C/C++:newcode经典例子
@ 测验:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
static char *s[] = {"black", "white", "pink", "violet"};
char **ptr[] = {s+3, s+2, s+1, s}, ***p;
p = ptr;
++p;
printf("%s", **p+1);
return 0;
}
结果:ink
@ 测验:
有语句:
int b[3][4];
正确的是:A
int *p[]={b[0],b[1],b[2]};
int *p[]=b;
int *p[2]={b[0],b[1],b[2]};
int *p[]=(int *[])b;
@测验:
class CBase
{
public:
CBase(){cout<<”constructing CBase class”<<endl;}
~CBase(){cout<<”destructing CBase class”<<endl;}
};
class CSub : public CBase
{
public:
CSub(){cout<<”constructing CSub class”<<endl;}
~CSub(){cout<<”destructing CSub class”<<endl;}
};
void main()
{
CSub obj;
}
程序输出结果?
@测验:
在32位cpu上选择缺省对齐的情况下,有如下结构体定义:
struct A{
unsigned a : 19;
unsigned b : 11;
unsigned c : 4;
unsigned d : 29;
char index;
};
则sizeof(struct A)的值为()
@ 测验:
已知int占4个字节,bool占1个字节。
unsigned int
value = 1024;
bool condition =
*((bool *)(&value));
if (condition)
value += 1; condition = *((bool *)(&value));
if (condition)
value += 1; condition = *((bool *)(&value));
问value, condition 的值为____。
@测验:
程序输出结果:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
~A() {
cout << "~A()";
}
};
class B{
public:
virtual ~B() {
cout << "~B()";
}
};
class C: public A, public B {
public:
~C() {
cout << "~C()";
}
};
int main() {
C * c = new C;
B * b1 = dynamic_cast<B *>(c);
A * a2 = dynamic_cast<A *>(b1);
delete a2;
}
@ 测验:
程序输出结果:(注:print已经声明过)
main(){
char str[]="Geneius";
print (str);
}
print(char *s){
if(*s){
print(++s);
printf("%c",*s);
}
}
@ 测验:
代码输出结果:
void main ()
{
char arr[2][4];
strcpy (arr[0],"you");strcpy (arr[1],"me");
arr[0][3]=’&’;
printf("%s \n",arr);
}
@ 测验:
代码输出结果:
using namespace std;
void print(char **str)
{
++str;
cout<<*str<<endl;
}
int main()
{
static char *arr[]={"hello", "world", "c++"};
char **ptr;
ptr=arr;
print(ptr);
return 0;
}
@测验:
程序的结果:编译出错
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "A:print()";
}
};
class B: private A
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "B:print()";
}
};
class C: public B
{
public:
void print()
{
A:: print();
}
};
int main()
{
C b;
b.print();
}
@测验:
在32位环境中,下面代码的运行结果:
#include<stdio.h>
class A
{
public:
A(){ printf("A");}
~A(){ printf("~A");
};
class B:public A
{
public;
B(){ printf("B");}
~B(){ printf("~B");}
};
int main()
{
A*c = new B[2];
delete[] c;
return 0;
}
答案:
ABAB~A~A
@测验:
程序的输出结果为:the
#include
void main()
{
char* a[ ] = { "hello", "the", "world"};
char** pa = a;
pa++;
cout<<*pa<<endl;
}
@测验:
代码正确的是:
class CBase {
int x;
public:
CBase(int n) {x = n;}
};
class CDerived : public CBase {
CBase y;
int z;
public:
CDerived(int a, int b, int c);
};
正确答案: B 你的答案: B
CDerive::CDerive(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){}
CDerive::CDerive(int a,int b,int c):CBase(a),y(b),z(c){}
CDerive::CDerive(int a,int b,int c):CBase(a),CDerive(b),z(c){}
CDerive::CDerive(int a,int b,int c):x(a),CBase(b),z(c){}
@测验:
代码正确的是:
class CBase {
int x;
public:
CBase(int n) {x = n;}
};
class CDerived : public CBase {
CBase y;
int z;
public:
CDerived(int a, int b, int c);
};
正确答案: B 你的答案: B
CDerive::CDerive(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){}
CDerive::CDerive(int a,int b,int c):CBase(a),y(b),z(c){}
CDerive::CDerive(int a,int b,int c):CBase(a),CDerive(b),z(c){}
CDerive::CDerive(int a,int b,int c):x(a),CBase(b),z(c){}
@测验:
在一台主流配置的PC机上,调用f(35)所需的时间大概是_______。几分钟
int f(int x) {
int s=0;
while(x-- >0) s+=f(x);
return max(s,1);
}
@测验:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned char i=7;
int j=0;
for(;i>0;i-=3)
{
++j;
}
printf("%d\n",j);
return 0;
}
请问该程序的输出是多少?
