Spring boot
过完年的时候,跟Thoughtworks的coach一起给项目的所有Web Service加继承测试。一直缺少一个Provider,一开始都是用Moco。不过Moco都是利用配置提供契约接口,毕竟是假的数据。而Spring boot利用很少的代码,就可以根据需要提供一个非常好的Provider。简单来说,Spring boot用于快速开发一个web服务。
约定大于配置
Spring boot采用的思想跟Maven一样都是约定大于配置。比如Maven有以下约定:
maven的目录文件结构
src-main-java:项目源代码
src-main-test:测试代码
src/main/resources:项目资源文件
target:存放生成class文件和所需的jar包
pom.xml:项目的maven配置
类似的,Spring boot有以下约定:
1.Spring boot默认的配置文件是且必须是application.yml文件或者application.properties文件,且唯一。
2.spring boot默认只会去src/main/resources文件夹下去找application配置文件
项目搭建
利用Intellij,新建一个Spring Initializr 项目,以web为模板。菜单:File-->New-->Project...-->Spring Initializr,
然后选择:Default:http://start.spring.io
如果没有 Spring in选项,先安装spring boot插件(有些 Intellij 是spring assistant)。
结果如上图,打开pom.xml文件,发现依赖如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>kaka</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>kaka</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>查看项目的依赖树:mvn dependency:tree
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:jar:2.0.3.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- org.hibernate.validator:hibernate-validator:jar:6.0.10.Final:compile
[INFO] | | +- org.jboss.logging:jboss-logging:jar:3.3.2.Final:compile
[INFO] | | \- com.fasterxml:classmate:jar:1.3.4:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework:spring-webmvc:jar:5.0.7.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-context:jar:5.0.7.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework:spring-expression:jar:5.0.7.RELEASE:compile也就是说,spring-boot-starter-web已经为我们引入了spring webmvc等。至此项目已经搭建完成。
应用入口
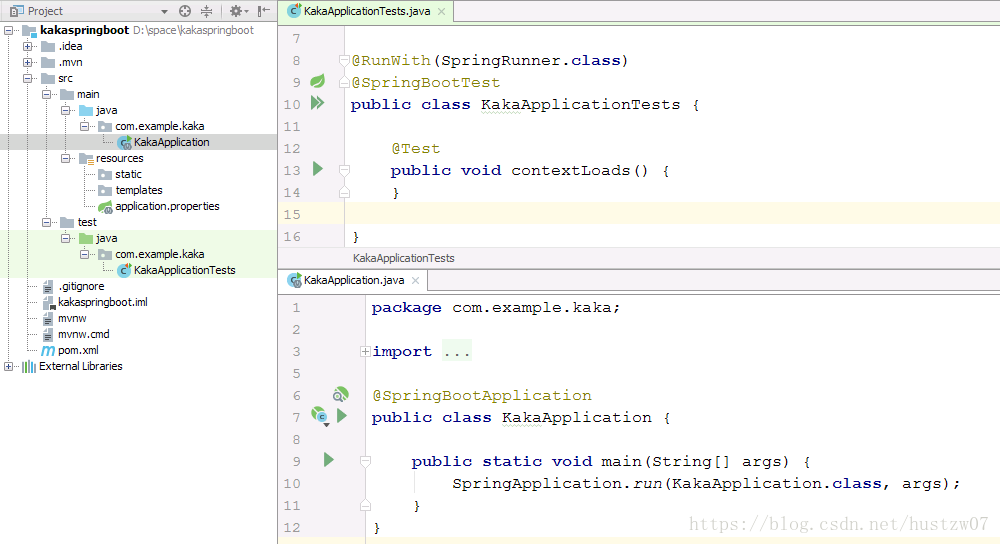
Spring Boot项目默认有有一个名为*Application的入口类,同时加上@SpringBootApplication注解。该类里有一个main方法,其实就是Java的main方法。
注意:Spring boot会自动扫描 @SpringBootApplication 所在类的同级包以及下一级包里的 Bean类。因此,该入口类就位于grounpID/arctifactID路径下。如上图的com.example.kaka.KakaApplication.java。点开@SpringBootApplication源码:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
String[] excludeName() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackages"
)
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackageClasses"
)
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
}发现它是多个注解的组合,可以理解为:@SpringBootApplication = @Configuration + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @ComponentScan
在同级目录下新建一个Controller。
package com.example.kaka;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class KakaController {
@RequestMapping("/kaka")
public String hello() {
return "Hello Kaka!";
}
}这里,注解@RestController:该注解相当于@Controller 和 @ResponseBody 注解
在KakaApplication.java运行程序即可启动。启动后,可以从控制台看到一些输出,其中有一句:
[ restartedMain] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
也就是说,Spring boot已经内置了 Tomcat,启动的时候默认 8080端口。因此,打开http://localhost:8080/kaka即可看到响应。
配置文件
Spring Boot使用一个全局的配置文件 application.properties 或 application.yml。注意这里不是 xml,貌似是因为要支持 yaml语言。
上边的项目中,用的是application.properties。
热部署
平常项目在开发时,为了热部署,都是采用Ant、JRebel等。Spring boot提供了devtools,直接通过JVM类加载,实现热部署。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional> <!-- 这个需要为 true 热部署才有效 -->
</dependency>在实际使用中,热部署可能不生效。可以按以下步骤解决。
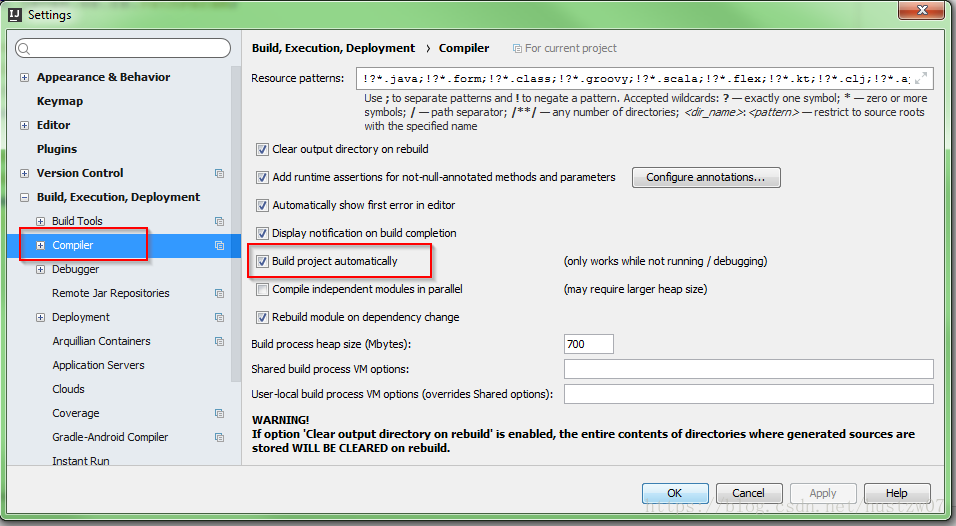
首先,设置勾选“Build project automatically”
