基于openstack stable queens版本阅读解析
基于 centos7.5 的linux系统
架构
如下所示,为cinder的官方架构说明:
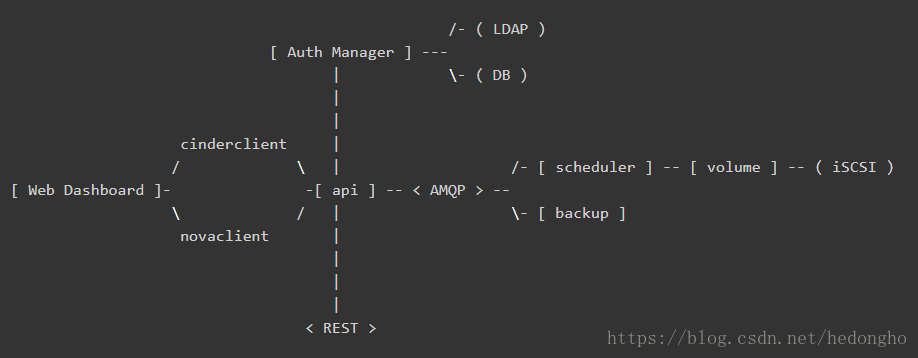
各个组件介绍如下:
- DB: sql database for data storage. Used by all components.
- Web Dashboard: potential external component that talks to the api.
- api: component that receives http requests, converts commands and communicates with other components via the queue or http.
- Auth Manager: component responsible for users/projects/and roles. Can backend to DB or LDAP. This is not a separate binary, but rather a python class that is used by most components in the system.
- scheduler: decides which host gets each volume.
- volume: manages dynamically attachable block devices.
- backup: manages backups of block storage devices.
本文档主要基于volume这组件进行解析,来描述cinder如何使用后端存储,而其提供的api和scheduler问题,可能会少量涉及。
代码可以直接通过github获取:git clone https://git.openstack.org/openstack/cinder.git
cinder主要的实现代码在cinder目录下,其service组件的入口位置均在cinder/cmd/{service}.py,{service}为cinder的各个service组件,如api、scheduler、volume等等。由于都是python代码,可读性比较强,知道main函数后,后面的一步步追踪就好了。
cinder volume service
cinder-volume服务是Cinder最关键的服务,负责对接后端存储驱动,管理volume数据卷生命周期。
在openstack中,所有服务组件都是使用eventlet和greenlet库实现非阻塞的任务线程切换处理,以实现服务的并发功能,该线程模型被openstack称为Green Thread,也就是协程。Green Thread 的上下文切换只会发生在eventlet或者greenlet库调用的时候(比如sleep, certain I/O calls)。
from eventlet import greenthread
...
greenthread.sleep(0)也就是说,从OS的角度来看,openstack service只有一个运行线程。如果某个green thread运行task时被阻塞了,即task调用的接口是阻塞,从而阻塞了thread,那么,service就会一直等待该线程执行结束,其它服务线程就无法进行切换。这会造成一个问题:cinder-volume服务会定时向数据库上报自己的状态,此时,如果volume服务调用比如ceph接口执行flatten操作(flatten操作时间可能会很长,是阻塞操作),导致thread一直阻塞,那么volume就不能及时上报自己的状态,导致集群认为volume服务挂了,执行HA的服务切换。基于此,需要确保volume的所有调用都是非阻塞的接口,即是(green)绿色安全接口,如果是阻塞性的接口,需要与tpool库一起使用。
cinder-volume启动流程
其main函数如下:
@@ file: cinder/cmd/volume.py
def main():
objects.register_all() # import cinder/objects目录下的所有模块
gmr_opts.set_defaults(CONF) # oslo_reports模块,用于生成错误报告,如内存泄漏等
CONF(sys.argv[1:], project='cinder',
version=version.version_string())
logging.setup(CONF, "cinder")
python_logging.captureWarnings(True)
priv_context.init(root_helper=shlex.split(utils.get_root_helper())) # oslo_privsep,service的执行权限设置
utils.monkey_patch() # monkey-patch,替换库比如socket、thread等,不改变import的行为,改变的是操作的指向函数
gmr.TextGuruMeditation.setup_autorun(version, conf=CONF)
global LOG
LOG = logging.getLogger(__name__)
...
