在 Spring MVC 的分析过程中,我们知道了 Spring mvc 默认会引入DispatcherServlet.properties 文件中的类(该文件和 DispatcherServlet 在同级目录) 的一些类。DispatcherServlet.properties 配置文件如下。
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
下面我们来看看 HandlerMapping 不同实现类的区别。
1. HandlerMapping
从 DispatcherServlet.properties 文件中得知。HandlerMapping 默认引入三个类BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
我们来看看他们的区别:
-
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:以beanName 作为key值 -
RequestMappingHandlerMapping:完成@Controller和@RequestMapping的解析,并将解析保存。请求发送时与请求路径进行匹配对应找到合适的Handler。RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了InitializingBean接口,会在afterPropertiesSet方法中。- 调用时机: 解析
@Controller和@RequestMapping注解是在afterPropertiesSet方法中进行的。匹配调用则是在DispatcherServlet doDispatch方法中的getHandler中调用了HandlerMapper中的getHandler中的getHandlerInternal方法。
- 调用时机: 解析
-
RouterFunctionMapping:RouterFunctionMapping是检索RouterFunction应用程序上下文中创建的所有bean 的类。
在 Spring mvc 加载 HandlerMapping 的代码分析中,我们知道,Spring 默认会加载 DispatcherServlet.properties 中的所有的 HandlerMapping。同时我们可以通过 DispatcherServlet.detectAllHandlerMappings 属性来控制是否加载所有的HandlerMapping,还是只加载唯一的HandlerMapping。
为了方便,先禁用寻找所有的HandlerMapping。
@Bean
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(){
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
// 设置false,则只寻找beanName 为 handlerMapping 的类,不加载所有HandlerMapping类
dispatcherServlet.setDetectAllHandlerMappings(false);
return dispatcherServlet;
}
1.1. BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping 顾名思义,就是根据beanName 来 进行映射。
我们创建一个Controller如下,这里有两点需要注意:
- 映射的Controller 需要实现
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller接口。 - beanName 需要以
‘/’开头。
@org.springframework.stereotype.Controller("/helloSimple")
public class HelloSimpleController implements Controller {
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
这里解释分析一下为什么要 beanName 以 ‘/’ 开头?
2.1.1 isHandler(beanType)
这个方法在 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 并没有具体实现,是供子类实现,目的是判断当前 Bean是否是 Handler (满足Handler 的条件)。我们这里来看看 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的实现。
- 我们来看
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping的源码如下, 可以很清楚的看到这里有对/的判断。寻找到以/开头的beanName 并作为url返回。public class BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping extends AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping { /** * Checks name and aliases of the given bean for URLs, starting with "/". */ @Override protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) { List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>(); // 判断 beanName 是否是 / 开头 if (beanName.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(beanName); } // 判断 beanName 的别名是否是 / 开头哦 String[] aliases = obtainApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName); for (String alias : aliases) { if (alias.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(alias); } } // 将是 / 的beanname 转化成数组并返回。 return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls); } }返回之后,在
AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping#detectHandlers方法中完成了Handler 的注册protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException { ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext(); String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, Object.class) : applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); // Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for. // 遍历所有的BeanName for (String beanName : beanNames) { // 获取到符合规则的Url String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) { // URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler. // 注册成handler registerHandler(urls, beanName); } } ... }我们来进一步看看Handler 注册的流程。注册流程其实很简单,其实就是利用
