import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class BoundedBuffer {
final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
final Object[] items = new Object[2];
int putptr, takeptr, count;
// 生产者方法,往数组里面写数据
public void put(Object x) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await(); //数组已满,没有空间时,挂起等待,直到数组“非满”(notFull)
items[putptr] = x;
if (++putptr == items.length) putptr = 0;
++count;
// 因为放入了一个数据,数组肯定不是空的了
// 此时唤醒等待这notEmpty条件上的线程
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 消费者方法,从数组里面拿数据
public Object take() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await(); // 数组是空的,没有数据可拿时,挂起等待,直到数组非空(notEmpty)
Object x = items[takeptr];
if (++takeptr == items.length) takeptr = 0;
--count;
// 因为拿出了一个数据,数组肯定不是满的了
// 此时唤醒等待这notFull条件上的线程
notFull.signal();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
代码是JAVA官方文档(Condition接口)中的一个例子。下面是调用该类的main方法。
/*
*都在lock处打断点,然后人为模拟获取锁的顺序:p2-->p1-->t2-->t3--t1
*
* */
public class TestThread6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BoundedBuffer bf = new BoundedBuffer();
new Thread(()->{
try {
bf.put(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
bf.put(2);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t2").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
bf.put(3);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t3").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(bf.take());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"p1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(bf.take());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"p2").start();
}
}
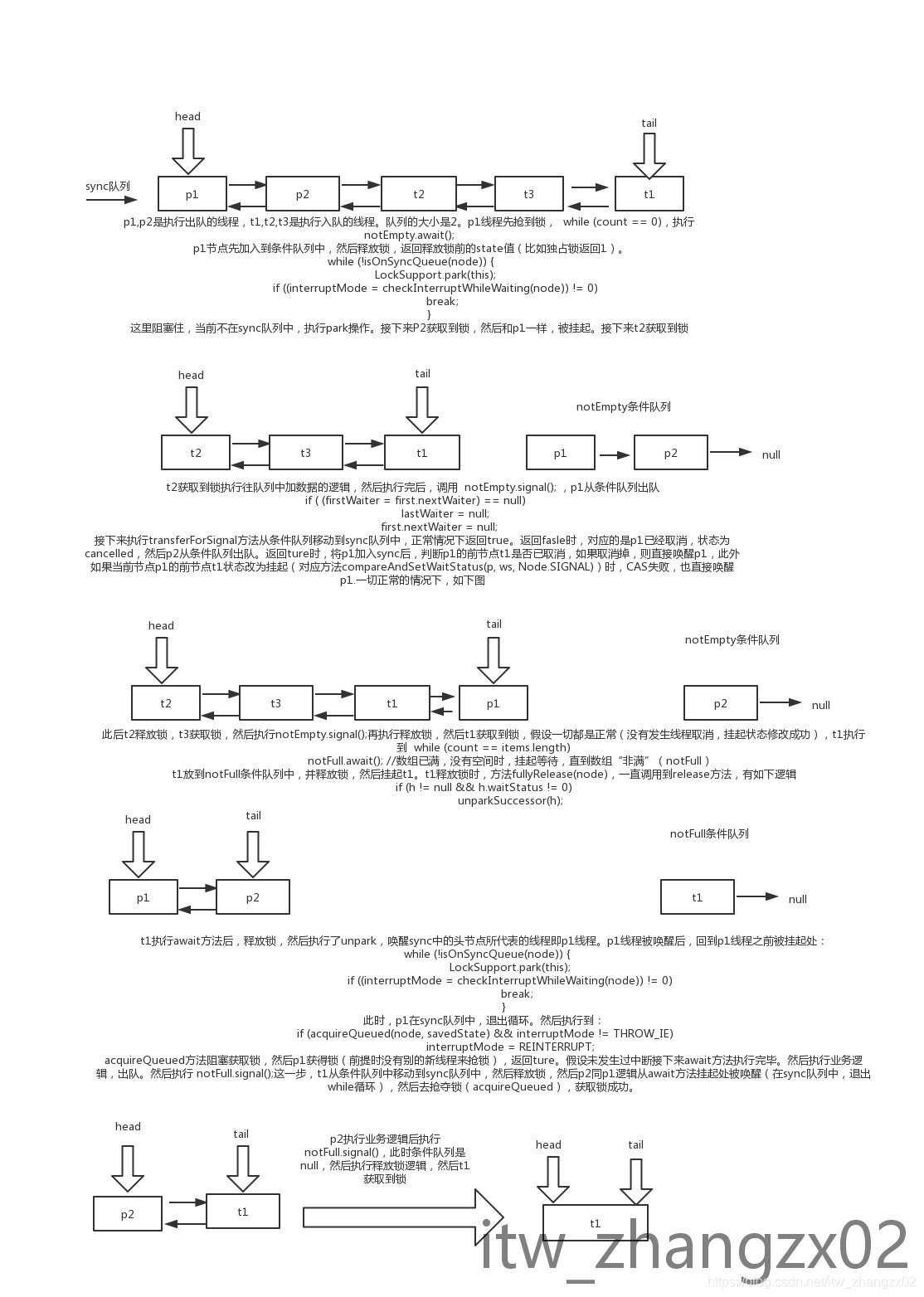
上图就是假设一切正常时的执行逻辑。
1.获取锁的lock()方法,非公平锁。
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
2.模拟获取锁的顺序:p1-->p2-->t2-->t3--t1
3.p1获取到锁,断点打住,别的线程执行获取锁时,addWaiter()将节点加入sync队列中。然后执行acquireQueued方法
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
4.模拟p1一直未释放锁也未执行await,执行shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire方法返回true,然后执行parkAndCheckInterrupt方法将当前线程挂起。依次执行,最后sync队列中节点顺序:p1-->p2-->t2-->t3--t1。
