目录
4. map set的析构,拷贝构造,operator=的实现:
0. 完整实现代码:
Map.h
//
// Created by yangzilong on 2022/11/12.
//
#ifndef STL_MAP_H
#define STL_MAP_H
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace yzl {
template<class K, class V>
class map {
struct MapKeyOfT {
const K &operator()(const pair<K, V> &p) {
return p.first;
}
};
public:
// ~map() {
// _t.destroy();
// }
~map() = default;
map() = default;
map(const map<K,V>& m) = default;
map& operator=(const map<K,V>& m) = default;
// 拷贝构造
// map(const map<K,V>& m) {
// _t = m._t;
// }
public:
// typedef __RBTree_Iterator<pair<K,V>, pair<K,V>&, pair<K,V>*> iterator;
// typedef __RBTree_Iterator<pair<K,V>, const pair<K,V>&, const pair<K,V>*> const_iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin() {
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator begin() const {
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end() {
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator end() const {
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator cbegin() const {
return _t.cbegin();
}
const_iterator cend() const {
return _t.cend();
}
public:
// Set和Map的insert:插入这个值,若Key已经存在,则返回对应已存在迭代器,和false
// 若Key不存在,则返回对应新元素迭代器,和true
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V> &kv) {
return _t.insert(kv);
}
// map的operator[],有添加元素的功能,若存在,则返回对应的value,若不存在,插入新元素,返回V();
V& operator[] (const K& key) {
return this->insert(make_pair(key, V())).first->second;
}
iterator find(const K& key) {
return _t.find(key);
}
const_iterator find(const K& key) const{
return _t.find(key);
}
bool empty() const {
return _t.empty();
}
void clear() {
_t.clear();
}
size_t size() const {
return _t.size();
}
private:
// const RBTree<K, pair<K,V>, MapKeyOfT>& copy() const{
// return RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>(_t.copy());
// }
private:
// map的底层红黑树中,结点内存储的是pair<K, V>。
RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
#endif //STL_MAP_H
Set.h
//
// Created by yangzilong on 2022/11/12.
//
#ifndef STL_SET_H
#define STL_SET_H
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace yzl {
template<class K>
class set {
struct SetKeyOfT {
const K &operator()(const K &key) {
return key;
}
};
public:
~set() = default;
set() = default;
set(const set& s) = default;
set& operator=(const set& s) = default;
public:
typedef RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> RBT;
typedef typename RBT::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin() {
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator begin() const {
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end() {
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator end() const {
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator cbegin() const {
return _t.cbegin();
}
const_iterator cend() const {
return _t.cend();
}
public:
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K &key) {
return _t.insert(key);
}
iterator find(const K& key) {
return _t.find(key);
}
const_iterator find(const K& key) const{
return _t.find(key);
}
bool empty() const {
return _t.empty();
}
void clear() {
_t.clear();
}
size_t size() const {
return _t.size();
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
#endif //STL_SET_H
RBTree.h
//
// Created by yangzilong on 2022/11/12.
//
#ifndef STL_RBTREE_H
#define STL_RBTREE_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace yzl {
enum Color {
RED,
BLACK
};
// 红黑树结点,用于封装map/set,仅保存pair or T
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode {
RBTreeNode(const T &data)
: _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _data(data) {}
RBTreeNode<T> *_left;
RBTreeNode<T> *_right;
RBTreeNode *_parent;
T _data;
Color _col;
};
// 红黑树的迭代器,存储的只有一个RBTreeNode*数据成员
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __RBTree_Iterator {
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
Node *_node;
__RBTree_Iterator(Node *node)
: _node(node) {}
// 解引用迭代器,得到结点中的元素类型
Ref operator*() {
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->() {
return &(_node->_data);
}
bool operator==(const __RBTree_Iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> &self) const {
return _node == self._node; // 比较迭代器里面结点指针的值,保存的是结点的地址。
}
bool operator!=(const __RBTree_Iterator &self) const {
return _node != self._node;
}
__RBTree_Iterator &operator++() // 迭代器前置++,使指针指向红黑树中序下一个值。
{
// 中序:左子树,根,右子树,此时相当于根遍历完了
if (_node->_right != nullptr) {
_node = _node->_right;
while (_node->_left) {
_node = _node->_left;
}
} else {
if (_node->_parent == nullptr) {
_node = _node->_parent;
}
if (_node == _node->_parent->_left) {
_node = _node->_parent;
} else {
while (_node->_parent != nullptr && _node == _node->_parent->_right) {
_node = _node->_parent;
}
_node = _node->_parent;
