Tinyhttpd是十大开源必读项目之一,通过不到600行的代码,即可剖析一个超轻量级http Web Server的本质,实践计算机网络,Unix网络编程和http的相关知识。
我把httpd.c在Ubuntu 14.04上重新实现了一遍,并添加了中文注释,希望对其有着更深入的了解。
流程图如下:
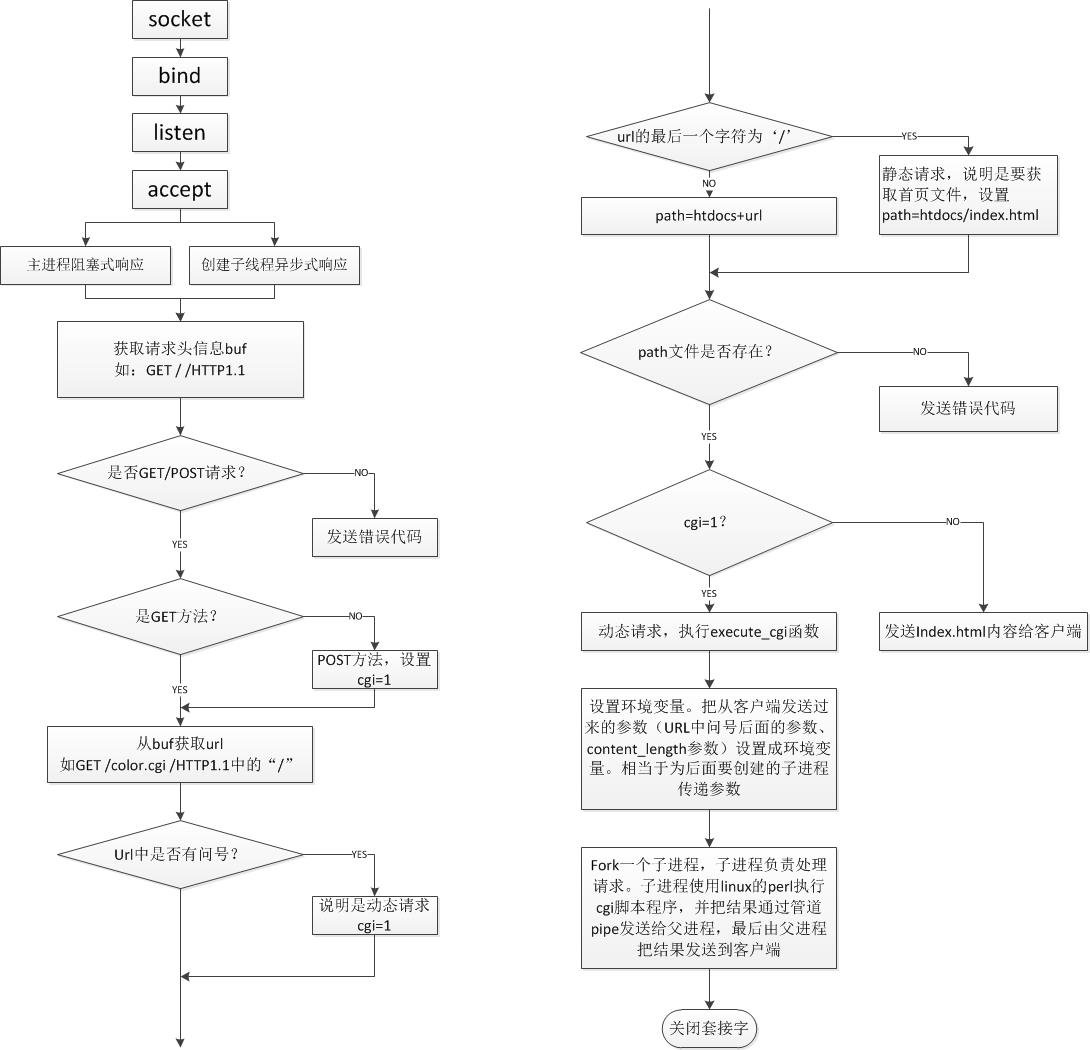
建议源码阅读顺序: main -> startup -> accept_request -> execute_cgi
每个函数的作用:
accept_request: 处理从套接字上监听到的一个 HTTP 请求,在这里可以很大一部分地体现服务器处理请求流程。
bad_request: 返回给客户端这是个错误请求,HTTP 状态吗 400 BAD REQUEST.
