Java值传递、引用传递
Java is always pass-by-value.若是基本数据类型,值为数据值;若是引用数据类型,其存储的是地址值。
【栈帧中局部变量表,存放基本数据类型变量和值;引用数据类型存放变量和对象地址值(堆中地址)),栈帧私有,堆中对象共享】
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Foo f = new Foo("f");
changeReference(f); // It won't change the reference!
modifyReference(f); // It will modify the object that the reference variable "f" refers to!
}
public static void changeReference(Foo a) {
Foo b = new Foo("b");
a = b;
}
public static void modifyReference(Foo c) {
c.setAttribute("c");
}
}

看更多例子:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40480/is-java-pass-by-reference-or-pass-by-value
一、what is a copy
分为两类:
- reference copy:create a copy of a reference variable pointing to an object.
- object copy:create a copy of the object itself.
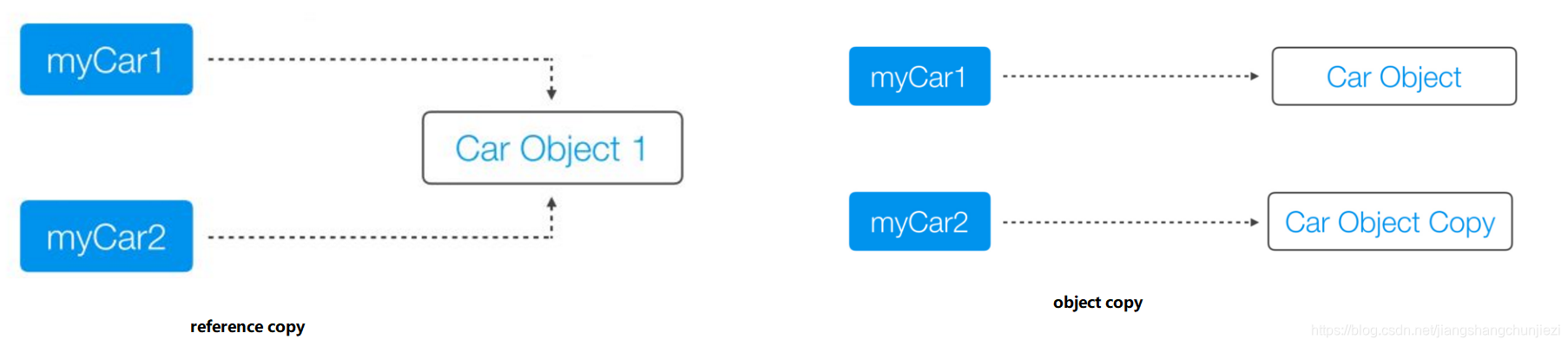
二、Shallow Copy & Deep Copy
Both a Deep Copy and a Shallow Copy are types of object copies.
An object copy usually called a clone,is created if we want to modify or move an object, while still preserving the original object.
1. Shallow Copy
A shallow copy of an object copies the ‘main’ object, but doesn’t copy the inner objects. The ‘inner objects’ are shared between the original object and its copy.Shallow copy is not 100% independent of original object.
inner object也就是引用类型,它是reference copy。
public class Dog {
private String name;
private List<Child> childs ;
public Dog(Dog dog) {
this.name = dog.name;
//shallow copy
this.childs=dog.childs; //reference copy
}
}
测试
List<Child> ls=new ArrayList<>();
ls.add(new Child("child0"));
Dog aDog = new Dog("Max",ls);
Dog copyDog=new Dog(aDog);
System.out.println(aDog==copyDog); //false
System.out.println(aDog.getChilds()==copyDog.getChilds()); //true

2.Deep Copy
a deep copy is a fully independent copy of an object. If we copied our Person object, we would copy the entire object structure.
To create a true deep copy, we need to keep copying all of the Dog object’s nested elements, until there are only primitive types and “Immutables” left.
(基本数据类型存放在堆对象中,immutable若更改则会创建对象,并不会影响之前的值)
public Dog(Dog dog) {
this.name = dog.name;
//deep copy
this.childs=new ArrayList<>(dog.getChilds());
//内部调用elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}

三、Cloneable
如上,通过构造函数,可以实现深复制和浅复制。Java还提供了Cloneable接口,它是一个marker interface。
public class A implements Cloneable{
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (A)super.clone();
}
}
public class Dog implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private List<Child> childs ;
private A a; //mutable fields所对应类也要实现Cloneable
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// return super.clone(); //shadow copy
//-------华丽的分割线-----------
//deep copy
cloneDog cl=(cloneDog)super.clone();
/* primitive fields are ignored, as their content is already copied
immutable fields like String are ignored
create new objects for any non-primitive, mutable fields
*/
cl.childs=new ArrayList<>(getChilds());
cl.a=(A)this.a.clone();
return cl;
}
}
四、Shallow copy Vs Deep Copy
- Shallow copies are inexpensive and easy to implement.
Deep copies are expensive as(因为) each referenced object has to be created separately. It is also more complex as object tree may be very long. - In case of shallow copy though a distinct copy of an object is created with its own set of fields but object references are shared.
In case of deep copy even for the referenced objects separate copies are created. - By default Object class’ clone method creates a shallow copy.
For creating a deep copy you need to override clone method and call the clone method on the referenced objects too.
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