# 基于系统类型启动服务
if os.name == 'nt':
# We cannot use oslo.service to spawn multiple services on Windows.
# It relies on forking, which is not available on Windows.
# Furthermore, service objects are unmarshallable objects that are
# passed to subprocesses.
_launch_services_win32()
else:
_launch_services_posix()什么是monkey-patch? monkey-patch指的是在执行时动态替换模块,而且通常是在startup的时候做,一般用于改变函数行为但不影响调用方式,比如在测试用例打桩调用过程、使用gevent时替换某些标准库使函数变成非阻塞等等。
举一个简单的例子,有两个模块 A 和 B,它们功能相同,但是B使用了另一种实现方式,使之性能要远远优于A模块。但是某个项目大量使用了模块A,如果要完全使用B来替换A的话,需要花费大量的精力。这时,monkey-patch就排上用场了。此时,可以在服务初始化时执行 monkey-patch如下:
def monkey_patch(m_source, m_decorator):
a = __import__(m_source)
b = __import__(m_decorator)
a.func = b.func当然实际使用时肯定不会那么傻的一个个函数去替换,一般会使用循环加setattr进行替换,具体可以参照cinder的monkey-patch写法。monkey-patch的原理其实是活用了python的模块在同一进程空间中只会import一次,其余import其实只是引用sys.modules的特性。所以如果程序中有用到module reload,那么,monkey-patch就会失效。
好了,言归正传,我们使用的时linux系统,因此重点关注_launch_services_posix()函数的处理,看看它到底做了什么东西。服务创建启动的流程如下:_launch_services_posix() --> _launch_service(),在_launch_service()中,首先创建服务,然后启动服务,并通知服务启动成功,其代码简化如下:
def _launch_services_posix():
# cinder.service
# 继续追踪,会发现get_launcher会返回一个oslo_service.service.ProcessLauncher的实例
# 关于oslo_service,具体可参照:https://docs.openstack.org/oslo.service/latest/reference/service.html
launcher = service.get_launcher()
# 基于backend启动后端存储服务,backend指配置文件中:
# [DEFAULT]
# enabled_backends = rbd0, rbd1
#
# [rbd0]
# volume_dirver = cinder.volume.drivers.rbd.RBDDriver
# backend_host = rbd:volume_pool
# ...
for backend in filter(None, CONF.enabled_backends):
_launch_service(launcher, backend)
_ensure_service_started() # 需要确保至少有一个backend service启动成功
launcher.wait() # Wait until all services have been stopped, and then return.
def _launch_service(launcher, backend):
...
try:
# 创建service服务
server = service.Service.create(host=host,
service_name=backend,
binary=constants.VOLUME_BINARY,
coordination=True,
cluster=cluster)
except Exception:
LOG.exception('Volume service %s failed to start.', host)
else:
# Dispose of the whole DB connection pool here before
# starting another process. Otherwise we run into cases where
# child processes share DB connections which results in errors.
# 完成 DB 连接池的处理
session.dispose_engine()
# posix: oslo_service.service.ProcessLauncher.launch_service()
launcher.launch_service(server) # 启动service
_notify_service_started() # 修改标志位,表明至少一个service已经成功启动ProcessLauncher.launch_service(service, workers=1)会基于workers的数量,fork多个子进程,每个子进程调用oslo_serivce.service.Launcher.launch_serivce()启动service服务。层层追踪,最后launcher_service会调用我们前面创建的server.start()函数,正式启动service。
在此之前,先看看create函数做了什么。在service.Service.create中,生成了一个service对象,在初始化了rpc、manager等,详细介绍如下代码所示(非关键地方省略):
class Service(service.Service):
"""Service object for binaries running on hosts.