cat: 读取服务器上某个文件写到 socket 套接字。
cannot_execute: 主要处理发生在执行 cgi 程序时出现的错误。
error_die: 把错误信息写到 perror 并退出。
execute_cgi: 运行 cgi 程序的处理,也是个主要函数。
get_line: 读取套接字的一行,把回车换行等情况都统一为换行符结束。
headers: 把 HTTP 响应的头部写到套接字。
not_found: 主要处理找不到请求的文件时的情况。
sever_file: 调用 cat 把服务器文件返回给浏览器。
startup: 初始化 httpd 服务,包括建立套接字,绑定端口,进行监听等。
unimplemented: 返回给浏览器表明收到的 HTTP 请求所用的 method 不被支持。
工作流程
(1) 服务器启动,在指定端口或随机选取端口绑定 httpd 服务。
(2)收到一个 HTTP 请求时(其实就是 listen 的端口 accpet 的时候),派生一个线程运行 accept_request 函数。
(3)取出 HTTP 请求中的 method (GET 或 POST) 和 url,。对于 GET 方法,如果有携带参数,则 query_string 指针指向 url 中 ? 后面的 GET 参数。
(4) 格式化 url 到 path 数组,表示浏览器请求的服务器文件路径,在 tinyhttpd 中服务器文件是在 htdocs 文件夹下。当 url 以 / 结尾,或 url 是个目录,则默认在 path 中加上 index.html,表示访问主页。
(5)如果文件路径合法,对于无参数的 GET 请求,直接输出服务器文件到浏览器,即用 HTTP 格式写到套接字上,跳到(10)。其他情况(带参数 GET,POST 方式,url 为可执行文件),则调用 excute_cgi 函数执行 cgi 脚本。
(6)读取整个 HTTP 请求并丢弃,如果是 POST 则找出 Content-Length. 把 HTTP 200 状态码写到套接字。
(7) 建立两个管道,cgi_input 和 cgi_output, 并 fork 一个进程。
(8) 在子进程中,把 STDOUT 重定向到 cgi_outputt 的写入端,把 STDIN 重定向到 cgi_input 的读取端,关闭 cgi_input 的写入端 和 cgi_output 的读取端,设置 request_method 的环境变量,GET 的话设置 query_string 的环境变量,POST 的话设置 content_length 的环境变量,这些环境变量都是为了给 cgi 脚本调用,接着用 execl 运行 cgi 程序。
(9) 在父进程中,关闭 cgi_input 的读取端 和 cgi_output 的写入端,如果 POST 的话,把 POST 数据写入 cgi_input,已被重定向到 STDIN,读取 cgi_output 的管道输出到客户端,该管道输入是 STDOUT。接着关闭所有管道,等待子进程结束。这一部分比较乱,见下图说明:

图 1 管道初始状态

图 2 管道最终状态
(10) 关闭与浏览器的连接,完成了一次 HTTP 请求与回应,因为 HTTP 是无连接的。
git地址:点击打开链接
- /*
- * httpd.c
- *
- * Created on: Apr 2, 2016
- * Author: root
- */
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<sys/socket.h>
- #include<sys/types.h>
- #include<netinet/in.h>
- #include<arpa/inet.h>
- #include<unistd.h>
- #include<ctype.h>
- #include<strings.h>
- #include<string.h>
- #include<sys/stat.h>
- #include<pthread.h>
- #include<sys/wait.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- #define ISspace(x) isspace((int)(x))//若x为空格字符,返回true
- #define SERVER_STRING "Server: jdbhttpd/0.1.0\r\n"
- void * accept_request(void *);//处理从套接字上监听到的一个 HTTP 请求,在这里可以很大一部分地体现服务器处理请求流程
- void bad_request(int);//返回给客户端这是个错误请求,HTTP 状态码 400 BAD REQUEST
