前面我们讲完了SqlSessionFactory的初始化,这里我们主要看一下如何通过SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession对象的,在获取SqlSession的同时,又做了哪些操作
在前面我们了解到最终获取的SqlSessionFactory其实是DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象,我们看一下这个对象的方法:
 这里可以看到,重载了获取session的方法,一共有8个方法:
这里可以看到,重载了获取session的方法,一共有8个方法:
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit) {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, autoCommit);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType) {
return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, null, false);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level) {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), level, false);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level) {
return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, level, false);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit) {
return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, null, autoCommit);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(Connection connection) {
return openSessionFromConnection(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), connection);
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection) {
return openSessionFromConnection(execType, connection);
}
我们可以看到最终都是调用了openSessionFromDataSource方法:
private SqlSession openSessionFromConnection(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection) {
try {
boolean autoCommit;
try {
autoCommit = connection.getAutoCommit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Failover to true, as most poor drivers
// or databases won't support transactions
autoCommit = true;
}
//获取到我们的环境配置
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//通过环境获取到配置的事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//通过事务工厂来生产一个事务
final Transaction tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(connection);
//初始化Executor 执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//生成DefaultSqlSession对象
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
1.通过环境获取到配置的事务
private TransactionFactory getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(Environment environment) {
//如果没有配置环境,或者是环境中没有配置事务工厂
//默认生成ManagedTransactionFactory
if (environment == null || environment.getTransactionFactory() == null) {
return new ManagedTransactionFactory();
}
//返回配置的事务工厂
return environment.getTransactionFactory();
}
我们看一下事务工厂TransactionFactory和Transaction的实现关系
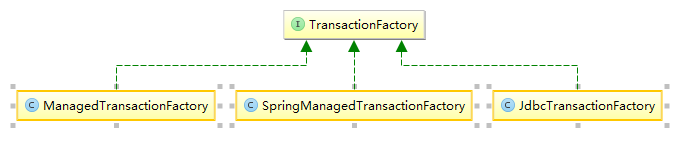
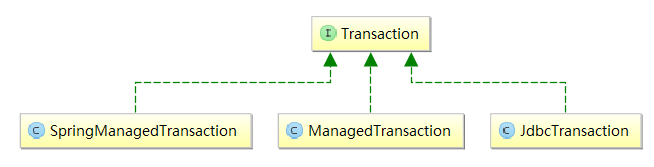
2.初始化Executor 执行器
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
//获取执行器类型
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//在执行器上添加插件链路
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
看下Executor的实现
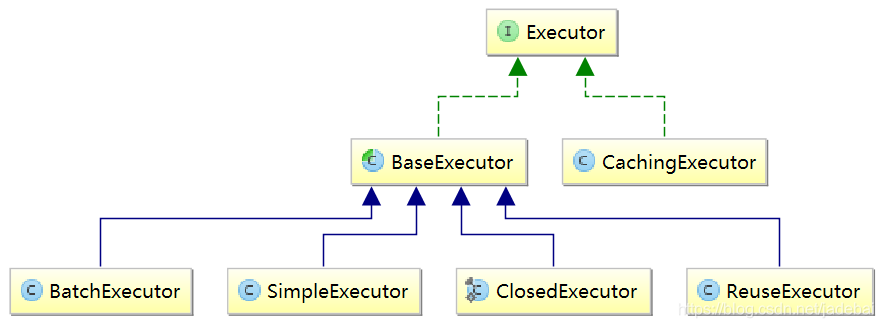
3.生成DefaultSqlSession对象
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
到这里就生成了SqlSession即DefaultSqlSession对象,并且把configuration和executor设置完成。





 本文探讨了如何通过SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession对象,详细解析了DefaultSqlSessionFactory的openSessionFromDataSource方法,包括事务工厂TransactionFactory、Transaction的交互,Executor执行器的初始化,以及最终生成DefaultSqlSession的过程。
本文探讨了如何通过SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession对象,详细解析了DefaultSqlSessionFactory的openSessionFromDataSource方法,包括事务工厂TransactionFactory、Transaction的交互,Executor执行器的初始化,以及最终生成DefaultSqlSession的过程。
















 656
656

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








