pthread_join函数负责线程的回收,回收系统分配的资源,主要是线程pcb。pthread_join的功能和waitpid类似。
pthread_join 的函数原型如下:
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
第一个参数是线程的id号
线程退出时使用pthead_exit()函数,返回退出状态。第二个参数获取线程的退出状态,由于pthead_exit(void *),所以为了获取返回值,需要使用二级指针去获取。如果不关心返回值,可以将第二个参数置为NULL
下面是pthread_join的用法,既可以传递数值,也可以传递结构体
#include "apue.h"
#include <pthread.h>
typedef struct {
int val;
char name[64];
}retval;
void *
mpthread1(void * arg)
{
printf("this is my first thread,pread_t is %lu\n",pthread_self());
pthread_exit((void*)2);
}
void *
mpthread2(void *arg)
{
printf("this is my second thread,pread_t is %lu\n",pthread_self());
retval *p = (retval *)malloc(sizeof(retval));
if( p == NULL)
pthread_exit((void *) p);
p->val = 100;
char buf[24] = "hello world";
strncpy(p->name,buf,strlen(buf));
pthread_exit((void *) p);
}
int
main(int argc,char **argv)
{
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
if( pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,mpthread1,NULL) != 0){
perror("pthread_create");
exit(1);
}
if( pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,mpthread2,NULL) != 0){
perror("pthread_create");
exit(1);
}
// huishou pthread
printf("main is sleeping \n");
sleep(1);
int **val;
pthread_join(tid1,(void **)val);
printf("pthread exit status is %p \n",*val);
retval *ret;
pthread_join(tid2,(void **)&ret);
if(ret != NULL){
printf("mpthread2 val is %d, str is %s\n",ret->val,ret->name);
free(ret);
}
return 0;
}
运行结果如下
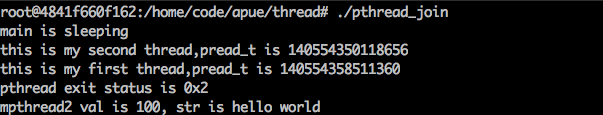





 本文介绍了Linux环境下线程的回收机制,重点关注pthread_join函数。该函数用于回收线程资源,其作用类似于waitpid。文章详细解析了pthread_join的函数原型和参数,并展示了如何获取线程的退出状态。示例代码演示了如何使用pthread_join来等待线程结束并获取返回值,包括传递数值和结构体的情况。
本文介绍了Linux环境下线程的回收机制,重点关注pthread_join函数。该函数用于回收线程资源,其作用类似于waitpid。文章详细解析了pthread_join的函数原型和参数,并展示了如何获取线程的退出状态。示例代码演示了如何使用pthread_join来等待线程结束并获取返回值,包括传递数值和结构体的情况。
















 970
970

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