- void cat(int,FILE *);// 读取服务器上某个文件写到 socket 套接字
- void cannot_execute(int);//主要处理发生在执行 cgi 程序时出现的错误
- void error_die(const char *);//把错误信息写到 perror 并退出
- void execute_cgi(int,const char *,const char *,const char *);//运行 cgi 程序的处理,也是个主要函数
- int get_line(int,char *,int);//读取套接字的一行,把回车换行等情况都统一为换行符结束
- void headers(int,const char *);//把 HTTP 响应的头部写到套接字
- void not_found(int);//主要处理找不到请求的文件时的情况
- void serve_file(int,const char *);//调用 cat 把服务器文件返回给浏览器
- int startup(u_short *);//初始化 httpd 服务,包括建立套接字,绑定端口,进行监听等
- void unimplemented(int);//返回给浏览器表明收到的 HTTP 请求所用的 method 不被支持
- /* HTTP协议规定,请求从客户端发出,最后服务器端响应该请求并返回。
- * 这是目前HTTP协议的规定,服务器不支持主动响应,所以目前的HTTP
- * 协议版本都是基于客户端请求,然后响应的这种模型。 */
- /*accept_request函数解析客户端请求,判断是请求静态文件还是cgi代码
- (通过请求类型以及参数来判定),如果是静态文件则将文件输出给前端,
- 如果是cgi则进入cgi处理函数*/
- void * accept_request(void *tclient)
- {
- int client=*(int *)tclient;
- char buf[1024];
- int numchars;
- char method[255];//请求方法GET or POST
- char url[255];//请求的文件路径
- char path[512];////文件相对路径
- size_t i,j;
- struct stat st;
- int cgi=0; //如果服务端决定这是个CGI程序,cgi为true
- char *query_string=NULL;
- numchars=get_line(client,buf,sizeof(buf));//从client中读取指定大小数据到buf
- i=0;
- j=0;
- //解析客户端的http请求报文
- /*接收字符处理:提取空格字符前的字符,至多254个*/
- while(!ISspace(buf[j])&&(i<sizeof(method)-1))
- {
- method[i]=buf[j];
- i++;
- j++;
- }
- method[i]='\0';
- //忽略大小写比较字符串,如果请求的方法不是 GET 或 POST 任意一个的话就直接发送 response 告诉客户端没实现该方法
- if(strcasecmp(method,"GET")&&strcasecmp(method,"POST"))
- {
- unimplemented(client);
- return NULL;
- }
- ////如果是 POST 方法就将 cgi 标志变量置一(true)
- if(strcasecmp(method,"POST")==0)//POST 类型
- cgi=1;
- i=0;
- while(ISspace(buf[j])&&(j<sizeof(buf)))//过滤空格字符,空格后面是URL
- j++;
- /*将buf中的非空格字符转存进url缓冲区,遇空格字符或满退出*/
- while(!ISspace(buf[j])&&(i<sizeof(url)-1)&&(j<sizeof(buf)))
- {
- url[i]=buf[j];
- i++;
- j++;
- }
- url[i]='\0';
- if(strcasecmp(method,"GET")==0)//GET类型
- {
- //用一个指针指向 url
- query_string=url;//请求信息
- while((*query_string!='?')&&(*query_string!='\0'))//截取'?'前的字符,如果遍历完毕也没找到字符'?'则退出循环
- query_string++;
- if(*query_string=='?')