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping#handlerMap中保存了url 和 Handler。key为 urlPath,value为handler实例。protected void registerHandler(String[] urlPaths, String beanName) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { Assert.notNull(urlPaths, "URL path array must not be null"); for (String urlPath : urlPaths) { registerHandler(urlPath, beanName); } } ... protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null"); Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null"); Object resolvedHandler = handler; // Eagerly resolve handler if referencing singleton via name. // 如果不是懒加载 && handler 是 String类型。 if (!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext(); // 如果是handler是单例,则从上下文中根据 beanName 获取handler 对象实例 if (applicationContext.isSingleton(handlerName)) { resolvedHandler = applicationContext.getBean(handlerName); } } // 判断 handlerMap 中已经保存了该 url Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath); if (mappedHandler != null) { // 如果该url 对应的两个不同的 handler,则抛出异常 if (mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot map " + getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath + "]: There is already " + getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped."); } } else { // 如果是 urlPath 是 / 开头。则设置为 根处理器 if (urlPath.equals("/")) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Root mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler)); } setRootHandler(resolvedHandler); } // 如果是 urlPath 是 / 开头。则设置为 默认处理器 else if (urlPath.equals("/*")) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Default mapping to " + getHandlerDescription(handler)); } setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler); } else { // 否则的话,保存到 handlerMap 中 this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Mapped [" + urlPath + "] onto " + getHandlerDescription(handler)); } } } }1.2 RequestMappingHandlerMapping
RequestMappingHandlerMapping,即我们平常最常用的一种形式,通过 @ResquestMapping 注解的方式来执行路径,由于下面有关于RequestMappingHandlerMapping注册流程的分析,这里就不再赘述 。1.3 RouterFunctionMapping
RouterFunctionMapping没用过 。
2. RequestMappingHandlerMapping
下面的解析以
RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例,因为RequestMappingHandlerMapping也是我们最常使用的HandlerMapping。2.1 Handler的注册
我们首先来看一下
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的结构图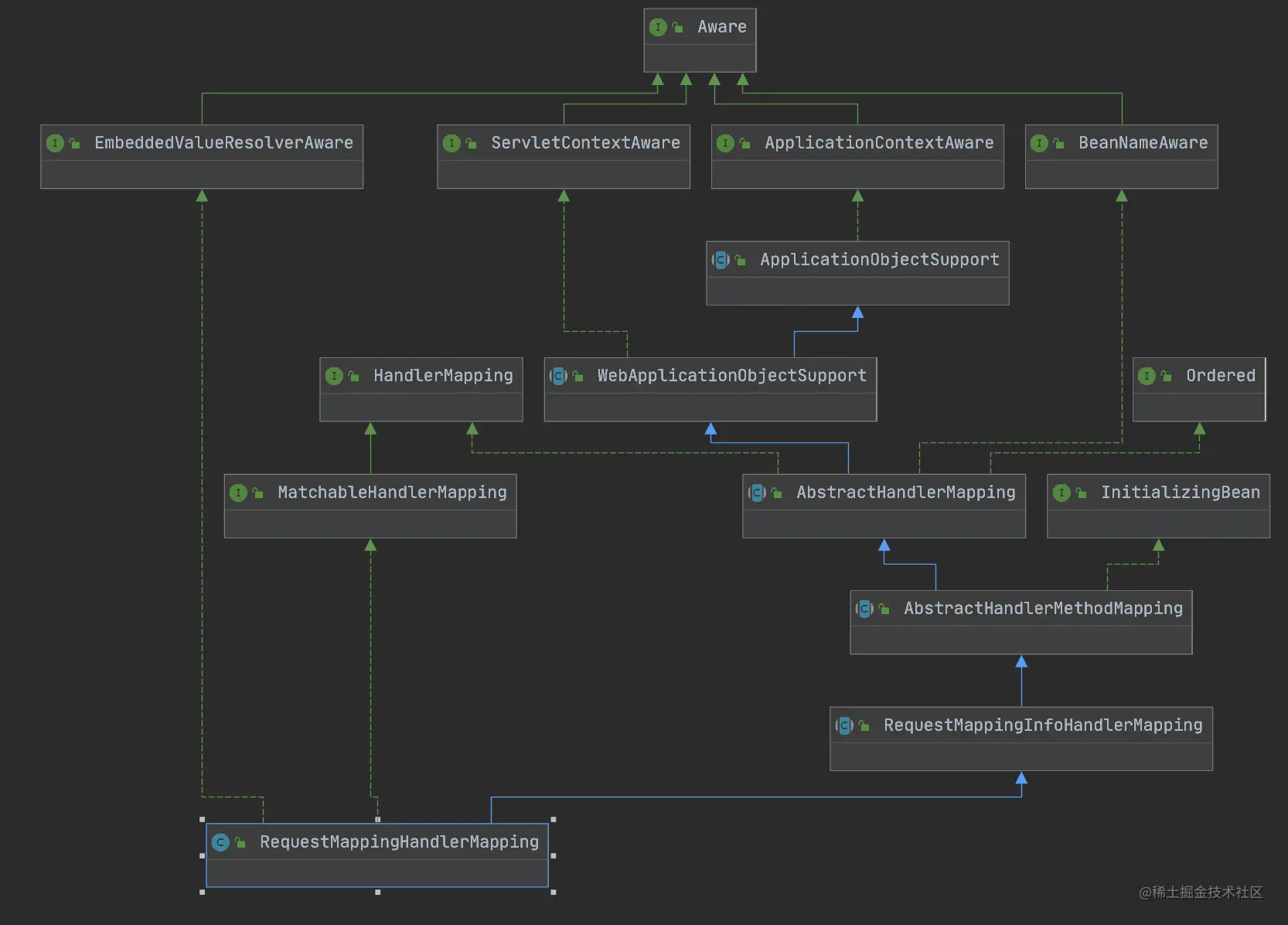
我们看到其实现了其实
RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了InitializingBean接口(实际上是AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现的。看了这么久的源码,我们可以大胆的猜测,对 Handler 的解析应该就在InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet方法中。我们来看一下
RequestMappingHandlerMapping#afterPropertiesSet的实现如下。
@Override @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public void afterPropertiesSet() { // 进行 RequestMapping 的配置 this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration(); this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper()); this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher()); this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch()); this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(useTrailingSlashMatch()); this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch()); this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager()); // 调用父类的 afterPropertiesSet 方法。 super.afterPropertiesSet(); }上面我们看到,其主要内容还是在父类的
afterPropertiesSet方法中。因此下面我们来看AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#afterPropertiesSet:private static final String SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX = "scopedTarget."; /** * Detects handler methods at initialization. * @see #initHandlerMethods */ @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { initHandlerMethods(); } /** * Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods. * @see #getCandidateBeanNames() * @see #processCandidateBean * @see #handlerMethodsInitialized */ protected void initHandlerMethods() { // getCandidateBeanNames() : 从 Spring 容器中获取所有候选的beanName。 for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) { // 如果beanName 不是以 SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX 开头,则进行处理 if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { // 1. 初始 候选的beanName processCandidateBean(beanName); } } // 这里就是打印了一下log日志 handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); }我们根据
initHandlerMethods的注释就可以知道initHandlerMethods的作用是扫描ApplicationContext,检测并注册Handler方法。我们可以看到其中的关键方法就是processCandidateBean(处理候选的Bean。这里实际完成了对 HandlerMethod 的解析和注册)。在processCandidateBean 方法中,完成了对 HandlerMethod 的解析和注册 。而processCandidateBean的具体实现在
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#processCandidateBean中。下面我们来看看具体实现