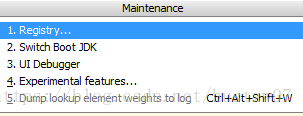
然后 Shift+Ctrl+Alt+/,选择Registry
最后,勾选以下选项即可。
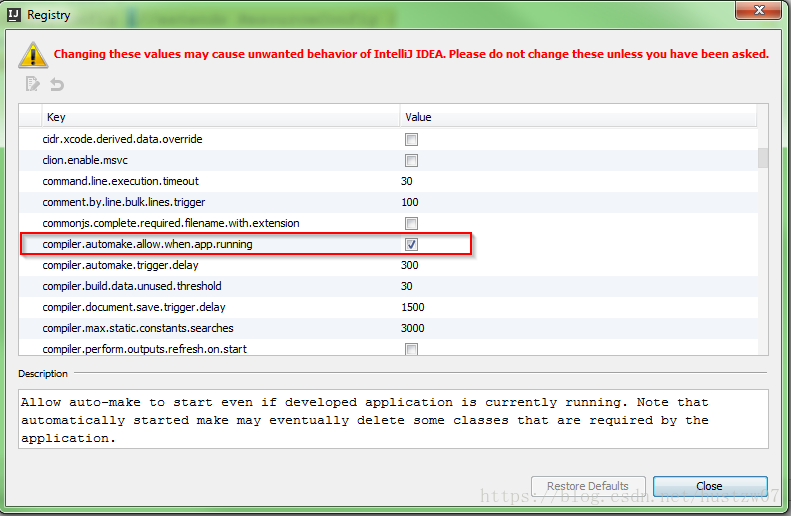
此时修改项目代码,IntelliJ会自动打包部署了。
Jersey
Web项目开发时,多数要提供Restful。Spring boot提供了Jersey的集成。只需添加以下依赖即可,同样不用指定version,它传递依赖Jersey。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jersey</artifactId>
</dependency>引入Jersey后,我们新建一个提供Restful的类
package com.example.kaka.jersey;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.inject.Singleton;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
@Component
@Singleton
@Path("/resource")
public class MyResource {
@Path("kaka/{name}")
@GET
public String hello(@PathParam("name") String name) {
return "Hello" + name;
}
}此时,在浏览器里面输入链接 http://localhost:8080/resource/kaka/zw,是访问不到Restful的。因为我们还没有对该Resource进行注册。
注册方式一
新建一个类,这里要保证该类能被Application类扫描到。
package com.example.kaka.jersey;
import org.glassfish.jersey.server.ResourceConfig;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.ws.rs.ApplicationPath;
@Component
@ApplicationPath("rest")
public class JerseyConfig extends ResourceConfig {
public JerseyConfig() {
register(MyResource.class);
}
}此时,输入新的链接即可访问,http://localhost:8080/rest/resource/kaka/zw
注意,这里使用@ApplicationPath("rest") 设置了应用的访问根路径。
注册方式二
另外,Spring boot的autoconfigure包下面还提供了一个Jersey注册的接口ResourceConfigCustomizer。
删掉上边的类,然后实现该接口:
package com.example.kaka.jersey;
import org.glassfish.jersey.server.ResourceConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.ResourceConfigCustomizer;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyResourceConfigCustomizer implements ResourceConfigCustomizer {
@Override
public void customize(ResourceConfig config) {
config.register(MyResource.class);
}
}实现了该接口的方法时,发现它依赖注入了ResourceConfig的实例,因此,需要给程序创建一个Bean
@SpringBootApplication
public class KakaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KakaApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ResourceConfig resourceConfig() {
return new ResourceConfig();
}
}此时为了做到跟上边一样的效果,即根路径是/rest,需要在 application.properties 文件中,添加下面一句话。
spring.jersey.application-path=rest注册方式三
改方式跟方式二类似,只不过是自己new ResourceConfig()。
在KakaApplication.java 中代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class KakaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KakaApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ResourceConfig resourceConfig() {
ResourceConfig config = new ResourceConfig();// 新建一个ResourceConfig 而不是实现 ResourceConfigCustomizer 接口
config.register(MyResource.class);
return config;
}
}该方式同样要保留 application.properties 里面的配置。其实该配置之所以生效,因为spring-jersey的以下代码:
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.jersey"
)
public class JerseyProperties {
private JerseyProperties.Type type;
private Map<String, String> init;
private final JerseyProperties.Filter filter;
private final JerseyProperties.Servlet servlet;
private String applicationPath;
public JerseyProperties() {
this.type = JerseyProperties.Type.SERVLET;
this.init = new HashMap();
this.filter = new JerseyProperties.Filter();
this.servlet = new JerseyProperties.Servlet();
}
// 省略其他代码
}即,使用spring.jersey 开头的配置。
多环境切换
springboot 提供多环境配置的机制,让开发者根据需要切换到不同的配置环境。在目录src\main\resources 下创建三个文件:
application-dev.properties
