预备知识
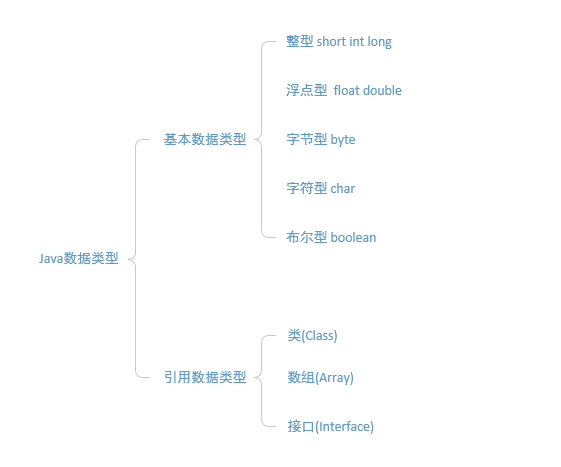
基本数据类型:基本数据类型指的是在栈(Stack)中直接分配内存的数据类型。在Java中基本数据类型有5类8种,分别是:
- 整型:short int long
- 浮点型:float double
- 字节型:byte
- 字符型:char
- 布尔型:boolean
对于上述这5类基本数据类型在方法调用作为参数被传递的时候,仅仅传递这个参数的值,被称之为值传递。
引用数据类型:引用数据类型指的是变量名(引用)存放在栈中,而变量实际的内容存放在堆(heap)中的一类数据类型。在Java中除了上述8种基本数据类型,其余的都是引用数据类型。引用数据类型可被分为3类:
- 类(Class)
- 数组(Array)
- 接口(Interface)
对于这3类数据类型在方法调用的时候传递的是该变量的引用副本,即引用传递。而其存放在堆中的实际内容不传递。
Java中的参数传递
下面用一段简单的Java程序以及运行结果来分析Java对于上述两类数据类型在作为方法调用参数时的传递过程。
Code:
class temp
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int num;
String str;
int[] array1= {1,2};
int[] array2= {1,2};
num = 8;
System.out.println("before call the function, num =" + String.valueOf(num));
testBasicDataType(num);
System.out.println("after call the function, num = " + String.valueOf(num));
System.out.println("before call the function, array = " + Arrays.toString(array1));
testQuoteDataTypeOfArray1(array1);
System.out.println("after call the function, array = " + Arrays.toString(array1));
System.out.println("before call the function, array = " + Arrays.toString(array2));
testQuoteDataTypeOfArray2(array2);
System.out.println("after call the function, array = " + Arrays.toString(array2));
str = "me";
System.out.println("before call the function, str =" + str);
testQuoteDataTypeOfString1(str);
System.out.println("after call the function, str = " + str);
str = "me";
System.out.println("before call the function, str =" + str);
testQuoteDataTypeOfString2(str);
System.out.println("after call the function, str = " + str);
}
public static void testBasicDataType(int num)
{
num=2;
System.out.println("In the function, num = " + String.valueOf(num));
}
public static void testQuoteDataTypeOfArray1(int[] array)
{
array[0]=3;
System.out.println("In the function, array = " + Arrays.toString(array));
}
public static void testQuoteDataTypeOfArray2(int[] array)
{
int[] array1 = new int[]{3,2};
array = array1;
System.out.println("In the function, array = " + Arrays.toString(array));