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) { Class<?> beanType = null; try { // 获取beanType beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { ... } // 如果 beanType != null && beanType 是 handler。在 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 中的判断是 bean被 @Controller 或者 @RequestMapping 注解修饰。则会进行bean的handler方法筛选 if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { // 筛选出合适的 HandlerMethod 注册 detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } }可以看到其逻辑并不复杂,我们有两个方法需要关注:
isHandler(beanType): 判断当前bean是否满足 Handler 条件detectHandlerMethods(beanName): 解析 handler 里面的方法并注册 下面我们来看一看逐一来看一看:
2.1.1 isHandler(beanType)
这个方法在 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 并没有具体实现,是供子类实现,目的是判断当前 Bean是否是 Handler (满足Handler 的条件)。我们这里来看看 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的实现。
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping 中 isHandler 的实现
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
可以看到,在 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 中 这里判断当前的bean 是否可以作为handler 的条件是 : bean被 @Controller 或者 @RequestMapping 注解修饰。则会进行bean的handler方法筛选。如果满足,则会通过 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#detectHandlerMethods方法来进行下一步的筛选Handler的方法筛选。
2.1.2. detectHandlerMethods(beanName)
detectHandlerMethods 的作用是筛选出合适的 Handler Method 方法,并进行注册。接下来来看看 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#detectHandlerMethods方法的具体实现。
// 检测 handler 方法并注册
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
// 获取 handlerType。这里传入的 handler如果是 String 就是 beanName,从上下文中获取type,否则就直接认为是 Handler
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
// 返回给定类的用户定义类:通常只是给定的类,但对于CGLIB生成的子类,则返回原始类
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 遍历当前bean的所有方法,筛选出合适的 handler 方法 以及 注解信息
// 这里需要注意的是 MethodIntrospector.selectMethods 底层将 getMappingForMethod 返回为null 的值给过滤掉了。
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
// 供子类实现
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
// 遍历所有的methods(这里的methods经过上面的筛选后,都是被 @RequestMapping 注解修饰的方法)
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
// 这里是针对 cglib 代理特殊处理。
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
//注册 HandlerMethod 。
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
在上述代码中通过 MethodIntrospector#selectMethods(...) 方法遍历了当前bean的所有方法,并调用 getMappingForMethod 方法进行处理。getMappingForMethod 方法在 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 中并未有具体实现,这里我们看看 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 中的实现。
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping 中的实现
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
// 转换成 RequestMappingInfo ,如果方法没有被 @RequestMapping 注解修饰,则会返回null
// 解析出来方法上 @RequestMapping 注解的各种信息
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
// 解析出来 bean 上 @RequestMapping 注解的各种信息
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
// 合并类和方法的 @RequestMapping 注解信息
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
// 获取前缀,拼接前缀
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
// 返回信息
return info;
}
getMappingForMethod 方法的作用是解析 方法上的@RequestMapping注解的信息并和类上 @RequestMapping 注解 的信息相结合。
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
// 获取当前方法上的 @RequestMapping 注解
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
// 获取自定义的方法条件
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
// 这里可以看到 如果 requestMapping = null,则会直接返回null,否则会封装成一个 RequestMappingInfo (包含 @RequestMapping 注解的各种参数) 返回。
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
2.1.3. registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping)
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); 看方法名字就知道 注册 HandlerMethod。下面我们看看具体实现
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping 中
@Override
public void registerMapping(RequestMappingInfo mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
super.registerMapping(mapping, handler, method);
updateConsumesCondition(mapping, method);
}
@Override
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, RequestMappingInfo mapping) {
super.registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping);
updateConsumesCondition(mapping, method);
}
...