}
}
return *this;
}
__RBTree_Iterator operator++(int) // 迭代器后置++
{
// 先保存,再++
auto ret = *this;
++(*this);
return ret;
}
__RBTree_Iterator &operator--() // 迭代器前置--,使指针指向红黑树中序前一个值
{
// 将结点指针变为中序前一个 右子树,根,左子树
if (_node->_left) {
_node = _node->_left;
while (_node->_right) {
_node = _node->_right;
}
} else {
Node *parent = _node->_parent;
while (parent != nullptr && _node == parent->_left) {
_node = parent;
parent = _node->_parent;
}
// 此时parent为空 或者 _node是parent的右子树根节点。
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
__RBTree_Iterator operator--(int) // 迭代器后置--
{
auto ret = *this;
--(*this);
return ret;
}
};
// 到目前为止,只有find函数里面使用了K模板参数,因为find需要使用key进行查询
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree {
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
~RBTree()
{
destroy();
}
RBTree() = default;
// 拷贝构造
RBTree(const RBTree& t) {
_root = t.copy();
}
RBTree& operator=(RBTree t) {
std::swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
public:
typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T, T &, T *> iterator;
typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T, const T &, const T *> const_iterator;
iterator begin() {
Node *cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left) {
cur = cur->_left;
}
return iterator(cur);
}
const_iterator begin() const {
Node *cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left) {
cur = cur->_left;
}
return const_iterator(cur);
}
iterator end() {
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator end() const {
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator cbegin() const {
Node *cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left) {
cur = cur->_left;
}
return const_iterator(cur);
}
const_iterator cend() const {
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
public:
bool empty() const {
return _root == nullptr;
}
size_t size() const {
return _size(_root);
}
iterator find(const K& key) {
KeyOfT kot;
Node* root = _root;
while(root != nullptr) {
if(kot(root->_data) > key) {
root = root->_left;
}
else if(kot(root->_data) < key) {
root = root->_right;
}
else {
return iterator(root);
}
}
return iterator(nullptr);
}
// const的map和set会使用这个find
const_iterator find(const K& key) const {
KeyOfT kot;
Node* root = _root;
while(root != nullptr) {
if(kot(root->_data) > key) {
root = root->_left;
}
else if(kot(root->_data) < key) {
root = root->_right;
}
else {
return const_iterator(root);
}
}
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T &data) {
// data的类型未知,可能是一个常规类型,可能是一个pair,因为map会传递T为pair<X,X>,此处需要取出Key进行比较(使用第三个模板参数)
KeyOfT kot;
if (_root == nullptr) {
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
Node *parent = nullptr;
Node *cur = _root;
while (cur != nullptr) {
if (kot(data) > kot(cur->_data)) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
} else if (kot(data) < kot(cur->_data)) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
} else {
// 已经存在
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node *newNode = cur;
cur->_col = RED;
if (kot(data) > kot(parent->_data)) {
parent->_right = cur;
} else {
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
// 插入新结点成功,且为红色。进行判断
// 进入下方循环后,parent一定为红,则parent一定不是根节点,则parent一定有父亲,有没有兄弟不一定。
while (parent && parent->_col == RED) {
Node *grandfather = parent->_parent;
Node *uncle = nullptr;
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
uncle = grandfather->_right;
else
uncle = grandfather->_left;
// 判断叔叔的情况,决定处理方式
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) {
// 叔叔存在且为红
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
} else {
// 叔叔不存在或者叔叔存在且为黑
if (parent == grandfather->_left && cur == parent->_left) {
// 此时,左左,右单旋+变色
// 先变色也可以
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
RotateR(grandfather);
} else if (parent == grandfather->_right && cur == parent->_right) {
// 右右,左单旋
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
RotateL(grandfather);
} else if (parent == grandfather->_right && cur == parent->_left) {
// cur为红,parent为红,grandfather为黑。
// 右左双旋。
// RotateR(parent);
// RotateL(grandfather);
// // 记住这里是上黑,下面俩红即可。
// cur->_col = BLACK;
// grandfather->_col = RED;
// 第二种实现方法,即单旋后变为双旋。
RotateR(parent);
std::swap(cur, parent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
RotateL(grandfather);
} else if (parent == grandfather->_left && cur == parent->_right) {
// RotateL(parent);
// RotateR(grandfather);
// // 记住这里是上黑,下面俩红即可。
// cur->_col = BLACK;
// grandfather->_col = RED;
RotateL(parent);
std::swap(cur, parent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
RotateR(grandfather);
}
break;
}
if (cur == _root) {
cur->_col = BLACK;
}
}
return make_pair(iterator(newNode), true);
}
// 看颜色还是看高度?
