1.EventLoopGroup
1、概念
EventLoopGroup 是一组 EventLoop,Channel 一般会调用 EventLoopGroup 的 register 方法来绑定其中一个 EventLoop,后续这个 Channel 上的 io 事件都由此 EventLoop 来处理(保证了 io 事件处理时的线程安全)
2、创建一个独立的EventLoopGroup
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 细分2:创建一个独立的 EventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup();
new ServerBootstrap()
// boss 和 worker
// 细分1:boss 只负责 ServerSocketChannel 上 accept 事件 worker 只负责 socketChannel 上的读写
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(), new NioEventLoopGroup(2))
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast("handler1", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override // ByteBuf
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
log.info(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); // 让消息传递给下一个handler
}
}).addLast(group, "handler2", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override // ByteBuf
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
log.info(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
启动客户端,连接这个服务端,在服务端控制台打印结果:

从结果看,是使用两个handler来处理消息的
再启动一个客户端,连接同一个服务端,发送消息后,发现这个客户端是与服务端的另外的线程进行的绑定

3、Channel与EventLoopGroup的绑定关系

4、handler执行中如何换人?
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {
final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);
// 下一个 handler 的事件循环是否与当前的事件循环是同一个线程
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
// 是,直接调用
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
// 不是,将要执行的代码作为任务提交给下一个事件循环处理(换人)
else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
});
}
}
源码分析:

● 如果两个 handler 绑定的是同一个线程,那么就直接调用
● 否则,把要调用的代码封装为一个任务对象,由下一个 handler 的线程来调用
2、Channel 数据通道
1、channel 的主要作用
● close() 可以用来关闭 channel
● closeFuture() 用来处理 channel 的关闭
○ sync 方法作用是同步等待 channel 关闭
○ 而 addListener 方法是异步等待 channel 关闭
● pipeline() 方法添加处理器
● write() 方法将数据写入
● writeAndFlush() 方法将数据写入并刷出
2、ChannelFuture的连接问题
(1)如果没有执行channelFuture.sync();方法,那么服务端可能接收不到客户端发送过来的消息,为什么?

带有Future,Promise的类型都是和异步方法配套使用,用来处理结果的。
(2)方式一:使用sycn方法同步处理结果
// 阻塞住当前线程,等待nio线程连接建立好了之后,才会向下运行
channelFuture.sync();


结果是由主线程处理的
(3)方式二:使用addListener(回调对象) 方法异步处理结果
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 1. 启动类
ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override // 在连接建立后被调用
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
// 连接到服务器端
// connect方法:是异步非阻塞的,主线程发起调用,真正执行connect是Nio里的线程
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
// 1.1 阻塞住,等待nio线程连接建立好了之后,才会向下运行
/*channelFuture.sync();
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
log.info("{}",channel);
channel.writeAndFlush("hello world!");*/
// 2.1 使用addListener(回调对象) 方法异步处理结果
channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
// 在nio线程连接建立后,会调用operationComplete方法
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
log.info("{}",channel);
channel.writeAndFlush("hello world!");
}
});
}

执行的结果是由NIO里面的线程打印处理的,这一点和方式一不同,说明程序把客户端与服务端的连接建立,发送数据等一些操作都交给NIO线程进行处理,Main主线程只做发起操作,不做后续处理。
3、ChannelFuture处理关闭操作
(1)同步处理,使用closeFuture.sync()方法
// 1. 启动类
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override // 在连接建立后被调用
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
// 连接到服务器端
// connect方法:是异步非阻塞的,主线程发起调用,真正执行connect是Nio里的线程
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
// 1.1 阻塞住,等待nio线程连接建立好了之后,才会向下运行
channelFuture.sync();
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
new Thread(()->{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
String line = scanner.nextLine();
if("q".equals(line)){
// 执行关闭操作
channel.close();
break;
}
channel.writeAndFlush(line);
}
},"input").start();
// 获取CloseFuture对象,1)同步处理关闭 2)异步处理关闭
ChannelFuture closeFuture = channel.closeFuture();
log.info("waiting close...");
closeFuture.sync();
group.shutdownGracefully();
log.info("close compose..");

