最近沉迷于码代码无法自拔。晚上睡觉之前脑子里都是白天的代码,充实!
习题27:记住逻辑关系
- 这部分b基本问题不大
- and:与
- or:或
- not:非
- !=:不等于
- ==:等于
- >=:大于等于
- <=:小于等于
- True:真
- False:假
真值表
| NOT | True? |
| not false | True |
| not true | False |
| OR | True? |
| True or False | True |
| True or True | True |
| False or True | True |
| False or False | False |
| AND | True? |
| True and False | False |
| True and True | True |
| False and True | False |
| False and False | False |
| NOT OR | True? |
| not(True or False) | False |
| not(True or True) | False |
| not(False or True) | False |
| not(False or False) | True |
| NOT AND | True? |
| not(True and False) | True |
| not(True and False) | False |
| not(False and True) | True |
| not(False and False) | True |
| != | True? |
| 1!=0 | True |
| 1!=1 | False |
| 0!=1 | True |
| 0!=0 | False |
| == | True? |
| 1==0 | False |
| 1==1 | True |
| 0==1 | False |
| 0==0 | True |
习题28:布尔表达式练习
print(True and False) # False
print(False and True) # False
print(1 == 1 and 2 == 1) # False
print("test" == "test") # True
print(1 == 1 or 2 != 1) # True
print(True and 1 == 1) # True
print(False and 0 != 0) # False
print(True or 1 == 1) # True
print("test" == "testing") # False
print(1 != 0 and 2 == 1) # False
print("test" != "testing") # True
print("test" == 1) # False
print(not(True and False)) # True
print(not(1 == 1 and 0 != 1)) # False
print(not(10 == 1 or 1000 == 1000)) # False
print(not(1 != 10 or 3 == 4)) # False
print(not("test" != "testing" and "Zed" == "Cool Guy")) # True
print(1 == 1 and not("testing" == 1 or 1 == 0)) # True
print("chunky" == "bacon" and not(3 == 4 or 3 == 3)) # False
print(3 == 3 and not("test" == "testing" or "Python" == "Fun")) # True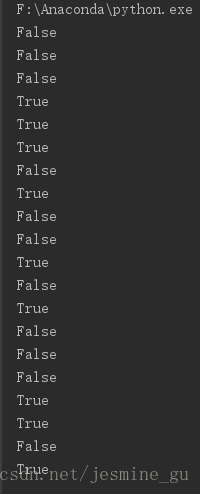
所有的布尔逻辑表达式都可以用下面的简单流程得到结果:
1. 找到相等判断的部分 (== or !=),将其改写为其最终值 (True 或 False)。
2. 找到括号里的 and/or,先算出它们的值。
3. 找到每一个 not,算出他们反过来的值。
4. 找到剩下的 and/or,解出它们的值。
5. 等你都做完后,剩下的结果应该就是 True 或者 False 了。
习题29:如果(if)
people = 20
cats = 30
dogs = 15
if people < cats:
print("Too many cats! The world is doomed!")
if people > cats:
print("Not many cats! The world is saved!")
if people < dogs:
print("The world is drooled on!")
if people > dogs:
print("The world is dry!")
dogs += 5
if people >= dogs:
print("People are greater than or equal to dogs.")
if people <= dogs:
print("People are less than or equal to dogs.")
if people == dogs:
print("People are dogs.")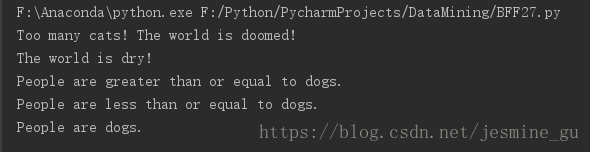
猜猜“if 语句”是什么,它有什么用处。在做下一道习题前,试着用自己的话回答下面的问题:
1. 你认为 if 对于它下一行的代码做了什么?
if后面是True才会继续执行下面的语句
2. 为什么 if 语句的下一行需要 4 个空格的缩进?
表示此代码属于这个if语句的
3. 如果不缩进,会发生什么事情?
不缩进,该语句就不受if的影响,都会执行
4. 把习题 27 中的其它布尔表达式放到``if 语句``中会不会也可以运行呢?试一下。
5. 如果把变量 people , cats , 和 dogs 的初始值改掉,会发生什么事情?
输出的内容根据if条件变化





 本文通过一系列练习介绍了布尔逻辑的基本概念及其在代码中的应用,并探讨了如何使用if语句来根据条件执行不同的代码路径。
本文通过一系列练习介绍了布尔逻辑的基本概念及其在代码中的应用,并探讨了如何使用if语句来根据条件执行不同的代码路径。

















 3370
3370

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