// 看颜色,因为高度正确不一定是红黑树
bool IsBalance() {
if (_root == nullptr)
return true;
if (_root->_col == RED) {
cout << "根节点为红色,错误" << endl;
return false;
}
int baseNum = 0;
return PrevCheck(_root, 0, 0);
}
void clear() {
destroy();
}
void destroy() {
_destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
Node* copy() const{
return _copy(_root, nullptr);
}
private:
Node* _copy(Node* root, Node* parent) const {
if(root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* ret = new Node(root->_data);
ret->_parent = parent;
// ret->_left = _copy(root->_left,root);
// ret->_right = _copy(root->_right, root);
ret->_left = _copy(root->_left,ret);
ret->_right = _copy(root->_right, ret);
return ret;
}
void _destroy(Node* root) const {
if(root == nullptr)
return;
_destroy(root->_left);
_destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
size_t _size(Node* root) const {
if(root == nullptr)
return 0;
return 1 + _size(root->_left) + _size(root->_right);
}
bool PrevCheck(Node *root, int baseNum, int blackNum) {
if (root == nullptr) {
if (baseNum == 0) {
baseNum = blackNum;
return true;
} else if (blackNum != baseNum) {
cout << "某条路径黑色结点数量不同,错误" << endl;
return false;
} else
return true;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
blackNum++;
else {
if ((nullptr != root->_left && root->_left->_col == RED) ||
(nullptr != root->_right && root->_right->_col == RED)) {
cout << "出现连续红色结点,错误" << endl;
return false;
}
}
return PrevCheck(root->_left, baseNum, blackNum)
&& PrevCheck(root->_right, baseNum, blackNum);
}
private:
void RotateL(Node *parent) {
Node *subR = parent->_right;
Node *subRL = subR->_left; // 可能为空
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