发现是主线程打印的。
(2)异步处理关闭
closeFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
log.info("close compose..");
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
});
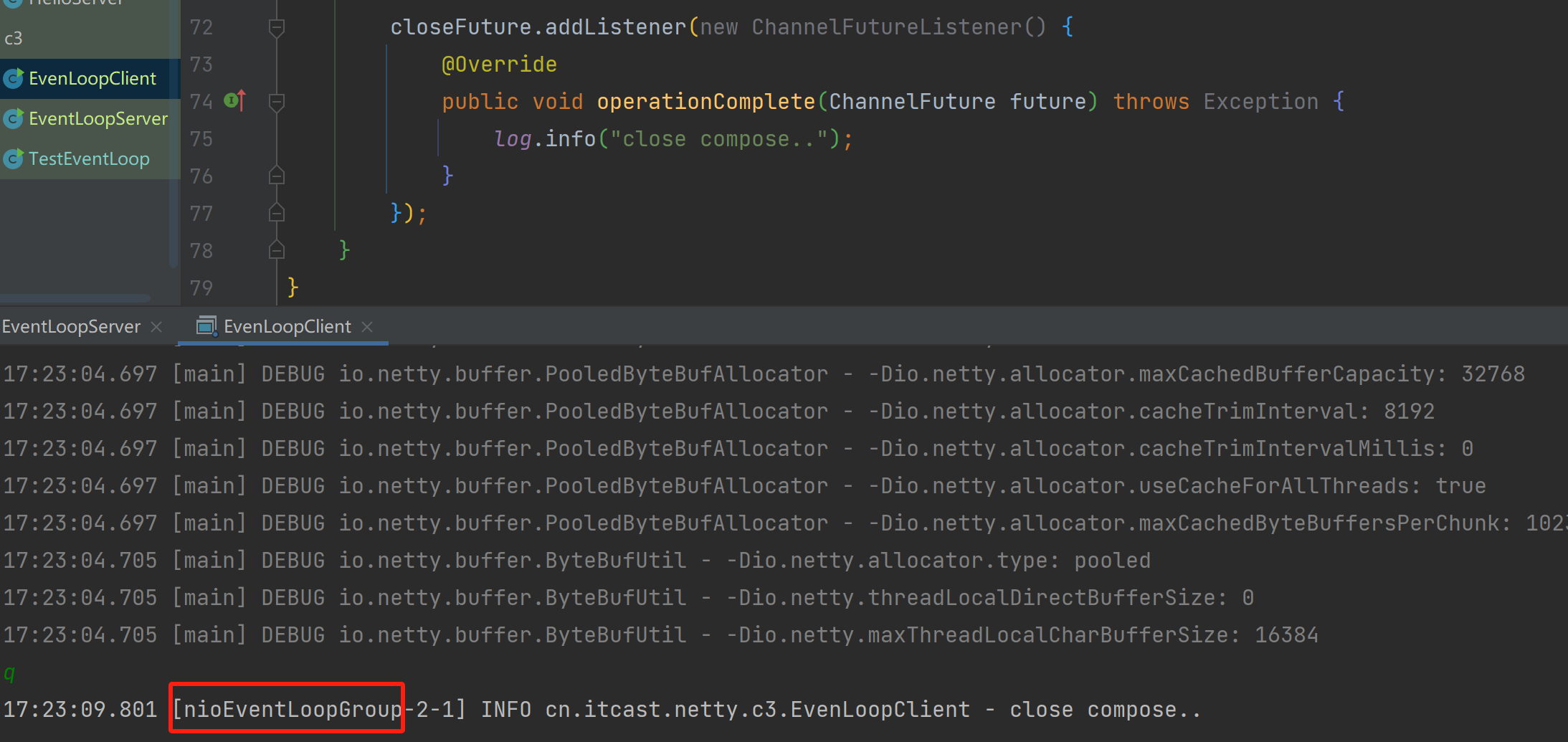
发现是nio里面的线程打印的。
group.shutdownGracefully();

3、Future
3.1、jdk中的Future
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 1.线程池
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 2、提交任务
Future<Integer> future = service.submit((new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("executor...");
return 50;
}
}));
// 主线程会等待线程池执行完产生结果后,再执行后面的结果,jdk中单的Future是同步阻塞等待的
log.info("waiting result...");
Integer res = future.get();
log.info("res:{}",res);
}