application-pp.properties
application-prd.properties
然后在 application.properties 中 如下设置即可:
spring.profiles.active=devspring-boot 根据该值,自动加载不同环境的配置
logback
spring boot官方推荐使用logback 配置日志,默认会加载 classpath:logback-spring.xml 或者 classpath:logback-spring.groovy。
在src/main/resource 文件夹下新建logback-spring.xml:
<configuration>
<!-- 文件输出格式 -->
<property name="PATTERN" value="%-12(%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS}) |-%-5level [%thread] %c [%L] -| %msg%n"/>
<!-- pp 文件路径 -->
<property name="PP_FILE_PATH" value="d:/pp.log"/>
<!-- prd 文件路径 -->
<property name="PRD_FILE_PATH" value="/opt/logs"/>
<!-- local -->
<springProfile name="dev">
<appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>${PATTERN}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<logger name="com.light.springboot" level="debug"/>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE"/>
</root>
</springProfile>
<!-- pp -->
<springProfile name="pp">
<!-- 每天产生一个文件 -->
<appender name="PP-FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<!-- 文件路径 -->
<file>${PP_FILE_PATH}</file>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!-- 文件名称 -->
<fileNamePattern>${PP_FILE_PATH}/info.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern>
<!-- 文件最大保存历史数量 -->
<MaxHistory>100</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<pattern>${PATTERN}</pattern>
</layout>
</appender>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="PP-FILE"/>
</root>
</springProfile>
<!-- prd -->
<springProfile name="prd">
<appender name="PRD_FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${PRD_FILE_PATH}</file>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${PRD_FILE_PATH}/warn.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern>
<MaxHistory>100</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<pattern>${PATTERN}</pattern>
</layout>
</appender>
<root level="warn">
<appender-ref ref="PRD_FILE"/>
</root>
</springProfile>
</configuration>注意:<springProfile>的name 属性是application.properties 中的 spring.profiles.active 的值。
JPA
Spring boot 可以很容易添加JPA资源,支持POJO(Plain Ordinary Java Object)。项目中添加以下依赖(这里我用的是MySQL)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>上边的库自带很多POJO用到的类。
新建三个实体:
部门:Deparment
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "deparment")
public class Deparment {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
public Deparment() {
}
// 省略 setter/getter
}
角色:Role
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Entity
@Table(name = "role")
public class Role implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
public Role() {
}
// 省略 setter/getter
}
用户:User
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonBackReference;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
public class User implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
private Date createDate;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "did")
@JsonBackReference
private Deparment deparment;
@ManyToMany(cascade = {}, fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinTable(name = "user_role", joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "user_id")}, inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "roles_id")})
