JUC高并发编程
5.1)ArrayList集合线程
5.1.1)ArrayList集合线程不安全案例展示
代码如下:
public class ArrayListErrorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建ArrayList集合
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 同时创建30个线程同时向集合中添加和获取元素
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
//向集合添加内容
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8));
//从集合获取内容
System.out.println(list);
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
输出:
Exception in thread "27" Exception in thread "17" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException at java.util.ArrayListItr.next(ArrayList.java:859) at java.util.AbstractCollection.toString(AbstractCollection.java:461) at java.lang.String.valueOf(String.java:2994) at java.io.PrintStream.println(PrintStream.java:821) at com.study.collection.ArrayListErrorDemo.lambda0(ArrayListErrorDemo.java:24) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) java.util.ConcurrentModificationException at java.util.ArrayListItr.next(ArrayList.java:859) at java.util.AbstractCollection.toString(AbstractCollection.java:461) at java.lang.String.valueOf(String.java:2994) at java.io.PrintStream.println(PrintStream.java:821) at com.study.collection.ArrayListErrorDemo.lambda0(ArrayListErrorDemo.java:24) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
发现报错,java.util.ConcurrentModificationException ——》并发修改异常
问题: 为什么会出现并发修改异常?
查看ArrayList的add方法源码 ,如下:
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
add() 方法没有添加 synchronized 关键字,即没有对多线程情况进行处理
5.1.2)ArrayList集合线程不安全解决方案
5.1.2.1)解决方案1-Vector
Vector 是矢量队列,它是JDK1.0版本添加的类;继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable 这些接口。 它是一个队列,支持相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。
Vector 实现了RandmoAccess接口,提供了随机访问功能。 可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象;这就是快速随机访问。
代码如下:
// Vector解决ArrayList集合线程不安全问题
public class VectorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Vector集合
List<String> list = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
//向集合添加内容
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8));
//从集合获取内容
System.out.println(list);
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
输出:
[2e6f3116, 6fe43ea3, 02fca385, b678c6a3, dd308329, ab1ed47c]
[2e6f3116, 6fe43ea3, 02fca385, b678c6a3, dd308329, ab1ed47c, 6940b25f, de6b1ff7, 762f2d14, c88c6146, 8eb58040, 0d628c6c, b0c3849e, 4bed8696, 11c2ac32, ea177a6a, 6c0e1f8f, 50040ab8, 7e3a1e0d, 9162aee6]
...
[2e6f3116, 6fe43ea3, 02fca385, b678c6a3, dd308329, ab1ed47c, 6940b25f, de6b1ff7, 762f2d14, c88c6146, 8eb58040, 0d628c6c, b0c3849e, 4bed8696, 11c2ac32, ea177a6a, 6c0e1f8f, 50040ab8, 7e3a1e0d, 9162aee6, 952f0041]
和ArrayList不同,Vector中的操作是线程安全的,为什么不会出现并发修改异常?
查看Vector的add()方法源码 ,如下:
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this Vector
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
Vector的add()方法添加了 synchronized关键字,所以不会出现并发修改异常
5.1.2.2)解决方案2-Collections
Collections提供了方法synchronizedList保证list是同步线程安全的,代码如下:
// Collections解决ArrayList集合线程不安全问题
public class CollectionsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Collections解决
List<String> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
//向集合添加内容
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8));
//从集合获取内容
System.out.println(list);
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
输出:
[504a67ec, f0176711, 78b9d3a6, faf52eb9, 1a8620a1]
[504a67ec, f0176711, 78b9d3a6, faf52eb9, 1a8620a1, 2f8b2783, 1d75042f, b2db93e2, a8c2132c, e7272b1f, abd7a302, 4769a65c]
...
[504a67ec, f0176711, 78b9d3a6, faf52eb9, 1a8620a1, 2f8b2783, 1d75042f, b2db93e2, a8c2132c, e7272b1f, abd7a302, 4769a65c]
没有并发修改异常,查看方法源码 :
/*
* <p>The returned list will be serializable if the specified list is
* serializable.
*
* @param <T> the class of the objects in the list
* @param list the list to be "wrapped" in a synchronized list.
* @return a synchronized view of the specified list.
*/
public static <T> List<T> synchronizedList(List<T> list) {
return (list instanceof RandomAccess ?
