文章目录
Aspect Oriented Programming 面向切面编程,是一种利用“横切”的技术(底层实现就是动态代理),对原有的业务逻辑进行拦截,并且可以在这个拦截的横切面上添加特定的业务逻辑,对原有的业务进行增强。
1. 框架部署
1.1 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.13.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.2.13.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
1.2 自定义模板
创建一个名为 spring-aop-xml 的模板,后缀为 xml ,模板内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
</beans>
1.3 创建配置文件
在 resource 目录下用 spring-aop-xml 模板创建文件 applicationContext.xml ,作为Spring的配置文件。
2. 框架使用
2.1 定义业务逻辑
我们想要在进行数据库的操作中,每个操作的前后都进行开始事务操作以及提交事务操作,如果每个操作后面都写上这两个方法,则未免太多余,故可以使用AOP切面编程。
public class TxManager {
public void begin(){
System.out.println("-----------开启事务");
}
public void commit(){
System.out.println("-----------提交事务");
}
}
2.2 配置AOP
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="bookDAO" class="com.mr.DAO.BookDAOImp"></bean>
<!---->
<bean id="txManager" class="com.mr.Utils.TxManager"></bean>
<aop:config>
<!--声明切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="book_all" expression="execution(* com.mr.DAO.*.*(..))"/>
<!--声明txManager为切面类-->
<aop:aspect ref="txManager">
<!--通知-->
<aop:before method="begin" pointcut-ref="book_all"/>
<aop:after method="commit" pointcut-ref="book_all"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
2.3 定义DAO实现方法
在这里就简单的象征性实现下,效果是一样的。
public class BookDAOImp {
public void update(){
System.out.println("更新书籍--------");
}
public void delete(){
System.out.println("删除书籍--------");
}
public void add(){
System.out.println("添加书籍--------");
}
}
2.4 方法测试
重新写一个测试文件来进行测试,测试文件代码如下:
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.通过Spring容器获取Student对象
BookDAOImp book1 = (BookDAOImp) context.getBean("bookDAO");
book1.delete();
}
}
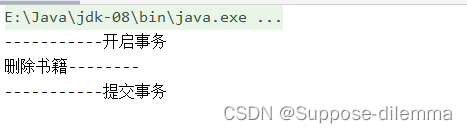
输出的结果如下所示:
3. AOP规则
3.1 切入点声明
<!--使用aop:pointcut标签声明切入点:切入点可以是一个方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="book_insert" expression="execution(* com.qfedu.dao.BookDAOImpl.insert())"/>
<!--BookDAOImpl类中所有无参数无返回值的方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="book_pc1" expression="execution(void com.qfedu.dao.BookDAOImpl.*())"/>
<!--BookDAOImpl类中所有无返回值的方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="book_pc2" expression="execution(void com.qfedu.dao.BookDAOImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--BookDAOImpl类中所有无参数的方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="book_pc3" expression="execution(* com.qfedu.dao.BookDAOImpl.*())"/>
<!--BookDAOImpl类中所有方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="book_pc4" expression="execution(* com.qfedu.dao.BookDAOImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--dao包中所有类中的所有方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="pc5" expression="execution(* com.qfedu.dao.*.*(..))"/>
<!--dao包中所有类中的insert方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="pc6" expression="execution(* com.qfedu.dao.*.insert(..))"/>
<!--dao包中所有类中的insert方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="pc7" expression="execution(* *(..))"/>
3.2 AOP通知策略
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.mr.Utils.MyAspect"></bean>
<aop:config>
<!--使用aop:pointcut标签声明切入点:切入点可以是一个方法-->
<aop:pointcut id="book_insert" expression="execution(* com.qfedu.dao.BookDAOImpl.insert())"/>
<aop:aspect ref="myAspect">
<!--aop:before 前置通知,切入到指定切入点之前-->
<aop:before method="method1" pointcut-ref="book_insert"/>
<!--aop:after 后置通知,切入到指定切入点之后-->
<aop:after method="method2" pointcut-ref="book_insert"/>
<!--aop:after-throwing 异常通知,切入点抛出异常之后-->
<aop:after-throwing method="method3" pointcut-ref="book_insert"/>
<!--aop:after-returning 方法返回值返回之后,对于一个Java方法而言return返回值也是方法的一部分
因此“方法返回值返回之后”和“方法执行结束”是同一个时间点,随意after 和 after-returning根据配置
的顺序决定执行顺序-->
<aop:after-returning method="method4" pointcut-ref="book_insert"/>
<aop:around method="method5" pointcut-ref="book_insert"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
around 环绕类型的通知对方法的要求如下:
//环绕通知的切点方法,必须准守如下的定义规则:
//1.必须带有一个ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数
//2.必须有Object类型的返回值
//3.在前后增强的业务逻辑之间执行Object v = point.proceed();
//4.方法最后返回v
public Object method5(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("~~~~~~~method5---before");
//此代码的执行,就表示切入点方法的执行
Object v = point.proceed();
System.out.println("~~~~~~~method5---after");
return v;
}
3.3 使用注意事项
- 如果要使用Spring aop面向切面编程,调用切入点方法的对象必须通过Spring容器获取
- 如果一个类中的方法被声明为切入点并且织入了切点之后,通过Spring容器获取该类对象,实则获取到的是一个代理对象
- 如果一个类中的方法没有被声明为切入点,通过Spring容器获取的就是这个类真实创建的对象





 本文详细介绍了Spring的面向切面编程(AOP)框架的使用,包括依赖添加、自定义模板、配置文件创建以及业务逻辑定义。通过AOP,可以在不修改原有业务代码的情况下,对特定方法进行增强,例如在数据库操作前后添加事务管理。文章还展示了切入点声明、通知策略及使用注意事项,帮助读者理解并掌握Spring AOP的实战应用。
本文详细介绍了Spring的面向切面编程(AOP)框架的使用,包括依赖添加、自定义模板、配置文件创建以及业务逻辑定义。通过AOP,可以在不修改原有业务代码的情况下,对特定方法进行增强,例如在数据库操作前后添加事务管理。文章还展示了切入点声明、通知策略及使用注意事项,帮助读者理解并掌握Spring AOP的实战应用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