subR->_left = parent;
Node *ppNode = parent->_parent; // 修改parent->parent之前,保存原先parent->parent
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root) {
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
} else {
if (parent == ppNode->_right) {
ppNode->_right = subR;
subR->_parent = ppNode;
} else {
ppNode->_left = subR;
subR->_parent = ppNode;
}
}
}
void RotateR(Node *parent) {
Node *subL = parent->_left;
Node *subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node *ppNode = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
subL->_right = parent;
if (parent == _root) {
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
} else {
if (parent == ppNode->_right) {
ppNode->_right = subL;
subL->_parent = ppNode;
} else {
ppNode->_left = subL;
subL->_parent = ppNode;
}
}
}
private:
RBTreeNode<T> *_root = nullptr;
};
//Self& operator++()
//{
// // 左子树, 根, 右子树,
// if(_node->_right != nullptr) {
// _node = _node->_right;
// while(_node->_left != nullptr) {
// _node = _node->_left;
// }
// }
// else {
// // 右为空
// if(_node == _node->_parent->_left) {
// _node = _node->_parent;
// }
// else {
// while (_node->_parent != nullptr && _node == _node->_parent->_right) {
// _node = _node->_parent;
// }
// _node = _node->_parent;
// }
// }
// return *this;
//}
//
//Self& operator--()
//{
// // 左子树,根,右子树。
// if(_node->_left != nullptr) {
// // 此时,根完了,有左子树,就去找左子树中最大的那个。
// _node = _node->_left;
// while(_node->_right != nullptr) {
// _node = _node->_right;
// }
// }
// else {
// // 左不为空,也就是可以理解为这颗子树结束了。
// // 看他是不是父节点的右,如果是,就恰好上去,不是就再去找父节点的父节点。
// if(_node == _node->_parent->_right) {
// _node = _node->_parent;
// }
// else {
