转自: 点击打开链接
1. 使用一个Reduce进行排序
MapReduce默认只是保证同一个分区内的Key是有序的,但是不保证全局有序,因此将所有的数据全部发送到一个Reduce,这样实现全排序。
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TotalSortV1 extends Configured implements Tool {
static class SimpleMapper extends
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
IntWritable intWritable = new IntWritable(Integer.parseInt(value.toString()));
context.write(intWritable, intWritable);
}
}
static class SimpleReducer extends
Reducer<IntWritable, IntWritable, IntWritable, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (IntWritable value : values)
context.write(value, NullWritable.get());
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.err.println("<input> <output>");
System.exit(127);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(getConf());
job.setJarByClass(TotalSortV1.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.setMapperClass(SimpleMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(SimpleReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(1);
job.setJobName("TotalSort");
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exitCode = ToolRunner.run(new TotalSort(), args);
System.exit(exitCode);
}
}2. 自定义分区函数实现全局有序
MapReduce默认的分区函数是HashPartitioner,源码如下: 转载自: 点击打开链接
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
这段代码实现的目的是将key均匀分布在Reduce Tasks上,例如:如果Key为Text的话,Text的hashcode方法跟String的基本一致,都是采用的Horner公式计算,得到一个int整数。但是,如果string太大的话这个int整数值可能会溢出变成负数,所以和整数的上限值Integer.MAX_VALUE(即0111111111111111)进行与运算,然后再对reduce任务个数取余,这样就可以让key均匀分布在reduce上。
使用自定义分区:
public static class IteblogPartitioner extends Partitioner<IntWritable, IntWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(IntWritable key, IntWritable value, int numPartitions) {
int keyInt = Integer.parseInt(key.toString());
if (keyInt < 10000) {
return 0;
} else if (keyInt < 20000) {
return 1;
} else {
return 2;
}
}
}在run()方法中:
job.setPartitionerClass(IteblogPartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(3);生成的文件part-r-00000、part-r-00001和part-r-00002三个文件实现了全局有序。
3. 使用TotalOrderPartitioner进行全排序
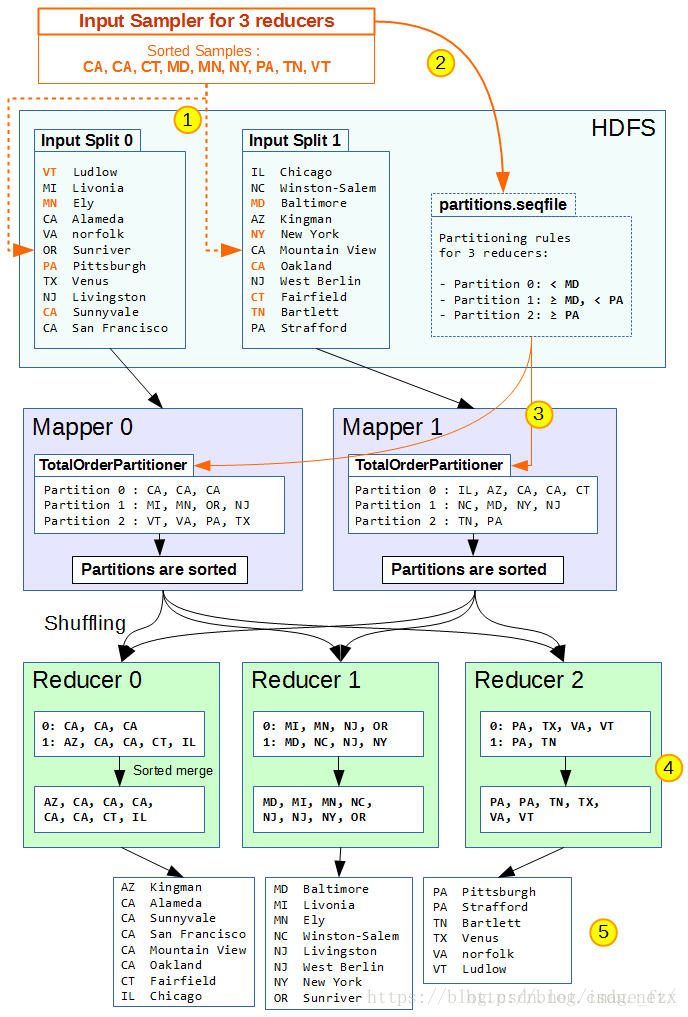
1、在开始Map之前,Mapreduce首先执行InputSampler对样本抽样,并生成partition file写入HDFS。InputSampler对输入split进行抽样,并使用sortComparator对抽样结果进行排序。常用抽样方法有:
- RandomSampler:按照给定频次,进行随机抽样。
- IntervalSampler:按照给定间隔,进行定间隔抽样。
- SplitSampler:取每个split的前n个样本进行抽样。
2、InputSampler在HDFS上写入一个partition file(sequence file),决定不同分区的key边界。对于n个Reducer,partition file有n-1个边界数据。Map的output按照partition file的边界不同,分别写入对应的分区。
3、Mapper使用TotalOrderPartitioner类读取partition file,获得每个Mapper使用TotalOrderPartitioner类。这个类读取partition file,确定每个分区的边界。
4、在shuffle阶段,每个Reducer会拉取对应分区中已排序的(key, value)。由于每个分区已按照partition file设置边界,这样分区1中的数据都比分区2小,分区2数据都比分区3小(假设升序排列)。
5、Reducer处理对应分区数据并写入HDFS后,输出数据也保持全局有序。
Total Order Partitioner简单实现
1)使用RandomSampler进行样本抽样。
- freq=0.01。抽样器采用0.01%(1%)从样本记录中进行抽样。
- numSamplers=1000。抽样器最多取1000个样本。如果抽样样本数达到上限,则新样本会覆盖已有样本。
- maxSplitsSampled=100。抽样器最多抽样100个splts。
2)InputSamer.writePartitionFile()写入HDFS。需要提前完成如下配置,
- 任务输入路径:通过FileInputFormat.SetInputPaths(),设定任务的输入数据路径,供抽样器进行抽样。- Reduce任务数量:确定写入partition file的边界数量(即Reduce任务数量减1)。
- Map的OutputKey类型:Map InputKey类型需要与Map OutputKey类型保持一致!
在run()方法中:
job.setNumReduceTasks(3);TotalOrderPartitioner.setPartitionFile(job.getConfiguration(), new Path(args[2]));
InputSampler.Sampler<Text, Text> sampler = new InputSampler.RandomSampler<>(0.01, 1000, 100);
InputSampler.writePartitionFile(job, sampler);
job.setPartitionerClass(TotalOrderPartitioner.class);参考: 点击打开链接





















 3178
3178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