正确答案: C 你的答案: C
2
死循环
173
172
@测验:

如下代码段,哪种描述是正确的()正确答案:2错,1,3正确
class A{};
void f(const A** p) {}
void g(const A* const* p) {}
void k(const A*& p) {}
void main() {
const A *ca = new A();
A *a = new A();
A** p = &a;
k(ca); //[1]
f(p); //[2]
g(p); //[3]
//...
}
参考博客:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/duyiwuer2009/article/details/39401801
@测验:
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void getmemory(char*p) {
p=(char *) malloc(100);
strcpy(p,"hello world");
}
int main( )
{
char *str=NULL;
getmemory(str);
printf("%s\n",str);
free(str);
return 0;
}
下述程序有什么问题?
正确答案: B 你的答案: D
正常输出’hello world"
错误的操作
输出"烫烫烫"
程序崩溃
@测验:
class A {
...
private:
int &a;
};
class B : public A {
...
private:
int a;
public:
const int b;
A c;
static const char* d;
A* e;
};
则构造函数中,成员变量一定要通过初始化列表来初始化的是____。b c
@测验:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
int a1;
protected:
int a2;
public:
int a3;
};
class B: public A{
int b1;
protected:
int b2;
public:
int b3;
};
class C:private B{
int c1;
protected:
int c2;
public:
int c3;
};
int main(){
B obb;
C obc;
cout<<obb.a1;//1
cout<<obb.a2;//2
cout<<obb.a3;//3
cout<<obc.b1;//4
cout<<obc.b2;//5
cout<<obc.b3;//6
cout<<obc.c3;//7
return 0;
}
下列程序编译时会出现错误,请根据行号选择错误位置( )正确答案: A D 你的答案: A D
1,2
2,5,7
3,4,7
4,5,6
@测验:
func(char para[100])
{
void *p = malloc(100);
printf("%d, %d\n", sizeof(para), sizeof(p));
}
正确答案: A 你的答案: A
4,4
@测验:
struct mybitfields
{
unsigned short a : 4;
unsigned short b : 5;
unsigned short c : 7;
} test
void main(void)
{
int i;
test.a = 2;
test.b = 3;
test.c = 0;
i = *((short *)&test);
printf("%d\n", i);
}
写出下列程序在X86上的运行结果:50
@测验:
struct A{
A() {}
~A() {}
int m1;
int m2;
};
struct B:A{
B() {}
~B() {}
int m1;
char m2;
static char m3;
};
struct C{
C() {}
virtual~C() {}
int m1;
short m2;
};
32位机器上,有三个类A B C定义如下, 请确定sizeof(A) sizeof(B) sizeof©的大小顺序.