// while(_node->_parent != nullptr && _node == _node->_parent->_left) {
// _node = _node->_parent;
// }
// }
// }
//}
}
#endif //STL_RBTREE_H
1. map set和红黑树的封装关系
下面探究的是,如何使用同一个类模板:RBTree< class K, class T, class KeyOfT> 来封装出map<K, V>,set<K>。它们之间的模板参数的对应关系是怎样的。
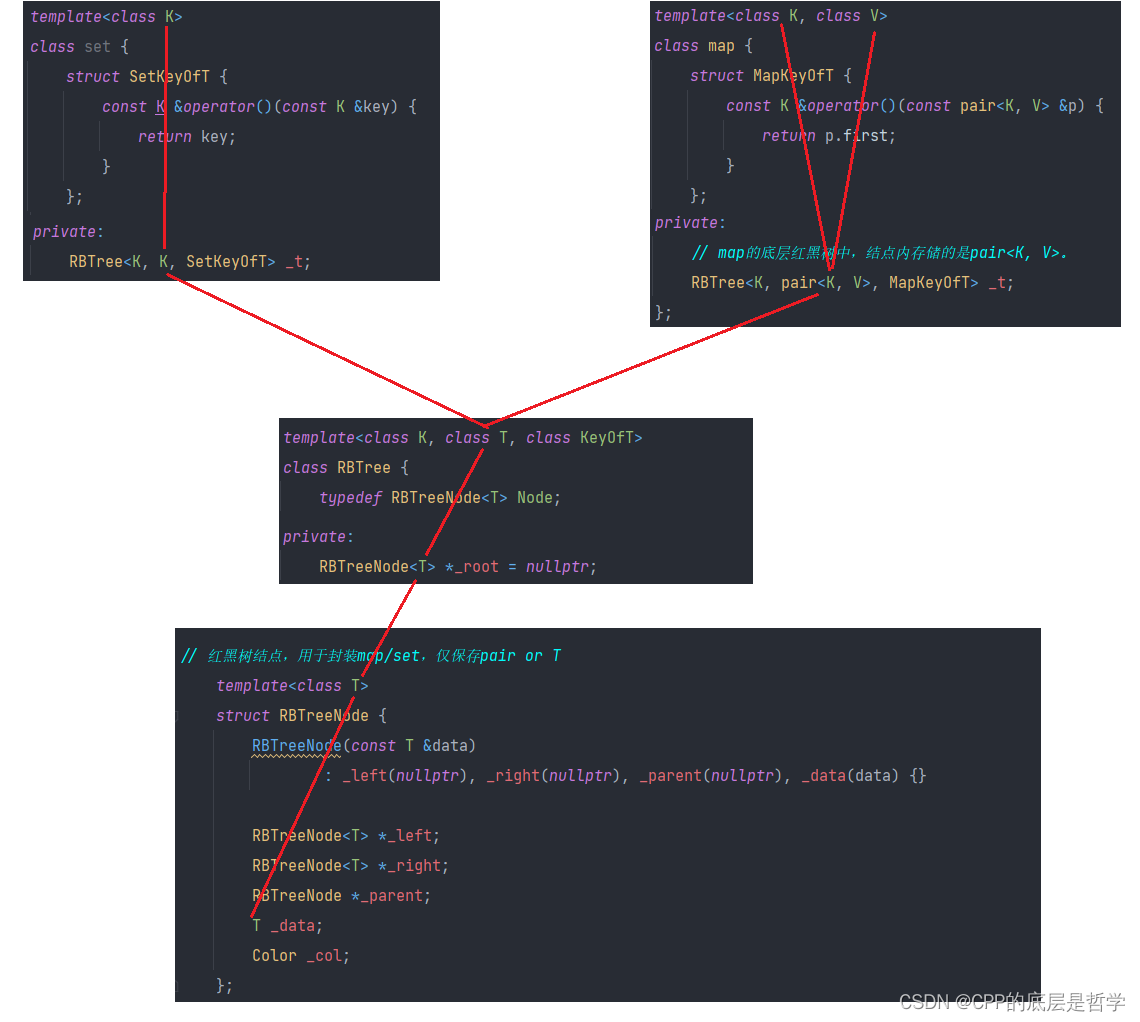
1. map是一个K V的类模板,set是一个K的类模板,这是肯定的。
2. 可以看到,红黑树的结点中,只有一个模板参数:T。故,事实上,map的红黑树结点中,存储的是pair<K,V>,而set的红黑树节点中,存储的是K。作为红黑树,它也不知道自己是KV模型,还是K模型。
3. RBTree有三个模板参数,暂且不讨论第三个。RBTree将第二个模板参数,作为传递给结点的模板参数,也就是pair<K,V> or K。对应了map和set中,定义RBTree数据成员时,传递的第二个类模板实参。
4. RBTree的第一个模板参数,存储的是map和set中的K,即关键字,这个类模板参数在很多地方都用不上,在find实现中需要使用(可能还有其他地方),因为find在map和set中,是通过关键字Key(K)来进行搜索的(返回迭代器),若只有第二个模板参数:pair<K,V> or K,则在map对应的RBTree中,无法实现find,因为无法得到关键字类型。(看find实现)
5. 在RBTree中,在insert等很多地方,需要比较结点中关键字的大小,而节点中的_data(T类型),可能是pair<K,V>,可能是K。无法直接通过_data(T)进行比较。故,RBTree的第三个模板参数是一个类,起仿函数的作用,用于提取红黑树结点中T中的关键字Key(K),对应map和set中的两个内部类。
2. map set成员函数实现:
这里并没有实现完全,map主流的有insert,operator[],find,empty,size,clear。而set中因为是K模型,故没有operator[]。
这些函数,除了map的operator[],函数实现全部在RBTree中,也就是红黑树实现了这些功能,map和set作为一个封装,只需要调用RBTree的对应成员函数即可。1. 只有在红黑树中才方便实现这些功能,因为根结点指针在RBTree中。2. 通过类模板,map和set没必要将类似的逻辑实现两份,而只在RBTree中实现一份也基于第三个仿函数模板参数。
1. insert:逻辑就是红黑树的插入逻辑。参数:value_type类型(pair or K),map中为pair,set中为key。而返回值是一个pair<iterator, bool>类型,pair.first返回对应结点的迭代器,而pair.second的bool类型,表明这个结点是已经存在的(false)还是新插入的(true)
2. map的operator[],有插入元素的作用。参数是一个key(K)类型,若关键字key对应元素已经存在,则返回对应value(V类型)。若不存在,则新插入一个pair<K, V>,这里的value使用V的默认构造结果。不过需要明白的是,map的operator[]主要作用是获取关键值key对应的value,当key不存在时插入是附加作用。
V& operator[] (const K& key) {
return this->insert(make_pair(key, V())).first->second;
}(上面相当于回顾std::map的insert和operator[]了)
3. map set的迭代器实现:
