LDA主题模型
0 入门
- Linear Discriminant Analysis 线性判别分析
- Latent Dirichlet Allocation 隐含狄利克雷分布
隐含狄利克雷分布(Latent Dirichlet Allocation)
概率主题模型
文本分类
NLP领域
1 数学基础
- 一个函数:Gamma函数
- 一个概念:共轭先验(conjugate prior)
- 一个理念:贝叶斯框架
- 两个模型:pLSA & LDA
- 二个近似推断算法:
- 吉布斯抽样(Gibbs sampling)(蒙特卡罗法)
采样 通过使用随机化方法完成近似 - 变分EM算法(variational EM algorithm)(近似算法)
使用确定性近似完成近似推断
- 吉布斯抽样(Gibbs sampling)(蒙特卡罗法)
- 三个参数估计:
- 极大似然估计(MLE)
- 最大后验证估计(MAP)
- 贝叶斯估计
- 五个个分布:二项分布 & 多项分布 & 贝塔分布 & Dirichlet分布 & 伯努利分布
2 文本建模
- Unigram Model
- Mixture of Unigram Model
- pLSA(文档-主题-词语)
- doc-topic
- topic-word
- EM算法
- E-step
- M-step
PRML
李航-小蓝书
统计学习方法
- LDA
| Vs | pLSA | LDA |
|---|---|---|
| 样本 | 随机 | 固定 |
| 参数 | 未知但固定 | 未知但不固定 随机变量 |
| 派系 | 频率派 | 贝叶斯派 |
参考文档
一文详解LDA主题模型
主题模型 LDA 入门
主题模型 LDA 入门(附 Python 代码
3 停用词
法一
安装stop_words库,使用get_stop_words模块加载
pip install stop_words
from stop_words import get_stop_words
get_stop_words('english')

法二
nltk.download模块下载&pd.read_csv读取
import nltk
nltk.download('stopwords')
#pd.read_csv('/home/shiyanlou/nltk_data/corpora/stopwords/english')
pd.read_csv('~/nltk_data/corpora/stopwords/english')

4 wordnet
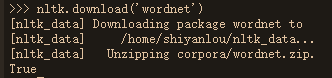
import nltk
nltk.download('wordnet')
5 实战#1
from nltk.stem.wordnet import WordNetLemmatizer
import string
import pandas as pd
import gensim
from gensim import corpora
doc1 = "Sugar is bad to consume. My sister likes to have sugar, but not my father."
doc2 = "My father spends a lot of time driving my sister around to dance practice."
doc3 = "Doctors suggest that driving may cause increased stress and blood pressure."
doc4 = "Sometimes I feel pressure to perform well at school, but my father never seems to drive my sister to do better."
doc5 = "Health experts say that Sugar is not good for your lifestyle."
# 整合文档数据
doc_complete = [doc1, doc2, doc3, doc4, doc5]
#加载停用词
stopwords=pd.read_csv('~/nltk_data/corpora/stopwords/english',index_col=False,quoting=3,sep="\t",names=['stopword'], encoding='utf-8')
stopwords=stopwords['stopword'].values
exclude = set(string.punctuation)
lemma = WordNetLemmatizer()
def clean(doc):
stop_free = " ".join([i for i in doc.lower().split() if i not in stopwords])
punc_free = ''.join(ch for ch in stop_free if ch not in exclude)
normalized = " ".join(lemma.lemmatize(word) for word in punc_free.split())
return normalized
doc_clean = [clean(doc).split() for doc in doc_complete]
# 创建语料的词语词典,每个单独的词语都会被赋予一个索引
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(doc_clean)
# 使用上面的词典,将转换文档列表(语料)变成 DT 矩阵
doc_term_matrix = [dictionary.doc2bow(doc) for doc in doc_clean]
# 使用 gensim 来创建 LDA 模型对象
Lda = gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel
# 在 DT 矩阵上运行和训练 LDA 模型
ldamodel = Lda(doc_term_matrix, num_topics=3, id2word = dictionary, passes=50)
# 输出结果
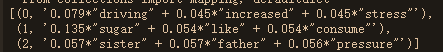
from pprint import pprint
pprint(ldamodel.print_topics(num_topics=3, num_words=3))
6 实战#2
# 文本数据
doc = [""]
# 分词
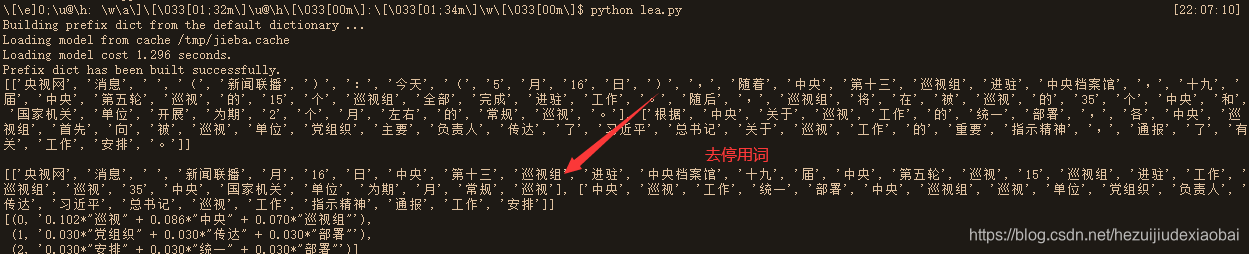
import jieba
doc = [jieba.lcut(s) for s in doc]
print(doc)
print()
# 去停用词
path = 'HIT.txt'
stop_word = []
with open(path, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
stop_word.append(line)
new_doc = []
for sentence in doc:
new_s = []
for v in sentence:
if v not in stop_word:
new_s.append(v)
new_doc.append(new_s)
print(new_doc)
# 文本向量化
import gensim
from gensim import corpora
# doc = [s.split() for s in doc]
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(new_doc)
DT = [dictionary.doc2bow(s) for s in new_doc]
# print(DT)
# Gensim LDA 模型
# 使用 gensim 来创建 LDA 模型对象
Lda = gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel
# 在 DT 矩阵上运行和训练 LDA 模型
ldamodel = Lda(DT, num_topics=3, id2word = dictionary, passes=50)
# 输出主题结果
print(ldamodel.print_topics(num_topics=3, num_words=3))




















 870
870

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