A service takes a manager and enables rpc by listening to queues based
on topic. It also periodically runs tasks on the manager and reports
it state to the database services table.
"""
@classmethod
def create(cls, host=None, binary=None, topic=None, manager=None,
report_interval=None, periodic_interval=None,
periodic_fuzzy_delay=None, service_name=None,
coordination=False, cluster=None):
"""Instantiates class and passes back application object."""
...
# 类方法,直接创建一个Service的对象,然后返回
service_obj = cls(host, binary, topic, manager,
report_interval=report_interval,
periodic_interval=periodic_interval,
periodic_fuzzy_delay=periodic_fuzzy_delay,
service_name=service_name,
coordination=coordination,
cluster=cluster)
return service_obj
def __init__(self, host, binary, topic, manager, report_interval=None,
periodic_interval=None, periodic_fuzzy_delay=None,
service_name=None, coordination=False, cluster=None, *args,
**kwargs):
super(Service, self).__init__()
# 初始化 rpc server
if not rpc.initialized():
rpc.init(CONF)
...
# manager:配置文件中的 volume_manager = cinder.volume.manager.VolumeManager
self.manager_class_name = manager
manager_class = importutils.import_class(self.manager_class_name)
self.service = None
self.manager = manager_class(host=self.host,
cluster=self.cluster,
service_name=service_name,
*args, **kwargs)
# 做了一些标加入集群的标志:self.add_to_cluster,sercvice_ref等等,具体用途不知道
# 猜测是确保service启动时与集群数据保持一致之类的,因为cinder服务的状态信息是上报到数据库的
ctxt = context.get_admin_context()
try:
service_ref = objects.Service.get_by_args(ctxt, host, binary)
service_ref.rpc_current_version = manager_class.RPC_API_VERSION
obj_version = objects_base.OBJ_VERSIONS.get_current()
service_ref.object_current_version = obj_version
self.added_to_cluster = (not service_ref.cluster_name and cluster)
if service_ref.cluster_name != cluster:
LOG.info(...)
if self.added_to_cluster:
# We pass copy service's disable status in the cluster if we
# have to create it.
self._ensure_cluster_exists(ctxt, service_ref)
service_ref.cluster_name = cluster
service_ref.save()
Service.service_id = service_ref.id
except exception.NotFound:
# We don't want to include cluster information on the service or
# create the cluster entry if we are upgrading.
self._create_service_ref(ctxt, manager_class.RPC_API_VERSION)
# We don't want to include resources in the cluster during the
# start while we are still doing the rolling upgrade.
self.added_to_cluster = True
setup_profiler(binary, host)
...在launch service时,最终调用了service的start()函数,该函数做了如下的事情(非必要部分代码省略):
class Service(service.Service):
def start(self):
self.model_disconnected = False
# 这是Tooz的python项目,是openstack为了解决分布式问题开发的一个灵活通用框架
# 主要解决分布式系统的通用问题,比如节点管理、主节点选举以及分布式锁等
# 在N版之前,cinder-volume都是基于文件锁的,只能Active-Passive部署HA模式,但还是有很多缺陷的
# 于是,开发使用Tooz库,让cinder支持分布式锁,使volume支持Active-Active模式
# 具体描述可参考博客:http://zhuanlan.51cto.com/art/201703/534778.htm
if self.coordination:
coordination.COORDINATOR.start()
self.manager.init_host(added_to_cluster=self.added_to_cluster,
service_id=Service.service_id)
# 启动rpc server服务
ctxt = context.get_admin_context()
endpoints = [self.manager]
endpoints.extend(self.manager.additional_endpoints)
obj_version_cap = objects.Service.get_minimum_obj_version(ctxt)
serializer = objects_base.CinderObjectSerializer(obj_version_cap)
target = messaging.Target(topic=self.topic, server=self.host)
self.rpcserver = rpc.get_server(target, endpoints, serializer)
self.rpcserver.start()
...