首先,明确容器迭代器需要哪些操作:无非就是 *解引用,==,!=,++,--。若迭代器所指容器元素中存储的是结构体,比如pair,则还有operator-> 。明确迭代器的行为类似于指针,故在map中迭代器解引用得到pair<K,V>,也就是底层红黑树结点中存储数据pair。而set中迭代器解引用就是得到key(K),也是底层红黑树中存储的数据。
回顾,vector,string。因为底层存储结构就是顺序存储,故它们的迭代器就是原生指针。改了个名字而已,因为原生指针完全支持迭代器的要求。
而list,因为底层存储不是连续存储,而是链式存储。故需要对结点指针进行封装:== != * ->就不说了。++变为next,--变为prev。
类似于list,对于map和set,底层数据结构为二叉树(平衡二叉搜索树),原生指针不满足迭代器的要求。故我们需要对结点指针进行封装。
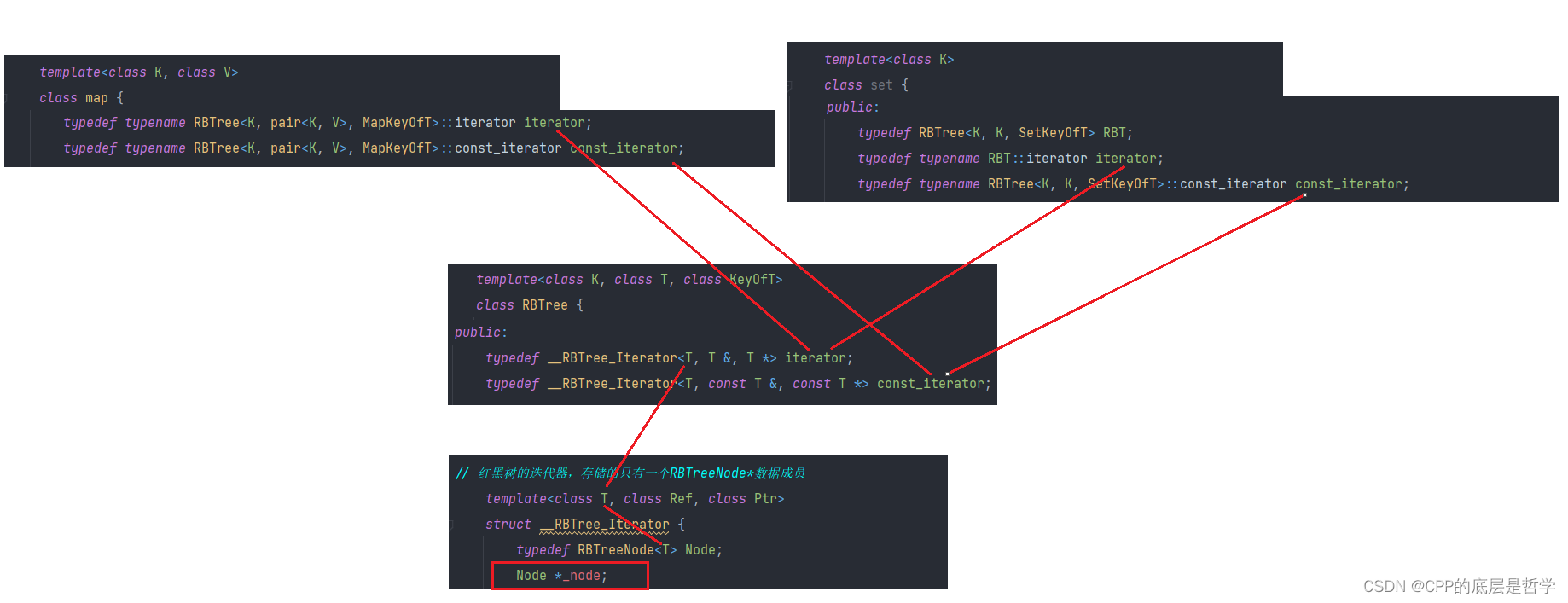
因为set和map仅仅是底层二叉树中结点存储的数据类型不同,故迭代器是可以只在底层RBTree中实现一份。
1. 迭代器中,只有一个结点指针数据成员。只需要一个value_type(T),而Ref Ptr用于定义operator* 和 operator->的返回值类型,用于区分iterator 和 const_iterator。(类似list的迭代器)
2. begin,end等函数的实现都在RBTree中,map和set只是调用对应的成员函数。
3. 有关实现逻辑:begin就是对红黑树左子叶结点指针进行包装,生成对应迭代器。也就是中序的第一个结点。而end,应该是中序最后一个结点的下一个。正确实现是:使用红黑树的另一种结构:根节点上方加一个头结点。而我这里的方法是:将end定义为iterator(nullptr),也能符合遍历逻辑,只是end--无法到中序最后一个结点。
4. 在__RBTree_Itrator中,++和--的逻辑值得注意,其实就是将指针变为中序的下一个结点或中序的上一个结点。且到达中序最后一个结点后,++根据逻辑会变为nullptr,对应end()的nullptr。(具体看代码)
5. 配合上适配器模式的反向迭代器,也可以实现map和set的反向迭代器,但是因为end的实现不完善,故可能无法适配。
4. map set的析构,拷贝构造,operator=的实现:
map和set只有一个RBTree实例化对象数据成员,而RBTree又是一个自定义类型,根据C++默认成员函数的规则,默认拷贝构造自动调用自定义类型数据成员的拷贝构造,析构,operator=同理
所以,只需要在RBTree中实现出拷贝构造,析构,operator=即可。 析构使用了destroy()成员函数,就是一个搜索树递归销毁逻辑。而拷贝构造和赋值用到了copy()成员函数,就是一个递归实现深拷贝搜索树的逻辑(注意结点中_parent指针的赋值)。
补:上方map set的实现中,对比STL少了比较仿函数类模板参数,对于那些不支持<运算符的类型,需要显式传递仿函数模板实参。比较简单,加一个模板参数,改一下某些地方即可
 封装红黑树实现C++ STL风格的map和set
封装红黑树实现C++ STL风格的map和set







 本文档详细展示了如何使用红黑树模板类RBTree封装C++ STL中的map和set,包括封装关系、成员函数、迭代器和析构/拷贝构造/赋值操作的实现。重点介绍了插入、查找和操作逻辑的红黑树核心算法。
本文档详细展示了如何使用红黑树模板类RBTree封装C++ STL中的map和set,包括封装关系、成员函数、迭代器和析构/拷贝构造/赋值操作的实现。重点介绍了插入、查找和操作逻辑的红黑树核心算法。
















 851
851

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








