【问题描述】请根据基本分页存储管理的原理,对若干进程进行内存分配,并根据页面计算给定的逻辑地址的物理地址。说明:为程序调试方便,请按照输入样例采用文件形式输入相应数据。
【输入形式】
【输出形式】
【样例输入】(说明:输入文件名为test.txt)
65536 //内存大小,单位为字节
2048 //页面大小,单位为字节
20480 //OS所占内存大小,单位为字节
3 //装入进程数量
P0 7680 //第1个进程名称及大小,单位为字节
0 2 //后面几行为第1个进程的页表
1 4
2 6
3 8
P1 10064.6 //第2个进程名称及大小,单位为字节
0 18 //后面几行为第2个进程的页表
1 31
2 7
3 5
4 29
P2 5734.4 //第3个进程名称及大小,单位为字节
0 14 //后面几行为第3个进程的页表
1 17
2 9
4 //需要转换的逻辑地址个数
P0 4865 //需要转换的逻辑地址的进程名和地址值,单位为字节
P1 1023
P2 4500
P0 10000
【样例输出】(说明:下面输出样例中所有的标点符号均为英文状态下的标点符号)
The total num of memory are 32 blocks,10 blocks has been used.//内存块数为*块,已使用*块。
Process P0 use 4 blocks. //进程*使用*块。
Process P1 use 5 blocks.
Process P2 use 3 blocks.
The total num of memory are 32 blocks,22 blocks has been used.//内存块数为*块,已使用*块。
P0:logic address 4865's pyhsical address is 13057. //逻辑地址*对应的物理地址为*。
P1:logic address 1023's pyhsical address is 37887.
P2:logic address 4500's pyhsical address is 18836.
P0:logic address 10000 is out of range.
代码实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
//定义页表项结构体
struct PTL{
int page;//页号
int block;//块号
bool operator==(const int& p){
return this->page==p;
}
};
//定义进程请求序列结构体
struct REQ{
string P_name;//进程名称
int add;//逻辑地址
};
//定义进程控制块结构体
struct PCB{
string P_name;//进程名称
float size;//进程大小
vector<PTL> pagetabale;//页表
bool operator==(const string& name) {
return this->P_name==name;
}
};
int main()
{
ifstream txtfile;
txtfile.open("test.txt");//打开输入文件
int n, y, o, num;//内存大小、页面大小、OS所占内存大小、装入进程数量
txtfile>>n>>y>>o>>num;
cout<<"The total num of memory are "<<ceil(double(n)/y)<<" blocks,"<<o/y<<" blocks has been used."<<endl;
//读取每个进程的信息,并创建进程控制块和页表
vector<PCB> pcbs;//存储所有进程控制块的向量
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
PCB pcb;
txtfile>>pcb.P_name>>pcb.size;
int page_num=ceil(pcb.size/y);//计算页面数
cout<<"Process "<<pcb.P_name<<" use "<<page_num<<" blocks."<<endl;//输出进程分配的块数
for(int j=0;j<page_num;j++){
PTL ptl;
txtfile>>ptl.page;
txtfile>>ptl.block;//读取页表项的块号
pcb.pagetabale.push_back(ptl);//将该页表项添加到进程的页表中
}
pcbs.push_back(pcb);//将该进程控制块添加到向量中
}
//输出内存使用情况
int used_blocks=o/y;//已使用的块数,初始为OS占用的块数
unsigned int i;
for(i=0;i<pcbs.size();i++){
used_blocks+=pcbs[i].pagetabale.size();//计算已使用的块数
}
cout<<"The total num of memory are "<<ceil(double(n)/y)<<" blocks,"<<used_blocks<<" blocks has been used."<<endl;
//读取需要转换的逻辑地址,并根据页表计算物理地址
int query_num;
txtfile>>query_num;
for(int i=0;i<query_num;i++){
REQ req;
txtfile>>req.P_name>>req.add;
bool found=false;
unsigned int j;
for(j=0;j<pcbs.size();j++){
if(pcbs[j].P_name==req.P_name){//如果找到了对应的进程
unsigned int k;
for(k=0;k<pcbs[j].pagetabale.size();k++){//遍历该进程的页表
if(pcbs[j].pagetabale[k].page<=req.add/y && (pcbs[j].pagetabale[k].page+1)>req.add/y){//找到了对应的页表项
found = true;
int physical_add = pcbs[j].pagetabale[k].block * y + (req.add % y);//计算物理地址
cout << req.P_name << ":logic address " << req.add << "'s pyhsical address is " << physical_add
<< "." << endl;
break;
}
}
if (found) {
break;
}
}
}
if (!found) {//如果没有找到对应的页表项
cout << req.P_name << ":logic address " << req.add << " is out of range." << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
test.txt文件输入格式样例:
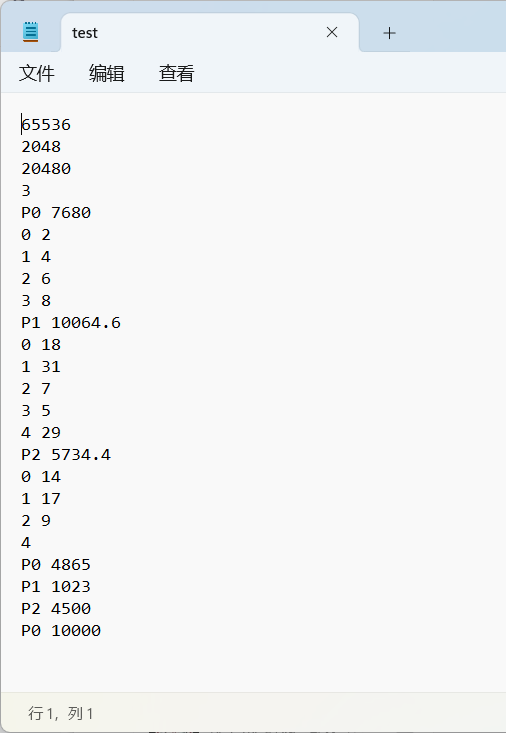
注意:test.txt文件要和代码文件放在同一文件夹内。




 文章描述了一个程序,用于根据分页存储管理原理对进程进行内存分配,并根据页面计算逻辑地址的物理地址。程序从文件读取内存大小、页面大小、操作系统占用内存和进程信息,然后进行地址转换。对于超出范围的逻辑地址,程序会给出错误提示。代码实现了这一过程,包括读取输入文件、创建页表、计算物理地址等功能。
文章描述了一个程序,用于根据分页存储管理原理对进程进行内存分配,并根据页面计算逻辑地址的物理地址。程序从文件读取内存大小、页面大小、操作系统占用内存和进程信息,然后进行地址转换。对于超出范围的逻辑地址,程序会给出错误提示。代码实现了这一过程,包括读取输入文件、创建页表、计算物理地址等功能。
















 8873
8873

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