- {
- //如果是 ? 的话,证明这个请求需要调用 cgi,将 cgi 标志变量置一(true)
- cgi=1;
- //从字符 ? 处把字符串 url 给分隔会两份
- *query_string = '\0';
- //使指针指向字符 ?后面的那个字符
- query_string++;
- }
- }
- //将前面分隔两份的前面那份字符串,拼接在字符串htdocs的后面之后就输出存储到数组 path 中。相当于现在 path 中存储着一个字符串
- sprintf(path, "htdocs%s", url);
- //如果 path 数组中的这个字符串的最后一个字符是以字符 / 结尾的话,就拼接上一个"index.html"的字符串。首页的意思
- if (path[strlen(path) - 1] == '/')
- strcat(path, "index.html");
- //根据路径找文件,并获取path文件信息保存到结构体st中
- if(stat(path,&st)==-1)
- {
- //如果不存在,那把这次 http 的请求后续的内容(head 和 body)全部读完并忽略
- while((numchars>0)&&strcmp("\n",buf))
- numchars=get_line(client,buf,sizeof(buf));//从客户端读取数据进buf
- //然后返回一个找不到文件的 response 给客户端
- not_found(client);
- }
- else//获取文件信息,执行成功
- {
- //文件存在,那去跟常量S_IFMT相与,相与之后的值可以用来判断该文件是什么类型的
- if((st.st_mode&S_IFMT)==S_IFDIR)
- //如果这个文件是个目录,那就需要再在 path 后面拼接一个"/index.html"的字符串
- strcat(path,"/index.html");
- if((st.st_mode&S_IXUSR)||(st.st_mode&S_IXGRP)||(st.st_mode&S_IXOTH))
- //如果这个文件是一个可执行文件,不论是属于用户/组/其他这三者类型的,就将 cgi 标志变量置一
- cgi=1;
- if(!cgi)//静态页面请求
- serve_file(client,path);//直接返回文件信息给客户端,静态页面返回
- else//动态页面请求
- execute_cgi(client,path,method,query_string);//执行cgi脚本
- }
- close(client);//关闭客户端套接字
- return NULL;
- }
- /*执行CGI脚本,execute_cgi函数负责将请求传递给cgi程序处理,服务器与cgi之间通过管道pipe
- * 通信,首先初始化两个管道,并创建子进程去执行cgi函数
- * 子进程执行cgi程序,获取cgi的标准输入输出通过管道传递给父进程,由父进程发送给客户端*/
- void execute_cgi(int client,const char *path,const char *method,const char *query_string)
- {
- char buf[1024];
- int cgi_output[2];
- int cgi_input[2];
- pid_t pid;
- int status;
- int i;
- char c;
- int numchars=1;
- int content_length=-1;
- //往buf中填东西以保证能进入下面的while
- buf[0]='A';
- buf[1]='\0';
- if(strcasecmp(method,"GET")==0)//如果是GET方法,查询/获取资源信息
- while((numchars>0)&&strcmp("\n",buf))//读取并忽略请求剩下的内容
- numchars=get_line(client,buf,sizeof(buf));
- else//POST一般用于更新资源信息
- {
- numchars=get_line(client,buf,sizeof(buf));
- //获取HTTP消息实体的传输长度
- ////这个循环的目的是读出指示 body 长度大小的参数,并记录 body 的长度大小。其余的 header 里面的参数一律忽略
- // //注意这里只读完 header 的内容,body 的内容没有读
- while((numchars>0)&&strcmp("\n",buf))
- {
- buf[15]='\0';
- if(strcasecmp(buf,"Content-Length:")==0)//是否为Content-Length字段
- content_length=atoi(&(buf[16]));//Content-Length用于描述HTTP消息实体的传输长度
- numchars=get_line(client,buf,sizeof(buf));
- }
- if(content_length==-1)
- {
- bad_request(client);//请求的网页数据为空,没有数据
- return;
- }
- }
- sprintf(buf,"HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- //建立管道,两个管道cgi_output[0]:读取端,cgi_output[1]:写入端
- if(pipe(cgi_output)<0)
- {
- cannot_execute(client);//管道建立失败,打印出错信息
- return ;
- }//管道只能在具有公共祖先的进程间进行,这里是父子进程之间
- if(pipe(cgi_input)<0)
- {
- cannot_execute(client);
- return ;
- }
- //创建子进程
- if((pid=fork())<0)
- {
- cannot_execute(client);
- return ;
- }
- //子进程用来执行CGI脚本
- //实现进程间的管道通信机制
- //子进程继承了父进程的pipe,然后通过关闭子进程output管道的输出端,input管道的写入端;
