leetocde.48:旋转图像-每日一题
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵表示一个图像。
将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
说明:
你必须在原地旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像
class Solution {
/*基本思路:先存储第i行第j个元素,然后将第j行n - i个元素赋值给它。
然后将第n - i行n - j个元素赋值给第j行n - i个
以此类推
*/
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int length = matrix.length;
for(int i = 0; i < length / 2; i++) { //行
for(int j = 0; j < (length + 1) / 2; j++) {//列
int temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[length - j - 1][i];
matrix[length - 1 - j][i] = matrix[length - 1 - i][length - 1 - j];
matrix[length - i - 1][length - j - 1] = matrix[j][length - i - 1];
matrix[j][length - i - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}

leetocde.15:三数之和-hot100
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例:
给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
满足要求的三元组集合为:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
/*基本思路:这种题很明显是首先要进行排序。原本的想法是用固定一个数,另外两个数去查哈希表,但是这样的话太复杂了
于是使用双指针。当前数和后面两数加起来,如果大于0就移动右指针,小于0就移动左。
等于0就加入结果集。此时,左右指针如果存在下一个数字相同,就需要继续移动左右指针直到不同
*/
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
int length = nums.length;
for(int i = 0; i < length - 2; i++) {
//当数字大于0时,由于左右指针的数肯定大于它,于是三者肯定大于0,直接返回
if(nums[i] > 0) return result;
//当前数跟前一个一样,就可以直接跳过了
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;
//左:相对于当前数字的下一个数字 右:最末尾的数字
int left = i + 1, right = length - 1;
while(left < right) {
//如果等于0
if(nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] == 0) {
//添加
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>(3);
temp.add(nums[i]);
temp.add(nums[left]);
temp.add(nums[right]);
result.add(temp);
//存在左指针下一个数等于当前左指针所指的数,就移动左指针。右指针同理。
//移动结束后左指针指的是最后一个相同的数
while(left < right && nums[left + 1] == nums[left]) left++;
while(left < right && nums[right - 1] == nums[right]) right--;
//再次移动,此时左指针指的是与上一次所指不同的数了。比如左指针所指是 1 2 2 2 3
//那么第一次是在第一个2,经过上面的while就指向第三个2
//接下来就是在3
left++;
right--;
}
//如果大于0,移动右,下面同理
else if(nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0) {
right--;
}
else {
left++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}

leetocde.4:寻找两个正序数组的中位数
给定两个大小为 m 和 n 的正序(从小到大)数组 nums1 和 nums2。请你找出并返回这两个正序数组的中位数。
进阶:你能设计一个时间复杂度为 O(log (m+n)) 的算法解决此问题吗?
//解法一:依次去两个数组中比较小的一个,取到第n/2个,但是需要判断奇偶
int length_1 = nums1.length;
int length_2 = nums2.length;
int length = length_1 + length_2;
int left = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int right = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int start_1 = 0, start_2 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= length / 2; i++) {
left = right;
if(start_1 < length_1 && (start_2 >= length_2 || nums1[start_1] < nums2[start_2])) {
right = nums1[start_1++];
}
else {
right = nums2[start_2++];
}
}
if((length & 1) == 0) {
return (left + right) / 2.0;
}
else {
return right;
}
class Solution {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
//思路:官方题解的视频,使用分割线来把两个数组分开,使得数组1和数组2的左边部分加起来等于n/2
//把较短的数组赋给nums1,防止越界
if(nums1.length > nums2.length) {
int[] temp = nums1;
nums1 = nums2;
nums2 = temp;
}
int m = nums1.length;
int n = nums2.length;
//左边数组加起来的元素个数
int totalLeft = (m + n + 1) / 2;
int left = 0;
int right = m;
while(left < right) {
//i为较短数组的下标 j为长数组的下标
int i = left + (right - left + 1) / 2;
int j = totalLeft - i;
//当第一个数组分割线左边大于第二个数组分割线右边时,说明此时的划分不符合,缩小范围
if(nums1[i - 1] > nums2[j]) {
right = i - 1;
} else {//同理 缩小范围
left = i;
}
}
int i = left;
int j = totalLeft - i;
int nums1LeftMax = i == 0 ? Integer.MIN_VALUE : nums1[i - 1];
int nums1RightMin = i == m ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : nums1[i];
int nums2LeftMax = j == 0 ? Integer.MIN_VALUE : nums2[j - 1];
int nums2RightMin = j == n ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : nums2[j];
if (((m + n) % 2) == 1) {
return Math.max(nums1LeftMax, nums2LeftMax);
} else {
return (double) ((Math.max(nums1LeftMax, nums2LeftMax) + Math.min(nums1RightMin, nums2RightMin))) / 2;
}
}
}
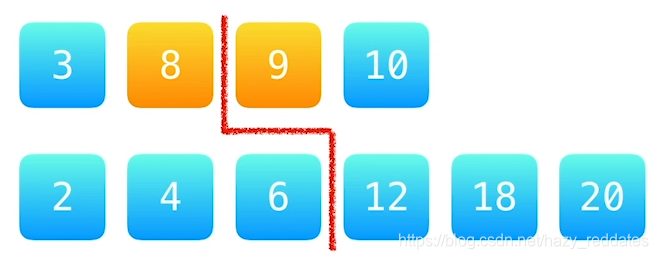

