rpn层的作用
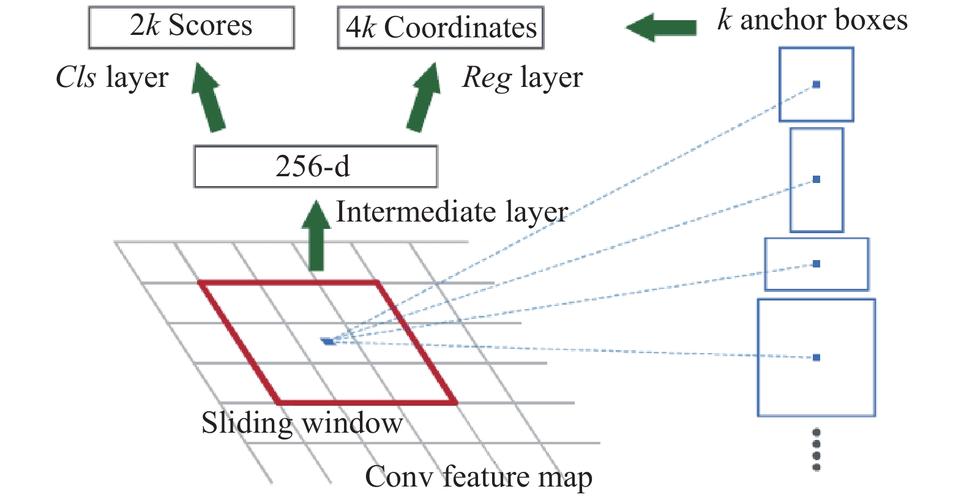
首先对特征图进行3*3的卷积得到256个通道的特征图,然后将得到的新的特征图进行1*1的卷积,分别给cls分类层以及reg回归层。
分类层目的是对特征框进行打分分类,区分哪些是背景,哪些是要识别的物体;
回归层目的是精确特征框中心点位置以及长宽的比例;
这里面的k是指锚点的数量,即特征点的数量。
# Shared convolutional base of the RPN
shared = KL.Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu',
strides=anchor_stride,
name='rpn_conv_shared')(feature_map)
#每个特征图来了都要进行一次3*3的卷积,所以称为共享
# Anchor Score. [batch, height, width, anchors per location * 2].
x = KL.Conv2D(2 * anchors_per_location, (1, 1), padding='valid',
activation='linear', name='rpn_class_raw')(shared)
#得分值,2*3得到6个结果值,2代表有一个前景和背景,3代表每个特征图的锚点有三个不同比例的特征框
# Reshape to [batch, anchors, 2]
rpn_class_logits = KL.Lambda(
lambda t: tf.reshape(t, [tf.shape(t)[0], -1, 2]))(x)
# Softmax on last dimension of BG/FG.
rpn_probs = KL.Activation(
"softmax", name="rpn_class_xxx")(rpn_class_logits)
# Bounding box refinement. [batch, H, W, anchors per location, depth]
# where depth is [x, y, log(w), log(h)]
x = KL.Conv2D(anchors_per_location * 4, (1, 1), padding="valid",
activation='linear', name='rpn_bbox_pred')(shared) #4个回归值
#回归值,3*4个结果值,3个候选框每一个都要得到4个回归值
# Reshape to [batch, anchors, 4]
rpn_bbox = KL.Lambda(lambda t: tf.reshape(t, [tf.shape(t)[0], -1, 4]))(x)
return [rpn_class_logits, rpn_probs, rpn_bbox]






 RPN层通过3*3卷积获取特征图,然后使用1*1卷积进行分类和回归操作。分类层负责判断锚点是背景还是目标物体,回归层则确定特征框的精确位置和比例。每个特征点对应多个锚点(k个),最终得到分类得分和边界框回归值。
RPN层通过3*3卷积获取特征图,然后使用1*1卷积进行分类和回归操作。分类层负责判断锚点是背景还是目标物体,回归层则确定特征框的精确位置和比例。每个特征点对应多个锚点(k个),最终得到分类得分和边界框回归值。
















 189
189

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