self.manager.init_host_with_rpc()
# 设置服务状态上报周期任务,这是集群判断cinder-volume服务是否正常运行的关键
if self.report_interval:
pulse = loopingcall.FixedIntervalLoopingCall(
self.report_state)
pulse.start(interval=self.report_interval,
initial_delay=self.report_interval)
self.timers.append(pulse)
# 设置周期性定时任务
# 其详细介绍具体参考博文:http://gtcsq.readthedocs.io/en/latest/openstack/periodic_task.html
if self.periodic_interval:
if self.periodic_fuzzy_delay:
initial_delay = random.randint(0, self.periodic_fuzzy_delay)
else:
initial_delay = None
periodic = loopingcall.FixedIntervalLoopingCall(
self.periodic_tasks)
periodic.start(interval=self.periodic_interval,
initial_delay=initial_delay)
self.timers.append(periodic)
此时,cinder-volume服务已经启动并正常运行,只有在收到所有service都stop后(launch.wait()), cinder-volume才退出。
大的启动流程就是这样,现在我们看看在service create时,是如何创建VolumeManager的,以及它是如何关联到特定的存储后端backend的。
class VolumeManager(manager.CleanableManager,
manager.SchedulerDependentManager):
"""Manages attachable block storage devices."""
def __init__(self, volume_driver=None, service_name=None,
*args, **kwargs):
# service_name: 即配置文件中enabled_backends = xxx1, xxx2 的值
# 因此,self.configuration即[xxx1]的section定义的配置
# 前面说过,[xxx]中定义了如下所示:
# [rbd0]
# volume_dirver = cinder.volume.drivers.rbd.RBDDriver
# backend_host = rbd:volume_pool
# ...
service_name = service_name or 'backend_defaults'
self.configuration = config.Configuration(volume_backend_opts,
config_group=service_name)
self._set_tpool_size(
self.configuration.backend_native_threads_pool_size)
if not volume_driver:
# Get from configuration, which will get the default
# if its not using the multi backend
volume_driver = self.configuration.volume_driver
vol_db_empty = self._set_voldb_empty_at_startup_indicator(
context.get_admin_context())
...
# import volume driver, like cinder.volume.drivers.rbd.RBDDriver
# import_object会import class 并返回一个class的实例,第一个参数是类名,其它是类初始化实例参数
self.driver = importutils.import_object(
volume_driver,
configuration=self.configuration,
db=self.db,
host=self.host,
cluster_name=self.cluster,
is_vol_db_empty=vol_db_empty,
active_backend_id=curr_active_backend_id)
...在初始化完VolumeManager后,也关联了其特定的存储后端驱动driver,此后的操作,都是通过driver去调相应的处理函数接口进行的。
Volume-Driver: ceph rbd
基于openstack和ceph rbd的完美结合,这里简单介绍一下openstack的cinder.volume.drivers.rbd.RBDDriver。RBDDriver是在ceph的python-rbd和python-rados接口的基础上,基于上层服务需求,定制化封装的一个接口驱动,其实际对rbd的管理操作还是通过调用ceph原生接口操作的。
RBDDriver这个文件主要包含三个类定义实现:RBDVolumeProxy,RADOSClient,RBDDriver。RBDDriver是最重要的,涵盖了所有的rbd管理操作,其余两个是辅助类,供driver调用的。比如RADOSClient方便client连接rados,open ioctx的功能;RBDVolumeProxy就是个rbd代理。
在这里科普一下,(懂ceph接口开发的可以略过),ceph分为rados和rbd两个python库,它们做的事情是不一样的。rados提供连接ceph存储系统的一些操作,一般是针对某个存储pool来操作的;rbd提供的则是如何操作特定image的功能。
# rados和rbd库的简单使用
import rados, rbd
#Examples.