- //关闭父进程output管道的写入断,input管道的输出端
- //子进程
- if(pid==0)
- {
- char meth_env[255];
- char query_env[255];
- char length_env[255];
- //复制文件句柄,重定向进程的标准输入输出
- //dup2的第一个参数描述符关闭
- dup2(cgi_output[1],1);//标准输出重定向到output管道的写入端
- dup2(cgi_input[0],0);//标准输入重定向到input管道的读取端
- close(cgi_output[0]);//关闭output的读取端
- close(cgi_input[1]);//关闭input的写入端
- //构造一个环境变量
- sprintf(meth_env,"REQUEST_METHOD=%s",method);
- //将这个环境变量加进子进程的运行环境中
- putenv(meth_env);
- //根据http请求的不同方法,构造并存储不同的环境变量
- if(strcasecmp(method,"GET")==0)
- {
- sprintf(query_env,"QUERY_STRING=%s",query_string);
- putenv(query_env);
- }
- else//POST
- {
- //设置content_length的环境变量
- sprintf(length_env,"CONTENT_LENGTH=%d",content_length);
- putenv(length_env);
- }
- //execl()包含于<unistd.h>中
- execl(path,path,NULL);//exec函数簇,执行CGI脚本,获取cgi的标准输出作为相应的内容发送给客户端
- //通过dup2重定向,标准输出内容进入管道output的输入端
- exit(0);//子进程退出
- } else /*父进程*/
- {
- //父进程关闭了cgi_output管道的写端和cgi_input管道的读端
- close(cgi_output[1]);
- close(cgi_input[0]);
- if(strcasecmp(method,"POST")==0)//如果是POST方法的话就继续读body的内容,并写到
- //cgi_input管道里让子进程去读
- /*接收POST过来的数据*/
- for(i=0;i<content_length;i++)
- {
- recv(client,&c,1,0);//从客户端接收单个字符
- write(cgi_input[1],&c,1);//写入input,然后重定向到了标准输入
- /*数据传输过程:input[1](父进程)-->input[0](子进程)[执行cgi函数]-->
- * STDIN-->STDOUT-->output[1](子进程)-->output[0](父进程)[将结果
- * 发送给客户端]*/
- }
- while(read(cgi_output[0],&c,1)>0)//读取output的管道输出到客户端,output输出端为cgi脚本执行后的内容
- send(client,&c,1,0);//将cgi执行的结果发送给客户端,即send到浏览器,如果不是POST则只有这一处理
- close(cgi_output[0]);//关闭剩下的管道端,子进程在执行dup2之后,就已经关闭了管道的一端通道
- close(cgi_input[1]);
- waitpid(pid,&status,0);//等待子进程终止
- }
- }
- /*从socket读取一行数据.以\r\n为行结束符
- * 参数:socket描述符
- * 保存数据的buffer
- * buffer的大小
- * 返回:存储的字节数(包括null)
- */
- int get_line(int sock,char *buf,int size)
- {
- int i=0;
- char c='\0';
- int n;
- //至多读取size-1个字符,最后一个字符置'\0'
- while((i<size-1)&&(c!='\n'))
- {
- n=recv(sock,&c,1,0);//读一个字符放到c中
- if(n>0)
- {
- if(c=='\r')//如果是回车符,继续读取
- {
- //使用MSG_PEEK标志是下一次读取依然可以得到这次读取的内容,可认为接收窗口不滑动
- n=recv(sock,&c,1,MSG_PEEK);
- if((n>0)&&(c=='\n'))//如果是回车换行符
- recv(sock,&c,1,0);//继续接收单个字符,实际上和上面那个标志位MSG_PEEK读取同样的字符,读完后删除输入队列的数据,即滑动窗口,c=='\n'
- else
- c='\n';//只是读取到回车符,则置为换行符,也终止了读取
- }
- buf[i]=c;//放入缓冲区
- i++;
- }
- else //没有读取到任何数据
- c='\n';
- }
- buf[i]='\0';
- return (i);//返回读到的字符个数(包括'\0')
- }
- /*服务器端套接字初始化设置*/
- int startup(u_short *port)
- {
- int httpd=0;
- struct sockaddr_in name;
- //socket()用于创建一个用于 socket 的描述符,函数包含于<sys/socket.h>
- //这里的PF_INET其实是与 AF_INET同义
- httpd=socket(PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
- if(httpd==-1)//创建socket失败
- error_die("socket");
- memset(&name,0,sizeof(name));
- name.sin_family=AF_INET;//地址簇
- //htons(),ntohs() 和 htonl()包含于<arpa/inet.h>
- //将*port 转换成以网络字节序表示的16位整数
- //指定端口
- name.sin_port=htons(*port);
- //INADDR_ANY是一个 IPV4通配地址的常量,包含于<netinet/in.h>