new SynchronizedRandomAccessList<>(list) :
new SynchronizedList<>(list));
}
5.1.2.3)解决方案3-CopyOnWriteArrayList
CopyOnWriteArrayLis相当于线程安全的ArrayList,和ArrayList一样,它是个可变数组;但是和 ArrayList不同的时,它具有以下特性:
-
它最适合于具有以下特征的应用程序:List大小通常保持很小,只读操作远多于可变操作,需要在遍历期间防止线程间的冲突;
-
它是线程安全的;
-
因为通常需要复制整个基础数组,所以可变操作(add()、set() 和 remove() 等)的开销很大;
-
迭代器支持 hasNext(), next()等不可变操作,但不支持可变remove()等操作。
-
使用迭代器进行遍历的速度很快,并且不会与其他线程发生冲突。在构造迭代器时,迭代器依赖于不变的数组快照。
CopyOnWriteArrayList 的核心思想就是复制思想,即拷贝一份:
当我们往一个容器添加元素的时候,不直接往当前容器添加,而是先将当前容器进行 Copy,复制出一个新的容器,然后新的容器里添加元素,添加完元素之后,再将原容器的引用指向新的容器,这时候会抛出来一个新的问题,也就是数据不一致的问题。如果写线程还没来得及写会内存,其他的线程就会读到了脏数据。
CopyOnWriteArrayList的核心技术就是 写时复制技术,流程如下图:
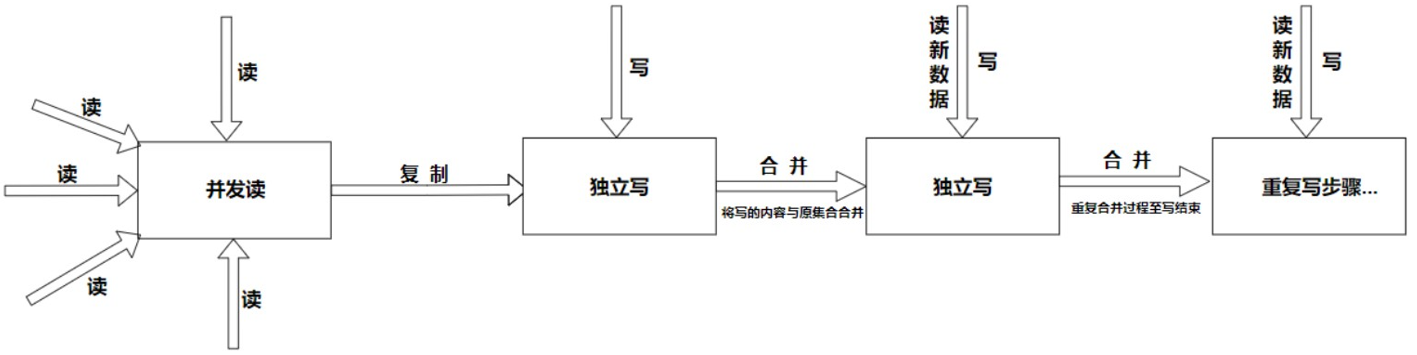
读集合数据时是并发读,写集合数据时是独立写,这样就避免了在写数据时导致的并发修改异常问题
代码如下:
// CopyOnWriteArrayList解决ArrayList集合线程不安全问题
public class CopyOnWriteArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// CopyOnWriteArrayList解决
List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
//向集合添加内容
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8));
//从集合获取内容
System.out.println(list);
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
输出:
[4578f50c, 6937bb8b, ce696b2a, d6b6f9da]
[4578f50c, 6937bb8b, ce696b2a, d6b6f9da, 970e0a0f, 569d7b7a, 39ac8475, 2aadbc14, 45df403d]
...
[4578f50c, 6937bb8b, ce696b2a, d6b6f9da, 970e0a0f, 569d7b7a, 39ac8475, 2aadbc14, 45df403d, 32c0db21, 62493f05, 4ac5126f, 507391bb, 0d3633fb, def2ef6d, 1f20ecd3, 73c1a75c, 7e506688, b07c30f2, e56914cd, c7e2e730]
没有并发修改异常原因分析:CopyOnWriteArrayList 的 add() 方法源码如下
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 上锁
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);
newElements[len] = e;
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
没有并发修改异常原因分析:动态数组与线程安全
下面从“动态数组”和“线程安全”两个方面进一步对 CopyOnWriteArrayList的原理进行说明
“动态数组”机制
-
它内部有个“volatile数组”(array)来保持数据;
-
在“添加/修改/删除”数据时,都会新建一个数组,并将更新后的数据拷贝到新建的数组中,最后再将该数组赋值给“volatile数组”, 这就是它叫做CopyOnWriteArrayList的原因
-
由于它在“添加/修改/删除”数据时,都会新建数组,所以涉及到修改数据的操作,CopyOnWriteArrayList效率很低;但是单单只是进行遍历查找的话, 效率比较高。
“线程安全”机制
-
通过volatile和互斥锁来实现的;
-
通过“volatile数组”来保存数据;一个线程读取volatile数组时,总能看到其它线程对该volatile变量最后的写入;这样通过volatile提供了“读取到的数据总是最新的”这个机制的保证。
-
通过互斥锁来保护数据。在“添加/修改/删除”数据时,会先“获取互斥锁”,再修改完毕之后,先将数据更新到“volatile数组”中,然后再“释放互斥锁”,就达到了保护数据的目的。





 本文解析了ArrayList在多线程环境下并发修改引发的ConcurrentModificationException,通过对比Vector、Collections.synchronizedList()和CopyOnWriteArrayList的线程安全实现,展示了如何避免并发修改异常并提高线程安全性。
本文解析了ArrayList在多线程环境下并发修改引发的ConcurrentModificationException,通过对比Vector、Collections.synchronizedList()和CopyOnWriteArrayList的线程安全实现,展示了如何避免并发修改异常并提高线程安全性。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








