一、单变量离散傅里叶变换
离散傅里叶变换公式:
根据公式,单变量离散傅里叶变是换将一维数组变换为傅里叶频率。设定一个大小为N的数组,t为X轴上的变量,取值为[0,n-1],f(t)为t=x出的值,计算机处理时,t即为输入数组下标index,f(t)为index对应位置数组中的值。
当μ=0时:
相当于整个输入数组直接求和。由于傅里叶变换计算涉及复数,可以将输入数组变换为复数形式,f(t)作为复数实部,虚部为0。根据欧拉公式:
在进行实际使用时,可将傅里叶变换为如下形式:
由于j为虚数,在实际计算过程中j=√-1是没有代入的,只需要计算复数的实部和虚数实部即可。
傅里叶变换核心代码:
public Complex[] dft(Complex[] C) {
int n = C.length;
if (n == 1) {
return C;
}
Complex[] result = new Complex[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result[i] = new Complex(0, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
double p = -2 * i * j * Math.PI / n;
Complex m = new Complex(Math.cos(p), Math.sin(p));
result[i] = result[i].add(C[j].multiply(m));
}
}
return result;
}
代码中,i相当于公式中的μ,j相当于t。
二、中心化
为了便于分析和操作需要将输入数组进行中心化,中心化公式:f’(t) = f(t)*(-1)t,即根据数组下标奇偶数,将下标为奇数的数乘以-1,把整个数组分为以0为中心的数组序列。
中心化代码:
public Complex[] dftShift(Complex[] C) {
int n = C.length;
Complex[] result = new Complex[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Complex m = new Complex(Math.pow(-1, i),0);
result[i] = C[i].multiply(m);
}
return result;
}
三、傅里叶谱
傅里叶谱,即傅里叶变换后的频谱图,频谱计算也就是计算复数模长。
复数模长计算公式:|C|=a2+b2
四、逆傅里叶变换
逆傅里叶变换公式:
傅里叶变换本质上就是把数据从时域/空间域变换到频率域,而逆傅里叶变换就是把数据再从频率域变换回时域/空间域。
逆傅里叶变换实现代码:
public Complex[] iDFT(Complex[] C) {
int n = C.length;
if (n == 1) {
return C;
}
Complex[] result = new Complex[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result[i] = new Complex(0, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
double p = 2 * i * j * Math.PI / n;
Complex m = new Complex(Math.cos(p), Math.sin(p));
result[i] = result[i].add(C[j].multiply(m));
}
result[i] = new Complex(result[i].getRealPart() / n, result[i].getImaginePart() / n);
}
return result;
}
五、离散傅里叶变换实现代码
public class DFT {
/**
* 计算离散傅里叶变换
*
* @param x
* @return
*/
public Complex[] dft(Complex[] C) {
int n = C.length;
if (n == 1) {
return C;
}
Complex[] result = new Complex[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result[i] = new Complex(0, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
double p = -2 * i * j * Math.PI / n;
Complex m = new Complex(Math.cos(p), Math.sin(p));
result[i] = result[i].add(C[j].multiply(m));
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 逆离散傅里叶变换
*
* @param C
* @return
*/
public Complex[] iDFT(Complex[] C) {
int n = C.length;
if (n == 1) {
return C;
}
Complex[] result = new Complex[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
result[i] = new Complex(0, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
double p = 2 * i * j * Math.PI / n;
Complex m = new Complex(Math.cos(p), Math.sin(p));
result[i] = result[i].add(C[j].multiply(m));
}
result[i] = new Complex(result[i].getRealPart() / n, result[i].getImaginePart() / n);
}
return result;
}
//中心化
public Complex[] dftShift(Complex[] C) {
int n = C.length;
Complex[] result = new Complex[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Complex m = new Complex(Math.pow(-1, i),0);
result[i] = C[i].multiply(m);
}
return result;
}
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
File in = new File("E:\\桌面\\1.jpg");
File out = new File("E:\\桌面\\4.txt");
BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(in);
int width = image.getWidth();
int height = image.getHeight();
int length = width * height;
Complex[] C = new Complex[length];
//将二维图片转为一维数组
for(int i = 0; i < width; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < height; j++) {
int rgb = image.getRGB(i, j);
int index = i * height + j;
C[index] = new Complex(rgb & 0xff, 0);
}
}
C = new DFT().dftShift(C);//中心化
Complex[] result = new DFT().dft(C);
Writer writer = new FileWriter(out);
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
writer.write(Double.toString(result[i].absValue()));//计算频谱
writer.write("\r\n");
}
writer.close();
}
测试图像:

频谱图:
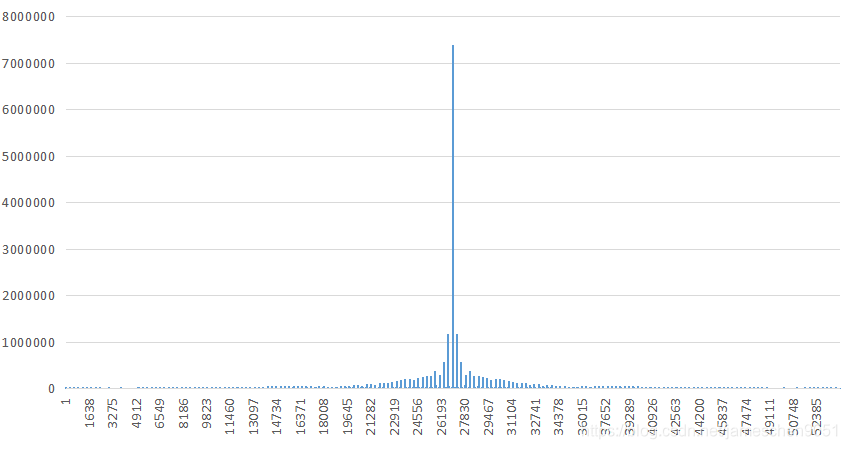





 本文深入解析了离散傅里叶变换(DFT)的基本原理及应用,涵盖单变量DFT公式、中心化处理、傅里叶谱计算、逆DFT及其实现代码。通过实例展示了如何将图像转换为频谱图。
本文深入解析了离散傅里叶变换(DFT)的基本原理及应用,涵盖单变量DFT公式、中心化处理、傅里叶谱计算、逆DFT及其实现代码。通过实例展示了如何将图像转换为频谱图。

















 1209
1209

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










