So Easy!
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2350 Accepted Submission(s): 729
Problem Description
A sequence Sn is defined as:
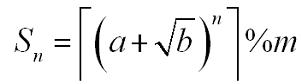
Where a, b, n, m are positive integers.┌x┐is the ceil of x. For example, ┌3.14┐=4. You are to calculate Sn.
You, a top coder, say: So easy!

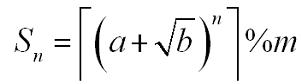
Where a, b, n, m are positive integers.┌x┐is the ceil of x. For example, ┌3.14┐=4. You are to calculate Sn.
You, a top coder, say: So easy!

Input
There are several test cases, each test case in one line contains four positive integers: a, b, n, m. Where 0< a, m < 215, (a-1)2< b < a2, 0 < b, n < 231.The input will finish with the
end of file.
Output
For each the case, output an integer Sn.
Sample Input
2 3 1 2013 2 3 2 2013 2 2 1 2013
Sample Output
4 14 4
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll a,b,n,m;
struct matrix {
ll f[2][2];
};
matrix mul(matrix A,matrix B){
matrix s;
memset(s.f,0,sizeof s.f);
ll i,j,k;
for(k=0;k<2;k++)
for(i=0;i<2;i++){
if(!A.f[i][k]) continue;
for(j=0;j<2;j++){
if(!B.f[k][j]) continue;
s.f[i][j]+=A.f[i][k]*B.f[k][j];
s.f[i][j]%=m;
}
}
return s;
}
matrix pow_mod(matrix A,ll k){
matrix s;
s.f[0][0]=s.f[1][1]=1;
s.f[0][1]=s.f[1][0]=0;
while(k){
if(k&1) s=mul(s,A);
A=mul(A,A);
k>>=1;
}
return s;
}
int main(){
while(cin>>a>>b>>n>>m){
matrix e;
ll p=2*a;
ll q=b-a*a;
e.f[0][0]=p;e.f[0][1]=1;
e.f[1][0]=q;e.f[1][1]=0;
e=pow_mod(e,n-1);
ll ans=((p*e.f[0][0]+2*e.f[1][0])%m+m)%m;
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}








 本文提供了一种高效的方法来解决特定序列计算问题,通过利用矩阵乘法和模运算简化了计算过程,使得原本复杂的计算变得简单易懂。
本文提供了一种高效的方法来解决特定序列计算问题,通过利用矩阵乘法和模运算简化了计算过程,使得原本复杂的计算变得简单易懂。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