// 对 @RequestBody 注解进行了进一步解析
private void updateConsumesCondition(RequestMappingInfo info, Method method) {
ConsumesRequestCondition condition = info.getConsumesCondition();
if (!condition.isEmpty()) {
for (Parameter parameter : method.getParameters()) {
MergedAnnotation<RequestBody> annot = MergedAnnotations.from(parameter).get(RequestBody.class);
if (annot.isPresent()) {
condition.setBodyRequired(annot.getBoolean("required"));
break;
}
}
}
}
其中 super.registerMapping(mapping, handler, method); 调用的是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#registerMapping 。如下
// RequestMappingInfo 和 MappingRegistration 的映射关系
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
// key是 RequestMappingInfo, value 是 HandlerMethod
private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// url 和 RequestMappingInfo 映射起来。
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
// 类名#方法名 和 HandlerMethod 的映射关系
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// HandlerMethod 和 CorsConfiguration 的映射关系
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final MappingRegistry mappingRegistry = new MappingRegistry();
// super.registerMapping(mapping, handler, method); 调用的是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#registerMapping 。如下
public void registerMapping(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Register \"" + mapping + "\" to " + method.toGenericString());
}
// 完成了handler method 的注册
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
下面我们来看看 this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method); 的具体实现 (AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry#register) 如下
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
// Assert that the handler method is not a suspending one.
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if ((parameterTypes.length > 0) && "kotlin.coroutines.Continuation".equals(parameterTypes[parameterTypes.length - 1].getName())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported suspending handler method detected: " + method);
}
}
// 加写锁
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
// 将 handler 和 method 封装成一个 HandlerMethod 实例
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
// 校验实例的合法性。即唯一性
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
// 保存映射关心, key是 RequestMappingInfo, value 是 HandlerMethod
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
// 获取url映射,如果是 restful 请求则获取不到。建立 url 和Mapping 的映射。
// 一个mapping 可以对应多个url
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
// 这里将url 和 mapping映射起来
// 在进行匹配的时候,就是先根据url找到合适的mapping,然后根据找到的mapping再去找到HandlerMethod
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
// 保存 类名#方法名 : HandlerMethod 的映射关系
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
// 这里解析出来的name 并不是完整的类名,而是类名的首字母组合。比如方法名是 DemoController.say() ,解析出来的name即为 DC#say。如果是 SayController.say()。解析出来则为 name = SC#say
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
//@CrossOrigin跨域注解请求的初始化配置
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
// 保存到 registry 中
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
2.1.4. 总结
经过上面的分析我们可以得知:
- Spring启动时加载
RequestMappingHandlerMapping。RequestMappingHandlerMapping在初始化的时候会从 Spring容器中获取bean - 遍历每个bean,判断是否满足成为
Handler的条件(bean被 @Controller 或者 @RequestMapping 注解修饰)。满足条件的作为 Handler进行下一步处理 - 通过反射获取每个 Handler 里面的方法,去判断是否被
@RequestMapping注解修饰,如果被修饰,则获取@RequestMapping注解的信息与类上面的@RequestMapping注解信息合并后注册HandlerMethod。
2.2 Handler 的筛选
当一个请求过来的的时候,会交由 DispatcherServlet 来进行请求分发。根据请求的 request 查找到对应的 handler。这里来分析一下这个查找过程。
DispatcherServlet 的查找方法是 DispatcherServlet#getHandler。如下
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
// 这里的 HandlerMapping 如果没有特殊操作,则默认是从配置文件中读取并加载的 HandlerMapping
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
// 调用HandlerMapping 的getHandler 方法。
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
mapping.getHandler(request); 调用的是 AbstractHandlerMapping#getHandler 方法。其实现如下:
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 1. 调用 getHandlerInternal 获取 handler 。该方法供子类实现
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
// 如果没有获取到 handler。则获取默认的handler
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
// 如果 handler 是 String类型,则会认为是 beanName。从Spring容器中获取 bean实例
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 2. 生成拦截器链路
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
2.2.1. getHandlerInternal(request)
该方法在 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal 中没有具体实现,是供不同的 HandlerMapping 子类自己实现的。这里我们直接看 RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping#getHandlerInternal
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
request.removeAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
try {
return super.getHandlerInternal(request);
}
finally {
ProducesRequestCondition.clearMediaTypesAttribute(request);
}
}
super.getHandlerInternal(request); 调用的是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal。如下
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 从 request 中解析出 请求路径
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 查找 HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
...
