以下是使用 C++ 实现面向对象编程中类关系的详细解释,包含完整语法和示例:
一、基础类定义
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
// 父类 Animal(基类)
class Animal {
protected:
std::string name;
public:
explicit Animal(const std::string& name) : name(name) {}
virtual void speak() const { // 虚函数支持多态
std::cout << name << " makes a sound" << std::endl;
}
virtual ~Animal() = default; // 虚析构函数
};
// 子类 Dog(继承)
class Dog : public Animal {
std::string breed;
public:
Dog(const std::string& name, const std::string& breed)
: Animal(name), breed(breed) {}
// override 关键字明确表示重写 (C++11+)
void speak() const override {
std::cout << name << " barks! (Breed: " << breed << ")" << std::endl;
}
};
二、建立联系的三种方式
- 继承 (Inheritance)
cpp
// 使用示例
int main() {
Dog my_dog("Buddy", "Golden Retriever");
my_dog.speak(); // 输出: Buddy barks! (Breed: Golden Retriever)
// 多态示例
Animal* animal = new Dog("Max", "Husky");
animal->speak(); // 输出: Max barks! (Breed: Husky)
delete animal;
return 0;
}
- 组合 (Composition)
cpp
class Engine {
public:
void start() const {
std::cout << "Engine starts: Vroom!" << std::endl;
}
};
class Car {
std::string model;
Engine engine; // 组合关系:直接成员对象
public:
explicit Car(const std::string& model) : model(model) {}
void drive() {
engine.start();
std::cout << model << " is moving" << std::endl;
}
};
// 使用示例
Car my_car("Tesla Model S");
my_car.drive();
// 输出:
// Engine starts: Vroom!
// Tesla Model S is moving
- 关联 (Association)
cpp
class Course {
std::string name;
public:
explicit Course(const std::string& name) : name(name) {}
const std::string& getName() const { return name; }
};
class Student {
std::string name;
std::vector<Course*> courses; // 关联关系:存储指针
public:
explicit Student(const std::string& name) : name(name) {}
void enroll(Course* course) {
courses.push_back(course);
std::cout << name << " enrolled in " << course->getName() << std::endl;
}
};
// 使用示例
Course math("Calculus");
Student alice("Alice");
alice.enroll(&math); // 输出: Alice enrolled in Calculus
三、完整示例:多种关系结合
cpp
// 继承 + 组合
class Person {
protected:
std::string name;
public:
explicit Person(const std::string& name) : name(name) {}
};
class Computer {
std::string serial;
public:
explicit Computer(const std::string& serial) : serial(serial) {}
const std::string& getSerial() const { return serial; }
};
class Employee : public Person { // 继承
int id;
Computer* computer; // 组合关系(通过指针)
public:
Employee(const std::string& name, int id)
: Person(name), id(id), computer(nullptr) {}
void assignComputer(Computer* comp) {
computer = comp;
}
void printInfo() const {
std::cout << name << " uses computer ";
if (computer) {
std::cout << computer->getSerial();
} else {
std::cout << "[None]";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
};
// 使用
Computer dev_computer("SN123");
Employee john("John Doe", 1001);
john.assignComputer(&dev_computer);
john.printInfo(); // 输出: John Doe uses computer SN123
四、C++ 特有重要特性
- 访问控制
cpp
class MyClass {
private: // 仅类内可访问
int secret;
protected: // 类内和派生类可访问
int internal;
public: // 完全公开
int visible;
};
- 内存管理
cpp
// 推荐使用智能指针管理关联关系
#include <memory>
class Project {
//...
};
class TeamMember {
std::shared_ptr<Project> currentProject; // 使用 shared_ptr
};
- 多态实现
cpp
class Shape {
public:
virtual double area() const = 0; // 纯虚函数
virtual ~Shape() = default;
};
class Circle : public Shape {
double radius;
public:
explicit Circle(double r) : radius(r) {}
double area() const override {
return 3.14159 * radius * radius;
}
};
// 使用基类指针操作派生类
Shape* shape = new Circle(5.0);
std::cout << "Area: " << shape->area() << std::endl;
delete shape;
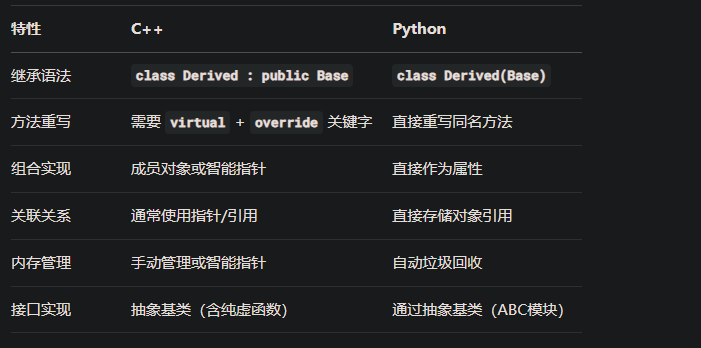
五、关键对比(C++ vs Python)
六、最佳实践建议
继承规范:
使用 public 继承表示 is-a 关系
为多态基类声明虚析构函数
使用 override 关键字明确重写
组合优化:
优先使用对象成员(值语义)
需要动态分配时使用 unique_ptr/shared_ptr
关联管理:
使用裸指针时明确所有权关系
推荐使用弱引用(weak_ptr)避免循环引用
多态控制:
纯虚函数实现接口:virtual void func() = 0;
使用 final 关键字禁止进一步重写
cpp
// 高级示例:接口设计
class Drawable {
public:
virtual void draw() const = 0;
virtual ~Drawable() = default;
};
class Circle final : public Drawable { // final 禁止继承
public:
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "Drawing a circle" << std::endl;
}
};
通过合理应用这些技术,可以在 C++ 中构建健壮的面向对象系统,同时兼顾性能和代码清晰度。























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










