我们知道,spring中有很多内置的过滤器,我们一个普通的请求,会经过下图这些过滤器的处理
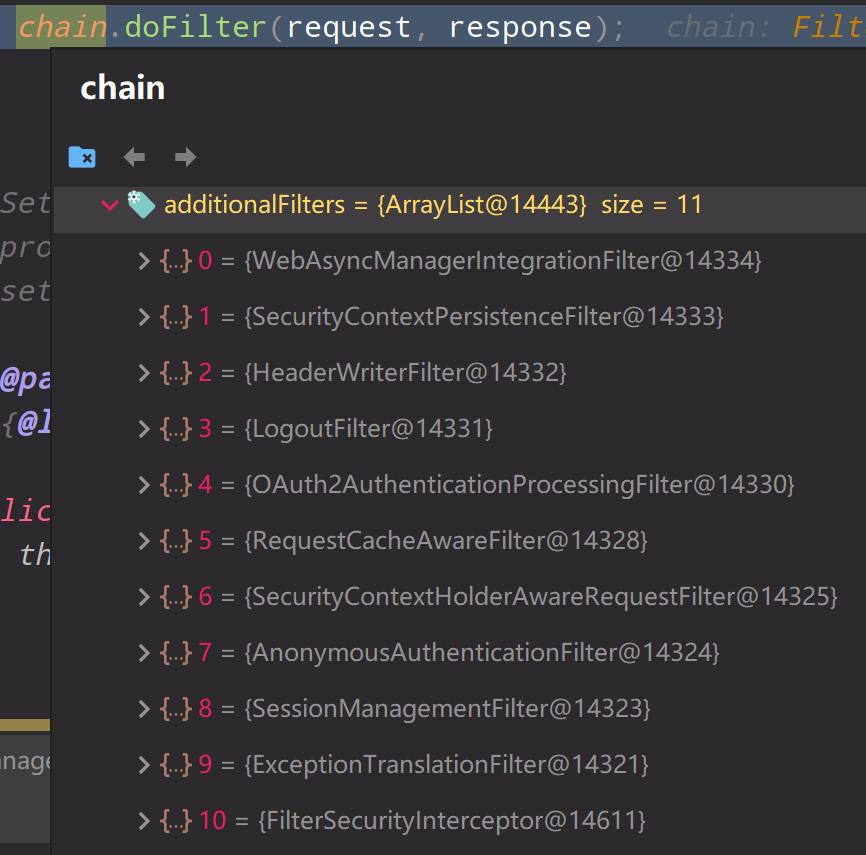
其中最重要的就是
org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.authentication.OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException,
ServletException {
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
final HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
final HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
Authentication authentication = tokenExtractor.extract(request);
if (authentication == null) {
if (stateless && isAuthenticated()) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Clearing security context.");
}
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("No token in request, will continue chain.");
}
}
else {
request.setAttribute(OAuth2AuthenticationDetails.ACCESS_TOKEN_VALUE, authentication.getPrincipal());
if (authentication instanceof AbstractAuthenticationToken) {
AbstractAuthenticationToken needsDetails = (AbstractAuthenticationToken) authentication;
needsDetails.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
}
Authentication authResult = authenticationManager.authenticate(authentication);
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication success: " + authResult);
}
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(authResult);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
}
}
catch (OAuth2Exception failed) {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication request failed: " + failed);
}
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationFailure(new BadCredentialsException(failed.getMessage(), failed),
new PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken("access-token", "N/A"));
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(failed.getMessage(), failed));
return;
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
这里会通过org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.authentication.BearerTokenExtractor#extract来获取请求header中的token信息(如Bearer 2c563440-bdd8-48a0-afca-f4ceb18c20ae)
public Authentication extract(HttpServletRequest request) {
String tokenValue = extractToken(request);
if (tokenValue != null) {
PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken authentication = new PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken(tokenValue, "");
return authentication;
}
return null;
}
如果能获取并正确解析,则按照已授权一路通行无阻,在具体的业务代码中还能获取到当前登录用户信息。
如果没有获取到token或解析失败,则按照未授权路线,判断当前访问的url是否允许匿名访问(可以看之前的文章,怎么配置匿名访问资源),如果不允许则抛出AccessDenied异常,这个过程是通过下面的代码实现的。
org.springframework.security.web.access.expression.WebExpressionVoter#vote
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException {
int deny = 0;
for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {
int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result);
}
switch (result) {
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED:
return;
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED:
deny++;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (deny > 0) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
}
// To get this far, every AccessDecisionVoter abstained
checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();
}
public int vote(Authentication authentication, FilterInvocation fi,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes) {
assert authentication != null;
assert fi != null;
assert attributes != null;
WebExpressionConfigAttribute weca = findConfigAttribute(attributes);
if (weca == null) {
return ACCESS_ABSTAIN;
}
EvaluationContext ctx = expressionHandler.createEvaluationContext(authentication,
fi);
ctx = weca.postProcess(ctx, fi);
return ExpressionUtils.evaluateAsBoolean(weca.getAuthorizeExpression(), ctx) ? ACCESS_GRANTED
: ACCESS_DENIED;
}