leetcode103:二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层序遍历。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
/*基本思路:有点蠢的做法,就是根据左右依次交替,把节点添加到链表的最左或是最右进行遍历
后面发现可以是跟普通层序遍历一样,只需要添加元素的时候添加到头或者尾就可以
*/
LinkedList<TreeNode> record = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return result;
record.offer(root);
boolean left = true;
while(!record.isEmpty()) {
int length = record.size();
List<Integer> tempList = new ArrayList<>();
//如果是按从左往右就跟普通层序一样
if(left) {
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
TreeNode temp = record.poll();
tempList.add(temp.val);
if(temp.left != null) record.addLast(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null) record.addLast(temp.right);
}
left = false;
} else { //如果是右往左,就添加到第i个位置上
for(int i = length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
TreeNode temp = record.remove(i);
tempList.add(temp.val);
if(temp.right != null) record.add(i, temp.right);
if(temp.left != null) record.add(i, temp.left);
}
left = true;
}
result.add(tempList);
}
return result;
}
}

leetcode.55:跳跃游戏-hot100
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
判断你是否能够到达最后一个位置。
示例 1:
输入: [2,3,1,1,4]
输出: true
解释: 我们可以先跳 1 步,从位置 0 到达 位置 1, 然后再从位置 1 跳 3 步到达最后一个位置。
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
//基本思路:从左往右遍历 如果找到第一个能到达终点的地方,就把这个点当作新的终点
//接着往下找 直到退出循环 否则的话说明无法到达
int length = nums.length;
if(length == 0 || length == 1) return true;
int now = length - 1;
//now为当前的终点下标
while(now > 0) {
//临时记录终点下标
int temp = now;
for(int i = 0; i < now; i++) {
if(nums[i] + i >= now) {
now = i;
}
}
//如果下标没有改变说明到不了这个终点直接退出
if(now == temp) {return false;}
}
return true;
}
}

