义是,前后缀相同的长度,j已经不相同了,j-1是相同的,所以回退到j-1,while判断条件相应变成j》0。
为什么s[i] == s[j]的时候,先j++然后next[i] = j? - 因为这才是重新开始匹配的位置,刚刚检测到s[i] == s[j]的时候,j这个地方已经匹配过了,当然要从j+1开始再匹配。
(2)next统一➕1
class Solution {
public:
void getNext(int* next, string s){
next[0] = -1;
int j = -1;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++){
while(j >= 0 && s[i] != s[j+1]){
j = next[j];
}
if(s[i] == s[j+1]){
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
}
j一开始要变成-1,因为统一都-1. 在比较的时候,应该拿s[j+1]来比,因为之前的j已经-1了。同时要检测的是j>=0,回退当然是回退到j。
当s[i] == s[j+1]的时候,j也要先++,虽然之前的j已经-1了,所以这里的j每次指向的刚好就是匹配的前缀和后缀的末尾,而不是(1)next数组都不➖1的时候的末尾+1,所以每次使用的时候,都是用的s[j+1]
本题难点
kmp算法
代码
next数组都不➖1的代码:
class Solution {
public:
void getNext(int* next, string s){
next[0] = 0;
int j = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++){
while(j > 0 && s[i] != s[j]){
j = next[j-1];
}
if(s[i] == s[j]){
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
}
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
int next[needle.size()];
int j = 0;
getNext(next, needle);
for(int i = 0; i < haystack.size(); i++){
while(j > 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j]){
j = next[j-1];
}
if(haystack[i] == needle[j]){
j++;
}
if(j == needle.size()){
return i-needle.size()+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
next统一➕1
class Solution {
public:
void getNext(int* next, string s){
next[0] = -1;
int j = -1;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++){
while(j >= 0 && s[i] != s[j+1]){
j = next[j];