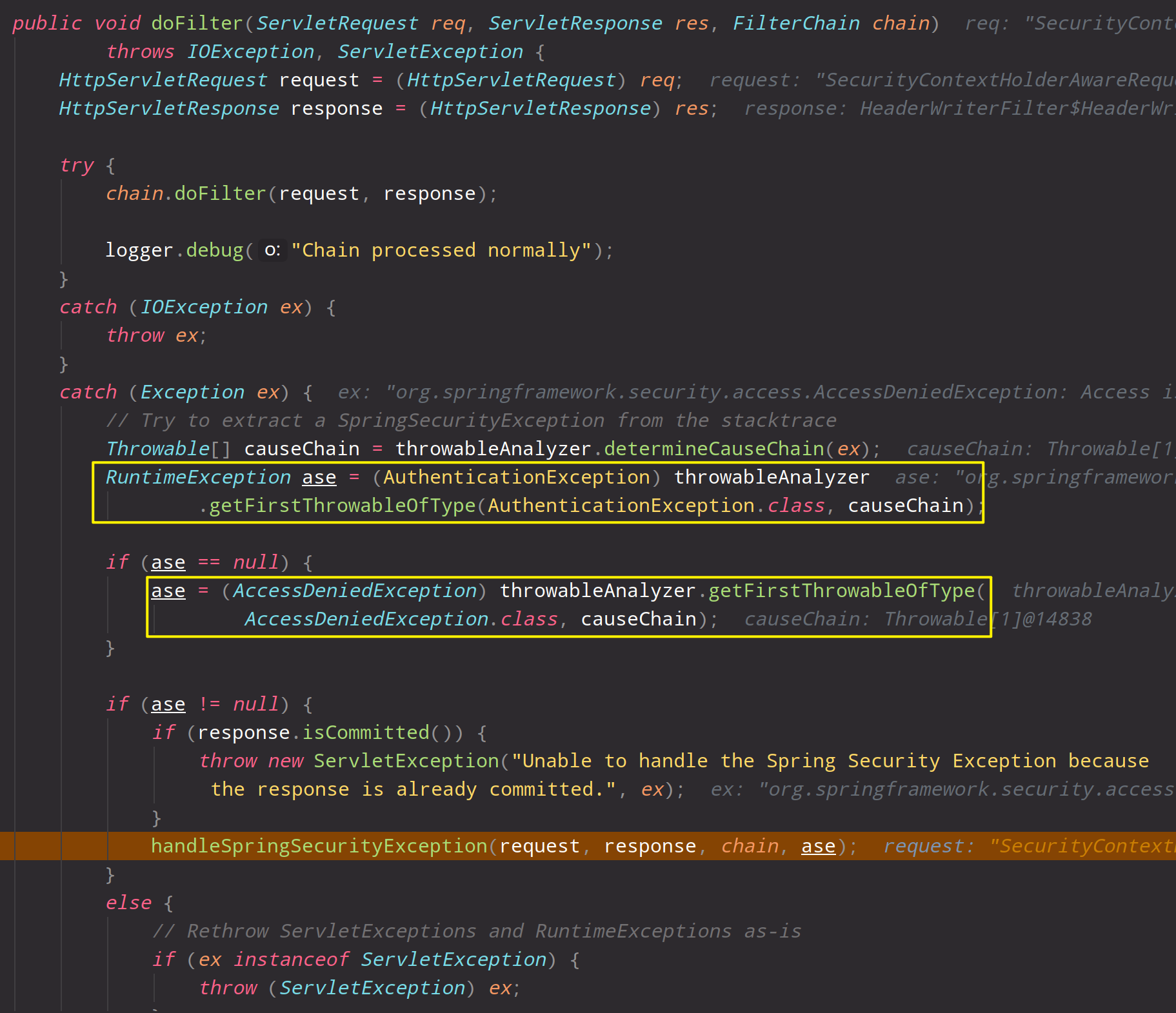
等到ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器中时,如果发现有异常,直接调用AuthenticationEntryPoint#commence来处理,这里也很重要,给了我们一个可以自己处理异常的机会。
org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter#sendStartAuthentication
protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException {
// SEC-112: Clear the SecurityContextHolder's Authentication, as the
// existing Authentication is no longer considered valid
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null);
requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
logger.debug("Calling Authentication entry point.");
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
}
就像这里的ResourceAuthExceptionEntryPoint是我们自定义的处理类
@Slf4j
@Component
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ResourceAuthExceptionEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) {
response.setCharacterEncoding(CommonConstants.UTF8);
response.setContentType(CommonConstants.CONTENT_TYPE);
R<String> result = new R<>();
result.setCode(HttpStatus.HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED);
if (authException != null) {
result.setMsg("error");
result.setData(authException.getMessage());
}
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED);
PrintWriter printWriter = response.getWriter();
printWriter.append(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(result));
}
}
可以返回一个自定义的json对象(一般前后端分离的项目中,都是ajax交互,所以json对象是最通用的数据结构)
{
"code": 401,
"msg": "error",
"data": "Full authentication is required to access this resource"
}
这样在终端获取到401的code时,可以通过全局拦截的配置(比如axios),控制页面跳转到登录页
// HTTPresponse拦截
axios.interceptors.response.use(res => {
const status = Number(res.status) || 200
const message = res.data.msg || errorCode[status] || errorCode['default']
if (status === 401) {
store.dispatch('FedLogOut').then(() => {
router.push({path: '/login'})
})
return
}
}, error => {
return Promise.reject(new Error(error))
})
好了,到这里,我们把一次页面请求的权限验证过程解析完了,能更清晰的认识OAuth的授权和验证原理了。





 解析OAuth2.0在Spring框架中的权限验证流程,包括请求处理、认证、异常处理等关键步骤,揭示OAuth的授权与验证原理。
解析OAuth2.0在Spring框架中的权限验证流程,包括请求处理、认证、异常处理等关键步骤,揭示OAuth的授权与验证原理。
















 4015
4015

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