A<C<B
@测验:
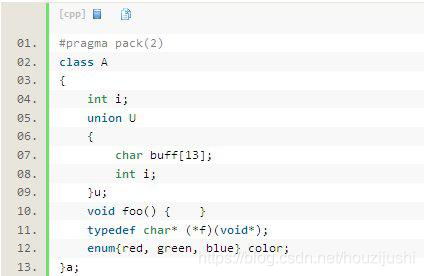
#pragma pack(2)
class A {
int i;
union U
{
char buff[13];
int i;
}u;
void foo() {}
typedef char* (*f)(void*);
enum(red, green, blue) color;
};
sizeof(a)的值是():22
@测验:
class A
{
public:
A()
{
printf(“0”);
}
A(int a)
{
printf(“1”);
}
A& operator=(const A& a)
{
printf(“2”);
return*this;
}
}
int main()
{
A al;
al=10;
}
有如下程序段:则程序输出是:012
@测验:
#include "stdio.h"
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
Init();
}
virtual void Init()
{
printf("Base Init\n");
}
void func()
{
printf("Base func\n");
}
};
class Derived: public Base
{
public:
virtual void Init()
{
printf("Derived Init\n");
}
void func()
{
printf("Derived func\n");
}
};
int main()
{
Derived d;
((Base *)&d)->func();
return 0;
}
该程序的执行结果:
Base Init
Base func
@测验:
声明一个指向含有10个元素的数组的指针,其中每个元素是一个函数指针,该函数的返回值是int,参数是int*,正确的是()
正确答案: C 你的答案: C
(int *p[10])(int*)
int [10]*p(int *)
int (*(*p)[10])(int *)
int ((int *)[10])*p
@测验:
class A{
public:
long a;
};
class B : public A {
public:
long b;
};
void seta(A* data, int idx) {
data[idx].a = 2;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
B data[4];
for(int i=0; i<4; ++i){
data[i].a = 1;
data[i].b = 1;
seta(data, i);
}
for(int i=0; i<4; ++i){
std::cout << data[i].a << data[i].b;
}
return 0;
}
程序输出结果:22221111
@测验:
void Func(char str_arg[100])
{
printf("%d\n",sizeof(str_arg));
}
int main(void)
{
char str[]="Hello";
printf("%d\n",sizeof(str));
printf("%d\n",strlen(str));
char*p=str;
printf("%d\n",sizeof(p));
Func(str);
}
32位系统下下面程序的输出结果为多少?
6 5 4 4
@测验:
class ClassA {
public:
virtual ~ ClassA() {
}
virtual void FunctionA() {
}
};
class ClassB {
public:
virtual void FunctionB() {
}
};
class ClassC: public ClassA, public ClassB {
public:
};
ClassC aObject;
ClassA* pA = &aObject;
ClassB* pB = &aObject;
ClassC* pC = &aObject;
下面那一个语句是不安全的
正确答案: A B C 你的答案: A B C
delete pA
delete pB
delete pC
@测验:
以下选项如果可以初始化正确,那么就会初始化正确,那么以下哪种语法在C++中初始化以后编译会错误?其中X为一C++类
正确答案: C D 你的答案: C D
const X * x
X const * x
const X const * x
X * const x
AB运行没问题,
C运行提示:error: duplicate ‘const’|
D运行提示:error: uninitialized const ‘x’ [-fpermissive]|
@测验:
const char str1[]=”abc”;
const char str2[]=”abc”;
const char *p1 = “abc”;
const char *p2 = “abc”;
判断下列说法哪个是正确的(注意是地址):______。
正确答案: E 你的答案: C
str1和str2地址不同,P1和P2地址相同。
str1和str2地址相同,P1和P2地址相同。
str1和str2地址不同,P1和P2地址不同。
str1和str2地址相同,P1和P2地址不同。
4个地址都不相同
@测验:
union Test
{
char a[4];
short b;
};
Test test;
test.a[0]=256;
test.a[1]=255;
test.a[2]=254;
test.a[3]=253;
printf("%d\n",test.b);
问题:在80X86架构下,输出什么值?
正确答案: B 你的答案: B
-128
-256
128
256
@测试:
myClass::foo(){
delete this;
}
..
void func(){
myClass *a = new myClass();
a->foo();
}
@测验:
int main(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
fork();
printf("-");
}
return 0;
}
请问下面的程序一共输出多少个“-”?
8
@测验:





 本文通过多个C/C++代码实例,详细解析了指针、数组、内存管理、类继承与多态等核心概念的应用技巧。从字符串操作到复杂的数据结构处理,深入浅出地介绍了这些知识点的实际应用。
本文通过多个C/C++代码实例,详细解析了指针、数组、内存管理、类继承与多态等核心概念的应用技巧。从字符串操作到复杂的数据结构处理,深入浅出地介绍了这些知识点的实际应用。
















 655
655

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