}
public static void testQuoteDataTypeOfString1(String s)
{
s = "you";
System.out.println("In the function, str = " + s);
}
public static void testQuoteDataTypeOfString2(String s)
{
String s1 = new String("you");
s = s1;
System.out.println("In the function, str = " + s);
}
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
运行结果:
- before call the function, num =8
In the function, num = 2
after call the function, num = 8- before call the function, array = [1, 2]
In the function, array = [3, 2]
after call the function, array = [3, 2]
before call the function, array = [1, 2]
In the function, array = [3, 2]
after call the function, array = [1, 2]- before call the function, str =me
In the function, str = you
after call the function, str = me
before call the function, str =me
In the function, str = you
after call the function, str = me
结果分析:
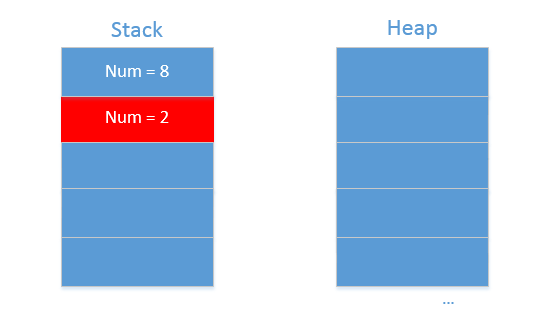
- 对于基础数据类型int,传递方式为最简单的值传递。只将变量num复制一份,无论在函数内部怎么修改这个变量的值,函数外部变量num的值保持不变。堆和栈的状态如下图:
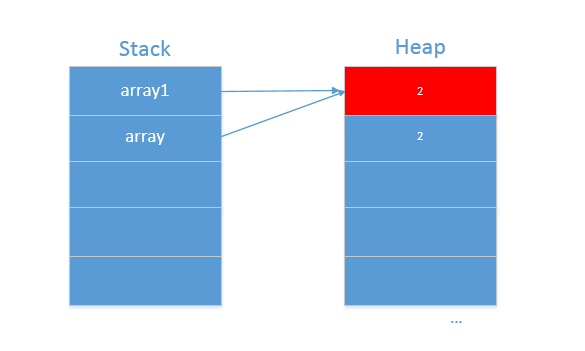
- 对于引用数据类型int[],传递方式为引用传递。将数组array1的一个引用传递到函数内部,在函数内部修改这个数组array1的值,函数外部的数组array1也会跟着一起修改,这和C语言中的指针非常相似。下面是在函数内部时的堆和栈的状态:
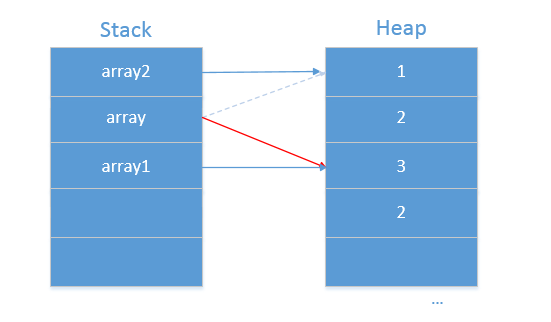
- 到这里总算明白了值传递和引用传递的区别,但这里字符串str是引用数据类型,传递的是字符串str的引用,而在函数中将其值修改为you,为什么str的值仍然是me?在这里还要说一个概念叫不可变对象(Immutable Objects)。不可变对象指的是初始化之后无论对该对象做出任何修改都将重新生成一个新的对象。在这里对字符串str的引用副本s执行赋值操作会重新生成一个新的对象,之后再将s指向这个新的对象,从而原来的字符串str根本没有修改。对不可变对象的赋值操作相当于执行new操作重新生成一个对象。下面是传递过程堆和栈的状态:
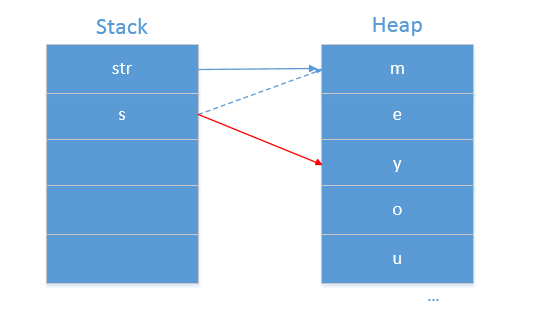
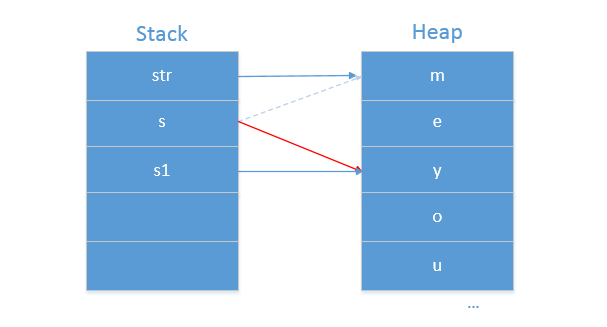
总结
方法调用的参数传递的实质都是传递栈中变量的一个副本,区别在于两种类型在栈中存放的形式不同。
相同点:
- 两种数据类型作为方法调用的参数时,传递的都是栈中内容的副本。
不同点:
- 对于基本数据类型,由于其在栈中存放的是该类型变量的值,所以作为方法参数传递的时候将其值传递到方法内部。
- 对于引用数据类型,由于其在栈中只存放该类型变量的引用(变量地址),所作为方法参数传递的时候将其引用传递给方法内部。





 本文深入探讨了Java中基本数据类型和引用数据类型的参数传递机制,通过实例解释了值传递和引用传递的区别,并介绍了不可变对象的概念。
本文深入探讨了Java中基本数据类型和引用数据类型的参数传递机制,通过实例解释了值传递和引用传递的区别,并介绍了不可变对象的概念。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