- //大多实现都将其定义成了0.0.0.0
- name.sin_addr.s_addr=htonl(INADDR_ANY);
- //bind()用于绑定地址与socket
- //如果传进去的sockaddr结构中的 sin_port 指定为0,这时系统会选择一个临时的端口号
- if(bind(httpd,(struct sockaddr *)&name,sizeof(name))<0)//bind失败
- error_die("bind");
- if(*port==0)//如果调用 bind 后端口号仍然是0,则手动调用getsockname()获取端口号
- {
- socklen_t namelen=sizeof(name);
- //getsockname()包含于<sys/socker.h>中
- //调用getsockname()获取系统内核给 httpd 这个 socket 随机分配的端口号
- if(getsockname(httpd,(struct sockaddr *)&name,&namelen)==-1)//getsockname失败
- error_die("getsockname");
- *port=ntohs(name.sin_port);//网络字节顺序转换为主机字节顺序,返回主机字节顺序表达的数
- }
- if(listen(httpd,5)<0)//服务器监听客户端请求。套接字排队的最大连接个数5
- error_die("listen");
- return (httpd);
- }
- /*告知客户端请求有错误*/
- void bad_request(int client)
- {
- char buf[1024];
- /*将字符存入缓冲区域,再通过send函数发送给客户端*/
- sprintf(buf,"HTTP/1.0 400 BAD REQUEST\r\n");
- send(client,buf,sizeof(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"Content-type: text/html\r\n");
- send(client,buf,sizeof(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"\r\n");
- send(client,buf,sizeof(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"<P>Your browser sent a bad request, ");
- send(client,buf,sizeof(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"such as a POST without a Content-Length.\r\n");
- send(client,buf,sizeof(buf),0);
- }
- /*将文件结构指针resource中的数据发送至client*/
- void cat(int client,FILE *resource)
- {
- char buf[1024];
- fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),resource);//从文件结构指针resource中读取数据,保存至buf中
- //处理文件流中剩下的字符
- while(!feof(resource))//检测流上的文件结束符,文件结束返回非0值,结束返回0
- {
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);//文件流中的字符全部发送给client
- fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),resource);
- /*从文件结构体指针resource中读取至多bufsize-1个数据(第bufsize个字符赋'\0')每次读取一行,如果不足bufsize,则读完该行结束.这里通过feof函数来判断fgets是否因出错而终止.另外,这里有文件偏移位置,下一轮读取会从上一轮读取完的位置继续
- */
- }
- }
- /*通知客户端CGI脚本不能被执行 500*/
- void cannot_execute(int client)
- {
- char buf[1024];
- /*回馈出错信息*/
- sprintf(buf,"HTTP/1.0 500 Internal Server Error\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"Content-type: text/html\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"<P>Error prohibited CGI execution.\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- }
- /*打印出错信息*/
- void error_die(const char *sc)
- {
- perror(sc);
- exit(1);
- }
- /*返回头部信息*/
- void headers(int client,const char *filename)
- {
- char buf[1024];
- (void)filename;
- strcpy(buf,"HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- strcpy(buf,SERVER_STRING);
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"Content-TYpe: text/html\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- strcpy(buf,"\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- }
- /*返回客户端404错误信息*/
- void not_found(int client)