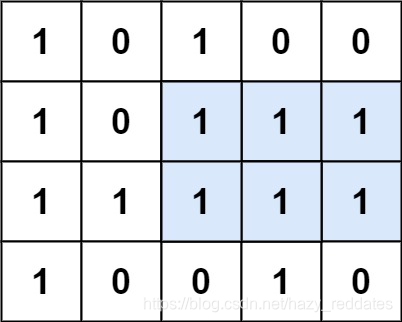
leetcode.85:最大矩形-每日一题
给定一个仅包含 0 和 1 、大小为 rows x cols 的二维二进制矩阵,找出只包含 1 的最大矩形,并返回其面积。
输出:6
class Solution {
public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {
//基本思路:先创建一个矩阵 对应位置存放对应行的连续个数,如:0 1 1 0存放为 0 1 2 0
//接着将其转换为一个求以i j为右下角坐标的最大矩阵问题
int row = matrix.length;
if(row == 0) return 0;
int col = matrix[0].length;
int[][] continuous = new int[row][col];
//创建对应的行连续记录数组
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if(matrix[i][j] == '0') {
continuous[i][j] = 0;
} else {
continuous[i][j] = j > 0 ? continuous[i][j - 1] + 1 : 1;
}
}
}
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
//如果当前点为0说明其不能构成一个矩形
if(continuous[i][j] == 0) {
continue;
}
//当前的最小长度
int width = continuous[i][j];
//当前的最大面积
int area = width;
for(int k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
//取较短者
width = Math.min(width, continuous[k][j]);
//取面积较大者
area = Math.max(area, width * (i - k + 1));
}
result = Math.max(area, result);
}
}
return result;
}
}

leetcode.84:柱状图中最大的矩形
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
解法一:
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
//基本思路:以当前柱子为右边界向左不断扩大取最大值
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < heights.length; i++) {
//当前柱子的面积
int width = heights[i];
int area = width;
for(int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
//往左进行扩大求面积
width = Math.min(width, heights[j]);
area = Math.max(area, (i - j + 1) * width);
}
//取最大值
result = Math.max(result, area);
}
return result;
}
}

解法二:
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
// 这里为了代码简便,在柱体数组的头和尾加了两个高度为 0 的柱体。
int[] tmp = new int[heights.length + 2];
System.arraycopy(heights, 0, tmp, 1, heights.length);
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
int area = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tmp.length; i++) {
// 对栈中柱体来说,栈中的下一个柱体就是其「左边第一个小于自身的柱体」;
// 若当前柱体 i 的高度小于栈顶柱体的高度,说明 i 是栈顶柱体的「右边第一个小于栈顶柱体的柱体」。
// 因此以栈顶柱体为高的矩形的左右宽度边界就确定了,可以计算面积🌶️ ~
while (!stack.isEmpty() && tmp[i] < tmp[stack.peek()]) {
int h = tmp[stack.pop()];
area = Math.max(area, (i - stack.peek() - 1) * h);
}
stack.push(i);
}
return area;
}
}

class Solution {
public int minPatches(int[] nums, int n) {
//基本思路:对于覆盖到[1, x)的区间,如果加上x就可以覆盖到[1,2x)
//同理,对于已经覆盖到[1, x)的区间,再来一个数 a 只要它小于x,就可以覆盖到[1, x+a)
//只需要判断数组中的下一个数是否大于x,如果是就说明要补充一个x,使区间能达到下一个数
//如果小于就使区间变成[1, x+a) 直至满足x>n(因为是开区间所以要大于)
long now = 1; //当前右边界
int index = 0;
int length = nums.length;
int result = 0;
while(now <= n) {
//下一个数小于now就直接使区间变成[1, now + next)
if(index < length && now >= nums[index]) {
now += nums[index++];
} else { //下一个数大于now就直接使区间变成[1, 2 * now) result + 1
now *= 2;
result++;
}
}
return result;
}
}






 这篇博客主要记录了LeetCode的一些经典题目,包括旋转图像、寻找三数之和、寻找两个正序数组的中位数、锯齿形层序遍历二叉树、跳跃游戏、最大矩形问题的解法,涉及数组、二叉树、动态规划等多个算法知识点。
这篇博客主要记录了LeetCode的一些经典题目,包括旋转图像、寻找三数之和、寻找两个正序数组的中位数、锯齿形层序遍历二叉树、跳跃游戏、最大矩形问题的解法,涉及数组、二叉树、动态规划等多个算法知识点。

















 1679
1679