5.接下来p1线程执行到 while (count == 0)处,然后执行notEmpty.await()。
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
LockSupport.park(this);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
6.addConditionWaiter方法:加入条件队列中,即将p2节点(为了方便描述p2节点代表线程p2,以此类推)加入条件队列notEmpty中。
7. int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
释放锁的逻辑,同时返回释放锁之前的state的值,此处是1,p1从sync队列中退出(之前p1是head节点)
8. isOnSyncQueue(node),此时p1不在sync队列中,执行while循环体中的方法 LockSupport.park(this) ,p1线程被挂起。
9.p2获取到锁,然后同p1,执行await方法加入条件队列notEmpty中,释放锁,同一时间t2获取到锁,然后执行挂起p2的逻辑。此时,对应第二个图。
10.t3获取锁之后,直接执行入队逻辑,然后执行 notEmpty.signal(),将条件队列 notEmpty中第一个节点p1移除出条件队列,然后初始化p1的ws状态,将p1加入sync队列中(enq方法),正常情况下不走if的逻辑,然后返回true。
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
描述的是,前节点t1已取消,直接唤醒。或者前节点t1的ws状态,CAS为Node.SIGNAL失败时,直接唤醒当前节点p1。此时,对应图三。
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);
}
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)
lastWaiter = null;
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) &&
(first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.
*/
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
/*
* Splice onto queue and try to set waitStatus of predecessor to
* indicate that thread is (probably) waiting. If cancelled or
* attempt to set waitStatus fails, wake up to resync (in which
* case the waitStatus can be transiently and harmlessly wrong).
*/
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
return true;
}
11.t3释放锁,然后t2获取锁,t2往队列里放数据,然后 notEmpty.signal(); p2同p1逻辑,从条件队列移动到sync队列中,然后t2释放锁,t1获取到锁。
12.由于此时队列已满,所以t1执行
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
t1挂起,t1加入条件队列notFull中,释放锁,然后挂起。
13.p1获取到锁,执行出队,然后 notFull.signal();t1从同步队列移动到sync队列中去,然后p1释放锁,p2获取到锁,此时对应图五左边部分。
14.p2执行业务逻辑,然后释放锁。
这只是一个简单的按照一切正常的逻辑执行时的程序运行逻辑,实际会考虑到中断,超时等情况会相对复杂。
总之,线程发生中断时,不会立即中断,还必须等该线程先获取到锁,然后才能对中断做响应。





 本文深入解析Java中的BoundedBuffer类,展示如何使用Condition接口实现生产者消费者模式。通过具体代码示例,阐述线程间如何通过锁和条件变量进行同步,确保数据正确性和线程安全。
本文深入解析Java中的BoundedBuffer类,展示如何使用Condition接口实现生产者消费者模式。通过具体代码示例,阐述线程间如何通过锁和条件变量进行同步,确保数据正确性和线程安全。
















 386
386

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