cluster = rados.Rados(conffile='ceph.conf')
cluster.connect() # 连接rados
ioctx = cluster.open_ioctx('rbd') # 打开特定pool如'rbd'的io,所有对ceph pool的io操作都是需要ioctx的
image = rbd.Image(ioctx, 'myimage') # 打开具体的image
image.copy(...) # 调用image的具体操作方法RBDDriver类其实就是image操作的封装,然后基于其业务考虑了很多,做了一些健壮性的处理,细看其实都差不多,就不一一描述了。这里简单描述下RBDVolumeProxy,其就是rbd代理,但做了一些额外的工作。
使用过ceph的都知道,rbd的部分管理命令运行时间是很长的,比如copy、flatten、delete操作等,基于块设备的大小,由几秒到几小时的跨度都是常见的。前面我们说过,openstack的服务都是使用eventlet和greenlet协程处理的,当driver调用copy或者flatten操作时,RBDDriver调用了ceph原生copy或flatten接口,由于ceph接口是非eventlet实现的(接口是阻塞的),那么cidner-volume服务就会一直卡在rbdDriver操作线程里,等待ceph返回操作结果。此时,cinder-volume的其它周期性任务如心跳上报等等便不能运行,导致整个cinder-volume服务不能使用。RBDVolumeProxy在一定程度上解决了这个问题,方法也很简单,将所有的rbd操作丢到tpool里。
tpool和eventlet的结合也是很常用的一种手段,tpool将阻塞的方法调用转变成’green‘的方法调用,非常适合使用c写的python接口。
class RBDVolumeProxy(object):
"""Context manager for dealing with an existing rbd volume.
This handles connecting to rados and opening an ioctx automatically, and
otherwise acts like a librbd Image object.
Also this may reuse an external connection (client and ioctx args), but
note, that caller will be responsible for opening/closing connection.
Also `pool`, `remote`, `timeout` args will be ignored in that case.
The underlying librados client and ioctx can be accessed as the attributes
'client' and 'ioctx'.
"""
def __init__(self, driver, name, pool=None, snapshot=None,
read_only=False, remote=None, timeout=None,
client=None, ioctx=None):
...
try:
self.volume = driver.rbd.Image(rados_ioctx,
utils.convert_str(name),
snapshot=snapshot,
read_only=read_only)
# 将rbd.Image丢到tpool里,那么所有的Image调用将变成green调用,即安全的
self.volume = tpool.Proxy(self.volume)
except driver.rbd.Error:
LOG.exception("error opening rbd image %s", name)
if self._close_conn:
driver._disconnect_from_rados(rados_client, rados_ioctx)
raise
...
# __getattr__是python的高级用法(参考python描述符介绍),
# 如果找不到对应的属性(方法),则查找self.volume的属性,即Image属性方法
# 因此,只要生成RBDVolumeProxy实例,就可以调用Ceph原生Image的所有操作方法
def __getattr__(self, attrib):
return getattr(self.volume, attrib)




 本文详细解析了Cinder Volume服务在OpenStack中的启动流程,特别是如何使用Ceph RBD作为后端存储驱动。文章介绍了Cinder Volume服务的主要组件及其职责,强调了Green Thread的概念以及避免服务阻塞的重要性。通过对cinder-volume服务的启动过程分析,展示了VolumeManager的创建和VolumeDriver的关联。Ceph RBD Driver是基于ceph的python-rbd和python-rados接口定制的,处理rbd的管理操作。文章还讨论了在处理长时间运行的操作时,如何通过tpool和eventlet结合来解决服务阻塞问题。
本文详细解析了Cinder Volume服务在OpenStack中的启动流程,特别是如何使用Ceph RBD作为后端存储驱动。文章介绍了Cinder Volume服务的主要组件及其职责,强调了Green Thread的概念以及避免服务阻塞的重要性。通过对cinder-volume服务的启动过程分析,展示了VolumeManager的创建和VolumeDriver的关联。Ceph RBD Driver是基于ceph的python-rbd和python-rados接口定制的,处理rbd的管理操作。文章还讨论了在处理长时间运行的操作时,如何通过tpool和eventlet结合来解决服务阻塞问题。
















 679
679

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