}
if(s[i] == s[j+1]){
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
}
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
int next[needle.size()];
int j = -1;
getNext(next, needle);
for(int i = 0; i < haystack.size(); i++){
while(j >= 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j+1]){
j = next[j];
}
if(haystack[i] == needle[j+1]){
j++;
}
if(j == needle.size()-1){
return i-needle.size()+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
459.重复的子字符串
题目链接
(1)文字讲解:https://programmercarl.com/0459.重复的子字符串.html
(2)视频讲解:
(3)题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/repeated-substring-pattern/description/
看到题解之前的想法
暴力,两个for循环,第一个for循环的目的是遍历所有可能的子串,第二个for循环,j每次➕本次尝试的子串的长度,然后检查这一段是否和子串严格相等(如果想要剪枝,可以先判断下字符串的长度是否可以整除本轮的子串长度)
看到题解之后的想法
两种方法
(1)库函数
如果一个字符串是由很多个重复子串组成的,那么将两个这样的字符串拼接在一起,中间肯定能组成一个相同的字符串。
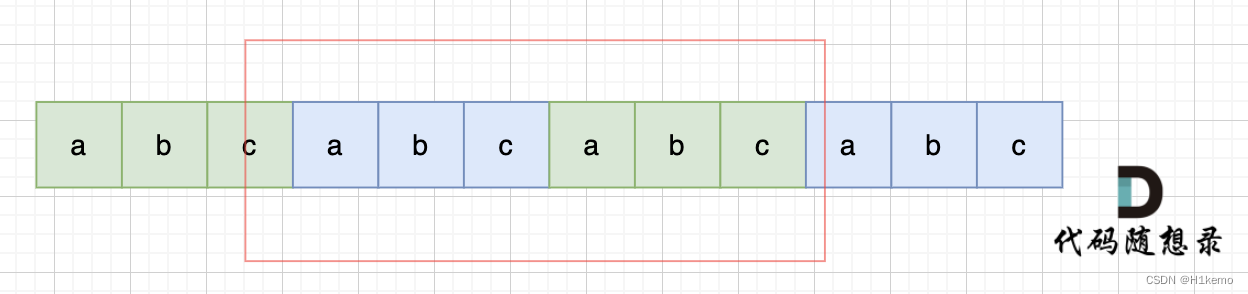
然后我们只需要找拼接后的字符串是否包含源字符串就行。为了防止找到原字符串,将拼接后的字符串的开头和末尾给erase掉。
(2)kmp算法
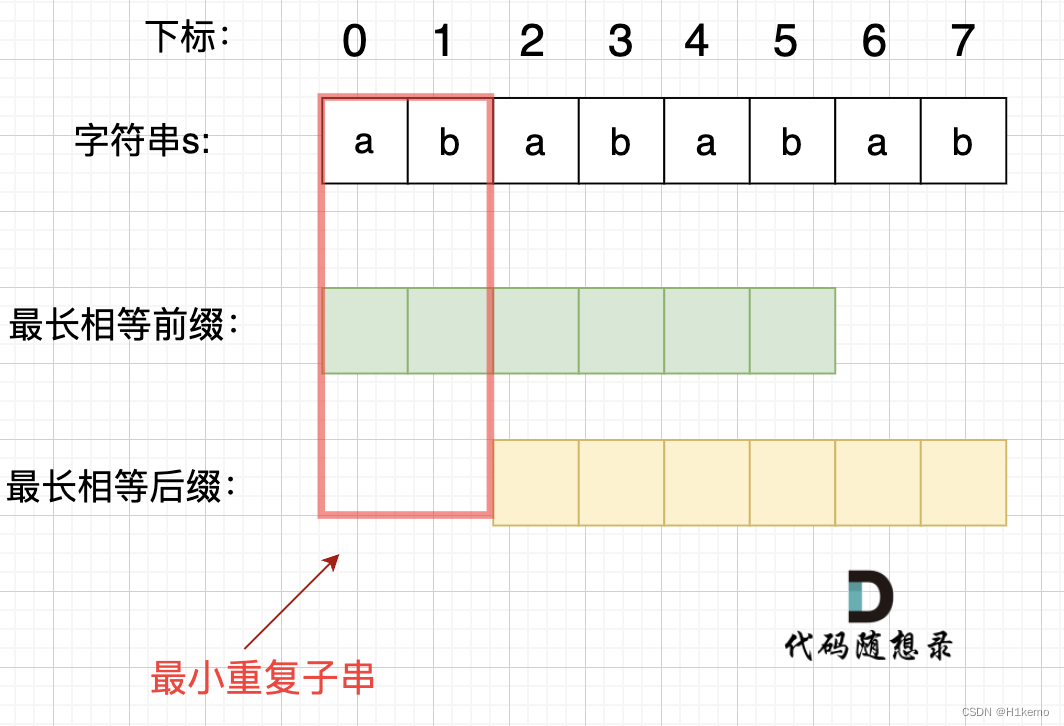
如果一个字符串是由很多个重复子串组成的,那么他的最长相同前后缀肯定是这个子串的重复,并且由于前缀不包含末尾字符,后缀不能包含开头字符,那么这个长相同前后缀不包含的部分,就是被重复的子串。
看图:
证明如下:
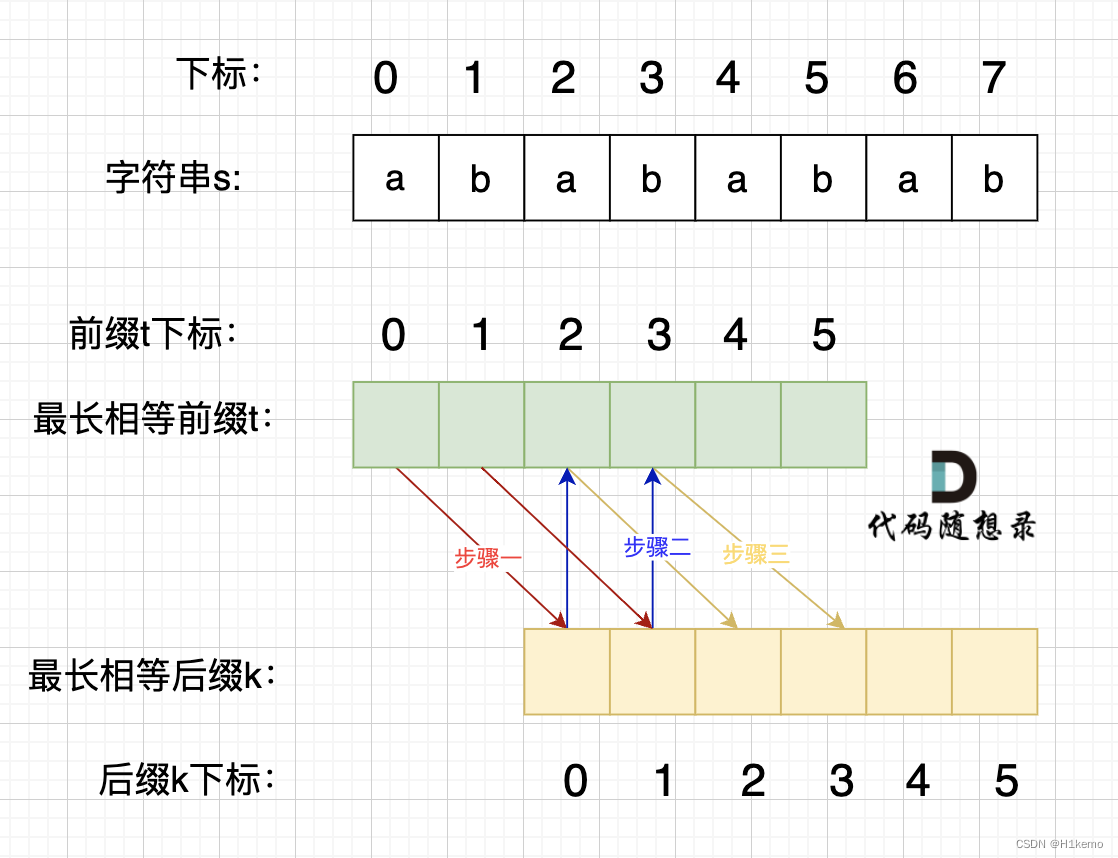
源字符串是s,最长前缀是t,最长后缀是k。
步骤一:t[01] = k[01] (前后缀相等)
步骤二:k[01] = t[23] (位置相同) 所以t[01] = t[23] 所以s[01] = s[23](位置相同)
步骤三:t[23] = k[23] (前后缀相等) 所以k[01] = k[23] s[23] = s[45](位置相同)
所以s[01] = s[23] = s[45]
然后只要s的长度可以整除子串,那么就返回true(防止abababa这种情况)
本题难点
1.kmp和库函数的灵活调用.
2.find找不到子串会返回std::string::npos
代码
next不减1:
class Solution {
public:
void getNext(int* next, string s){
int j = 0;
next[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++){
while(j > 0 && s[i] != s[j]){
j = next[j-1];
}
if(s[i] == s[j]){
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
}
bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string s) {
int next[s.size()];
getNext(next, s);
if(next[s.size()-1] != 0){
int subLen = s.size() - next[s.size()-1];
if(s.size()%subLen == 0){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
next➖1:
class Solution {
public:
void getNext(int* next, string s){
int j = -1;
next[0] = -1;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++){
while(j >= 0 && s[i] != s[j+1]){
j = next[j];
}
if(s[i] == s[j+1]){
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
}
bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string s) {
int next[s.size()];
getNext(next, s);
if(next[s.size()-1] != -1){
int subLen = s.size() - (next[s.size()-1]+1);
if(s.size()%subLen == 0){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
使用库函数的解法:
class Solution {
public:
bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string s) {
string t = s+ s;
t.erase(t.begin());
t.erase(t.end()-1);
if (t.find(s) != std::string::npos) return true;
return false;
}
};




 本文介绍了如何使用KMP算法解决LeetCode中的strStr()问题,以及如何在重复子字符串问题中运用KMP算法和库函数方法。重点讨论了next数组的不同写法以及两种方法的应用策略。
本文介绍了如何使用KMP算法解决LeetCode中的strStr()问题,以及如何在重复子字符串问题中运用KMP算法和库函数方法。重点讨论了next数组的不同写法以及两种方法的应用策略。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








