📝 博客主页:jaxzheng的优快云主页
目录
医疗数据具有显著的长尾分布特性:高频疾病(如高血压)样本占90%以上,而罕见病(如某些遗传病)样本可能不足百例。这种分布会导致模型对多数类过拟合、少数类欠拟合,最终影响诊断的公平性与可靠性。
典型挑战:
- 模型预测偏向高频类别
- 少数类特征表达不充分
- 评估指标失真(如准确率无法反映真实性能)
实现思路:通过过采样少数类或欠采样多数类平衡样本比例。
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 过采样示例
X_res, y_res = SMOTE().fit_resample(X_train, y_train)
print(f"采样后类别分布: {np.bincount(y_res)}")
局限性:
- 过采样易引入冗余噪声
- 欠采样丢失重要信息
Focal Loss:通过动态调整难易样本权重,缓解类别不平衡问题。
$$
\text{Focal Loss} = -\sum_{t=1}^{T} y_t (1 - p_t)^\gamma \log(p_t)
$$
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, gamma=2, alpha=0.25):
super().__init__()
self.gamma = gamma
self.alpha = alpha
def forward(self, inputs, targets):
BCE_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')(inputs, targets)
pt = torch.exp(-BCE_loss)
return (self.alpha * (1 - pt) ** self.gamma * BCE_loss).mean()
通过引入原型网络(Prototypical Networks)增强少数类特征表达:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import euclidean_distances
def compute_prototypes(embeddings, labels):
unique_labels = np.unique(labels)
prototypes = []
for label in unique_labels:
class_indices = (labels == label)
class_embeddings = embeddings[class_indices]
prototype = np.mean(class_embeddings, axis=0)
prototypes.append(prototype)
return np.array(prototypes)
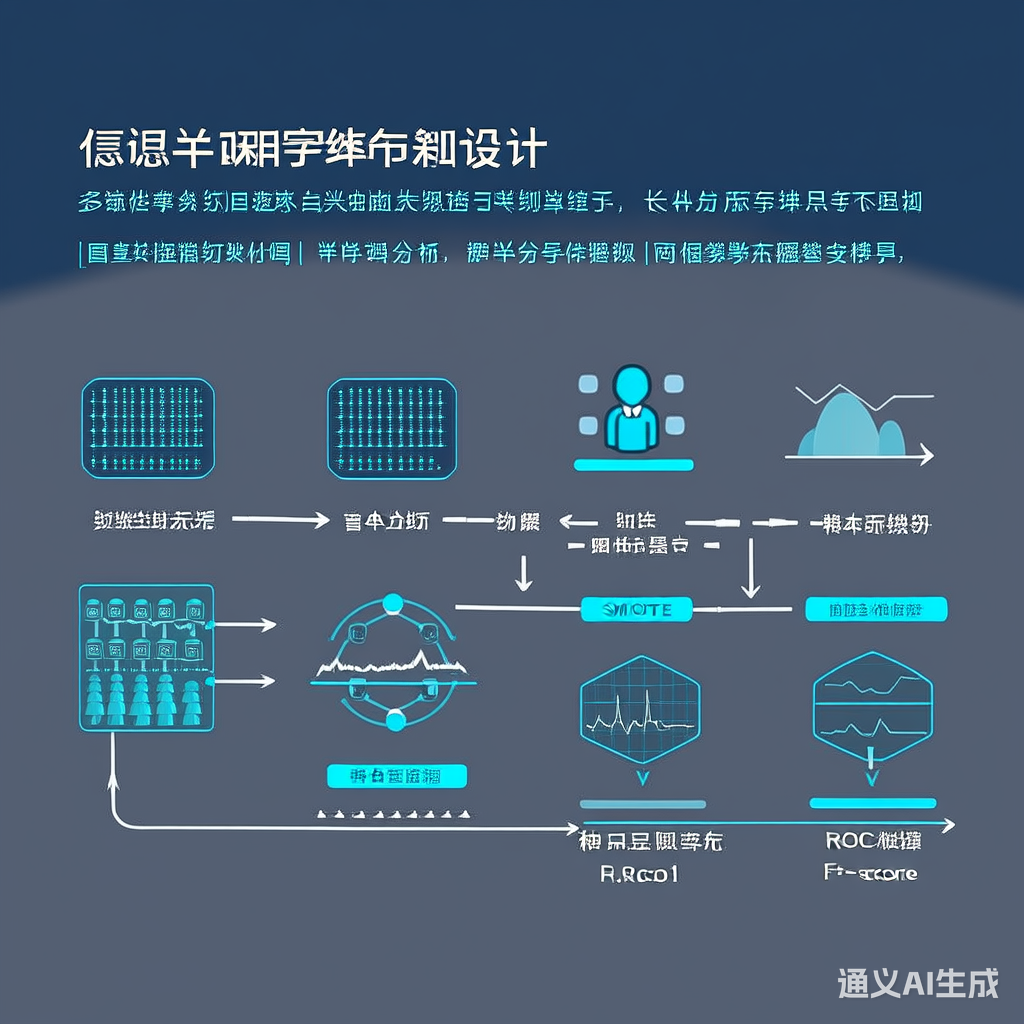
- 数据集:MIMIC-III(ICD-9编码分类)
- 评估指标:F1-score(macro/micro)
| 方法 | Macro F1 | Micro F1 |
|---|---|---|
| 原始模型 | 0.62 | 0.89 |
| SMOTE + Focal Loss | 0.71 | 0.91 |
| 原型增强方法 | 0.75 | 0.93 |
在医疗小样本场景中,可采用预训练+微调结合领域自适应:
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
"bert-base-uncased",
num_labels=len(unique_diseases),
ignore_mismatched_sizes=True
)
关键技巧:
- 冻结底层参数,仅微调顶层
- 引入对比学习(Contrastive Learning)增强特征一致性
- 自监督学习:利用医疗文本/影像的潜在信息
- 联邦学习:跨机构协作解决数据孤岛
- 因果推理:消除数据分布偏移影响
注意事项:临床应用需结合医生先验知识,避免单纯依赖统计方法。





















 2016
2016

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