3.2、Netty中的Future
Netty中的Future是继承自jdk中的Future的,Netty中的Future支持异步操作
NioEventLoopGroup eventExecutors = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoop eventLoop = eventExecutors.next();
Future<Integer> future = eventLoop.submit((new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
log.info("nio eventExecutors...");
return 60;
}
}));
/**
* 方式一:是主线程等待线程池返回结果后,再执行get()方法打印结果,同步处理
*/
/*log.info("waiting result...");
Integer res = future.get();
log.info("res:{}",res);*/
/**
* 2、方式二:都是使用线程池中的线程处理的结果,异步处理
*/
future.addListener((new GenericFutureListener<Future<? super Integer>>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<? super Integer> future) throws Exception {
log.info("res:{}",future.getNow());
}
}));
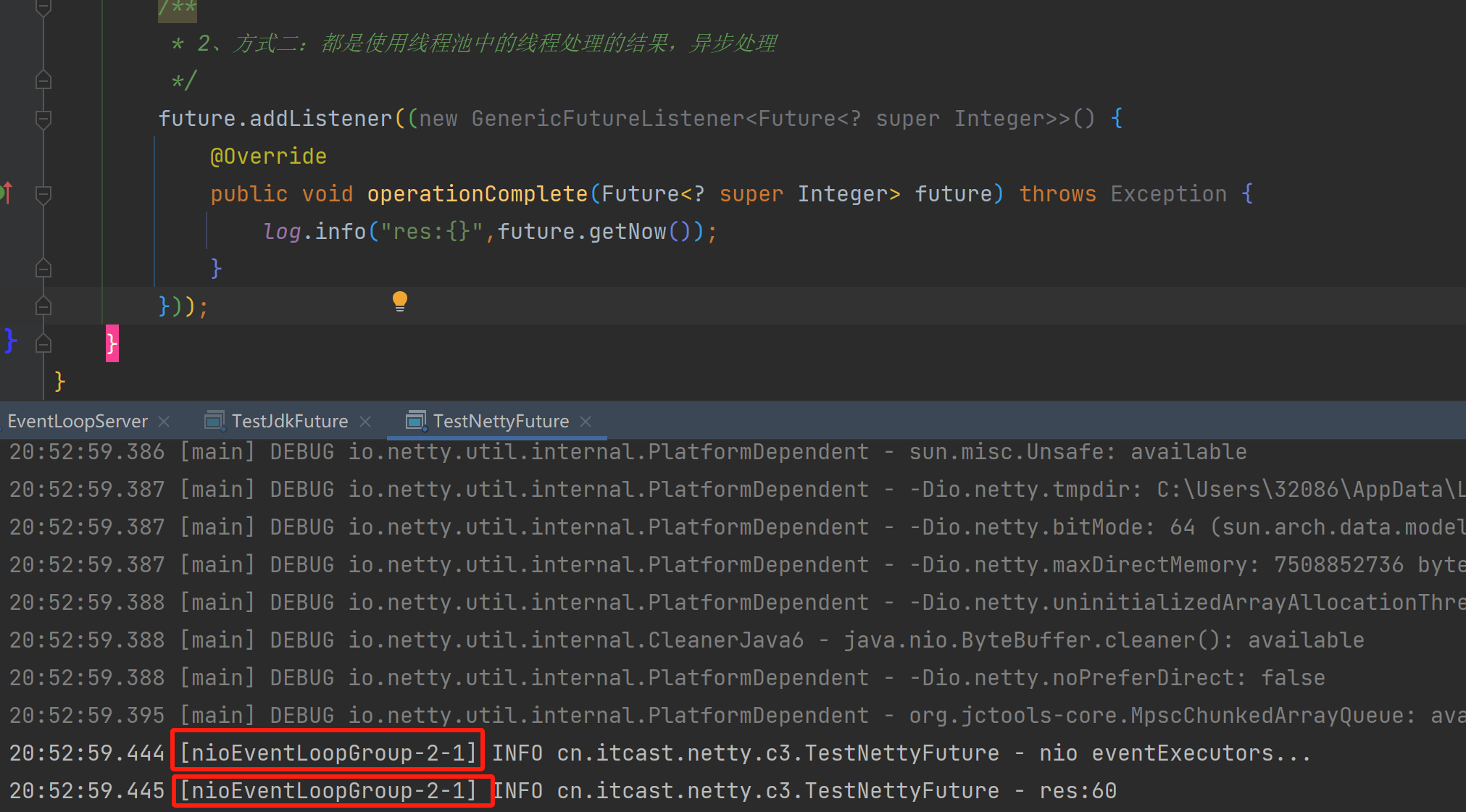
以上操作Future都是由线程池产生的
4、Promise
promise里面有三个方法
1)promise.setSuccess(80);:设置结果
2)promise.setFailure(e);:出现异常时,设置异常信息
3)promise.get();:获取结果
promise可以主动创建,这不同于Future的被动创建
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 1、准备EventLoop对象
EventLoop eventLoop = new NioEventLoopGroup().next();
// 2、可以主动创建promise,用于盛放结果的容器
DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(eventLoop);
new Thread(()->{
log.info("计算结果...");
try {
int i = 10 / 0;
Thread.sleep(1000);
promise.setSuccess(80);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
promise.setFailure(e);
}
}).start();
log.info("等待结果...");
log.info("结果是:{}",promise.get());
}
正常情况:

异常情况:





















 1286
1286

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