- {
- char buf[1024];
- sprintf(buf,"HTTP/1.0 404 NOT FOUND\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,SERVER_STRING);
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"<HTML><TITLE>Not Found</TITLE>\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"<BODY><P>The server could not fulfill\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"your request because the resource specified\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"is unavailable or nonexistent.\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"</BODY></HTML>\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- }
- /*返回文件数据,用于静态页面返回*/
- void serve_file(int client,const char *filename)
- {
- FILE *resource=NULL;
- int numchars=1;
- char buf[1024];
- //确保buf里面有东西,能进入下面的while循环
- buf[0]='A';
- buf[1]='\0';
- //循环作用是读取并忽略掉这个http请求后面的所有内容
- while((numchars>0)&&strcmp("\n",buf))
- numchars=get_line(client,buf,sizeof(buf));
- //以只读方式打开文件
- resource=fopen(filename,"r");
- if(resource==NULL)
- not_found(client);
- else
- {
- //打开成功后,将这个文件的基本信息封装成response的头部(header)并返回
- headers(client,filename);
- //接着把这个文件的内容读出来作为response的body发送到客户端
- cat(client,resource);
- }
- fclose(resource);//关闭文件
- }
- /*提示客户端web method请求不被支持*/
- void unimplemented(int client)
- {
- char buf[1024];
- sprintf(buf,"HTTP/1.0 501 Method Not Implemented\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,SERVER_STRING);
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"<HTML><HEAD><TITLE>Method Not Implemented\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"</TITLE><HEAD>\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"<BODY><P><TITLE>HTTP request method not supported.\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- sprintf(buf,"</BODY></HTML>\r\n");
- send(client,buf,strlen(buf),0);
- }
- int main()
- {
- int server_sock=-1;
- u_short port=0;
- int client_sock=-1;
- //sockaddr_in 是IPV4的套接字地址结构。定义在<netinet/in.h>
- struct sockaddr_in client_name;
- socklen_t client_name_len=sizeof(client_name);
- pthread_t newthread;
- server_sock=startup(&port);
- printf("httpd running on port %d\n",port);
- /*多线程并发服务器模型*/
- while(1)
- {
- //阻塞等待客户端的连接
- //主线程
- client_sock=accept(server_sock,(struct sockaddr *)&client_name,&client_name_len);
- if(client_sock==-1)//accept失败
- error_die("accept");
- //创建工作线程,执行回调函数accept_request,参数client_sock
- if(pthread_create(&newthread,NULL,accept_request,(void *)&client_sock)!=0)//创建线程失败
- perror("pthread_create");
- }
- close(server_sock);//关闭套接字,就协议栈而言,即关闭TCP连接
- return 0;
- }
from 点击打开链接




 本文剖析Tinyhttpd,一个超轻量级HTTP Web Server,介绍其核心功能及工作流程,涉及HTTP请求处理、CGI脚本执行等内容。
本文剖析Tinyhttpd,一个超轻量级HTTP Web Server,介绍其核心功能及工作流程,涉及HTTP请求处理、CGI脚本执行等内容。
















 805
805

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