private List<Role> roles;
public User() {
}
// 省略 setter/getter
}然后为每个entity创建一个repository接口,其中一个如下:
@Repository
public interface DeparmentRepository extends JpaRepository<Deparment, Long> {
}另外两个类似
在 resources/appplication.yml 中配置我们的数据库连接:
spring:
application:
name: my-service
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/world?characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: Password1
jpa:
database: MYSQL
show-sql: true
#Hibernate ddl auto (validate|create|create-drop|update)
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
naming-strategy: org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
properties:
hibernate:
dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect此时,添加测试即可。
import com.example.cloudclient.entity.Deparment;
import com.example.cloudclient.entity.Role;
import com.example.cloudclient.entity.User;
import com.example.cloudclient.repository.DeparmentRepository;
import com.example.cloudclient.repository.RoleRepository;
import com.example.cloudclient.repository.UserRepository;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.notNullValue;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertThat;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@ComponentScan
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class CloudclientApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
}
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CloudclientApplicationTests.class);
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
DeparmentRepository deparmentRepository;
@Autowired
RoleRepository roleRepository;
@Before
public void initData() {
userRepository.deleteAll();
roleRepository.deleteAll();
deparmentRepository.deleteAll();
Deparment deparment = new Deparment();
deparment.setName("development");
deparmentRepository.save(deparment);
assertThat(deparment.getId(), is(notNullValue()));
User user = new User();
user.setName("user");
user.setCreateDate(new Date());
user.setDeparment(deparment);
Role role = new Role();
role.setName("kaka");
roleRepository.save(role);
List<Role> roles = roleRepository.findAll();
assertThat(roles, is(notNullValue()));
user.setRoles(roles);
userRepository.save(user);
assertThat(user.getId(), is(notNullValue()));
}
@Test
public void findPage() {
Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(0, 10, new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "id"));
Page<User> page = userRepository.findAll(pageable);
assertThat(page, is(notNullValue()));
for (User user : page.getContent()) {
logger.info("=========user======== user name:{}, deparment name:{}, role name:{}", user.getName(), user.getDeparment().getName(), user.getRoles().get(0).getName());
}
}
}
AngularJS
一个Web项目也需要前台的集成,这里我使用AngularJS。








 本文是Spring Boot的入门教程,涵盖了约定大于配置的概念、项目搭建、应用入口、配置文件、热部署、Jersey RESTful API的实现以及多环境切换等核心内容。Spring Boot简化了Web服务的开发,提供内置的Tomcat服务器,支持通过devtools实现热部署,并能方便地与AngularJS进行前端集成。
本文是Spring Boot的入门教程,涵盖了约定大于配置的概念、项目搭建、应用入口、配置文件、热部署、Jersey RESTful API的实现以及多环境切换等核心内容。Spring Boot简化了Web服务的开发,提供内置的Tomcat服务器,支持通过devtools实现热部署,并能方便地与AngularJS进行前端集成。
















 1792
1792

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