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
// 通过 url 获取匹配路径
// springMVC会在初始化的时候建立URL和相应RequestMappingInfo的映射,这点在上面的解析中我们可以知道。如果不是restful接口,这里就可以直接获取到。
// 这里是通过 urlLookup 获取的 RequestMappingInfo
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 将匹配的 Mapping 保存到 matches 中。
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
// 如果上面没有获取到匹配的路径,则只能遍历所有的 mapping。
// 由于会遍历所有的 RequestMapping。所以性能会随着 RequestMapping数量的增加降低
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
// 如果 matches 不为空,则说明有匹配的 Mapping
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
// 如果合适的 Mapping 不止一个,则筛选出最合适的
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
...
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping)));
}
}
}
...
// this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
// 也就是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry#getMappingsByUrl
@Nullable
public List<T> getMappingsByUrl(String urlPath) {
return this.urlLookup.get(urlPath);
}
2.2.2 getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request)
AbstractHandlerMapping#getHandlerExecutionChain。主要目的是将配置中对应的拦截器加入到执行链中,以保证这些拦截器可以有效的作用于目标对象
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 构建一个执行链
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
// 解析出来 请求路径
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, LOOKUP_PATH);
// 遍历所有的拦截器,如果拦截器匹配符则加入到执行链中。adaptedInterceptors 是在 Mapping 初始化的时候加载的
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
关于 adaptedInterceptors、interceptors 两个拦截器集合:adaptedInterceptors 是 AbstractHandlerMapping 在初始化的时候实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口,在 ApplicationObjectSupport#setApplicationContext 方法中调用 initApplicationContext 方法,进行了 adaptedInterceptors 的初始化。而 interceptors 则可以通过 set 方法进行注入。
// AbstractHandlerMapping
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors);
initInterceptors();
}
...
// 从容器中 获取所有MappedInterceptor类型的拦截器
protected void detectMappedInterceptors(List<HandlerInterceptor> mappedInterceptors) {
mappedInterceptors.addAll(BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
obtainApplicationContext(), MappedInterceptor.class, true, false).values());
}
2.2.3 总结
总结部分:
-
List directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);这个方法是非常直观的根据URL来获取,springMVC会在初始化的时候建立URL和相应RequestMappingInfo的映射。如果不是restful接口,这里就可以直接获取到了。 -
如果1中已经获取到,则调用方法
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request)进行匹配校验。 -
如果1中未获取到匹配方法信息,则调用方法
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);进行全局(all mappings)扫描匹配(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet())。且会把所有的RequestMappingInfo都遍历完才会停止,也就是说项目中的@RequestMapping方法越多,这个匹配的效率就越低,性能越差。 -
在遍历过程中,SpringMVC首先会根据@RequestMapping中的headers, params, produces, consumes, methods与实际的HttpServletRequest中的信息对比,剔除掉一些明显不合格的RequestMapping。 如果以上信息都能够匹配上,那么SpringMVC会对RequestMapping中的path进行正则匹配,剔除不合格的。接下来会对所有留下来的候选@RequestMapping进行评分并排序。最后选择分数最高的那个作为结果。




 本文深入探讨了Spring MVC中的HandlerMapping,包括BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RouterFunctionMapping。重点分析了BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping的工作原理,如isHandler方法的实现,以及RequestMappingHandlerMapping的Handler注册和筛选过程。
本文深入探讨了Spring MVC中的HandlerMapping,包括BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerMapping和RouterFunctionMapping。重点分析了BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping的工作原理,如isHandler方法的实现,以及RequestMappingHandlerMapping的Handler注册和筛选过程。
















 1057
1057

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








