
专栏导读
本专栏收录于《华为OD机试真题(Python/JS/C/C++)》。
刷的越多,抽中的概率越大,私信哪吒,备注华为OD,加入华为OD刷题交流群,每一题都有详细的答题思路、详细的代码注释、3个测试用例、为什么这道题采用XX算法、XX算法的适用场景,发现新题目,随时更新。
一、题目描述
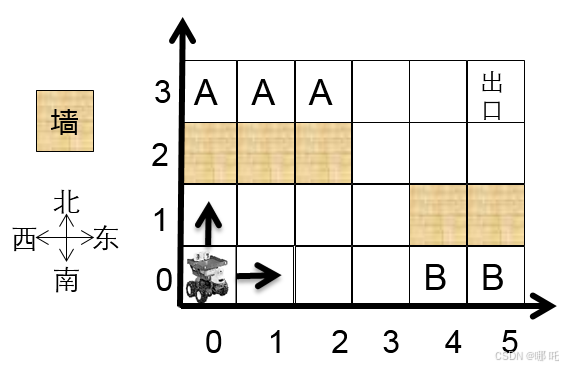
房间由XY的方格组成,例如下图为6*4的大小。每一个方格以坐标(x, y)描述。
机器人固定从方格(0, 0)出发,只能向东或者向北前进。出口固定为房间的最东北角,如下图的方格(5, 3)。用例保证机器人可以从入口走到出口。
房间有些方格是墙壁,如(4, 1),机器人不能经过那儿。
有些地方是一旦到达就无法走到出口的,如标记为B的方格,称之为陷阱方格。
有些地方是机器人无法到达的,如标记为A的方格,称之为不可达方格,不可达方格不包括墙壁所在的位置。
如下示例图中,陷阱方格有2个,不可达方格有3个。
请为该机器人实现路径规划功能:给定房间大小、墙壁位置,请计算出陷阱方格与不可达方格分别有多少个。
二、输入描述
第一行为房间的X和Y(0 < X,Y <= 1000)
• 第二行为房间中墙壁的个数N(0 <= N < X*Y)
• 接着下面会有N行墙壁的坐标
同一行中如果有多个数据 以一个空格隔开,用例保证所有的输入数据均合法。(结尾不带 回车换行)
三、输出描述
陷阱方格与不可达方格数量,两个信息在一行中输出,以一个空格隔开。(结尾不带回车换行)
四、测试用例
测试用例1:
1、输入
6 4
5
0 2
1 2
2 2
4 1
5 1
2、输出
2 3
3、说明
该输入对应上图示例中的迷宫,陷阱方格有2个,不可达方格有3个
测试用例2:
1、输入
6 4
4
2 0
2 1
3 0
3 1
2、输出
0 4
3、说明
该输入对应的迷宫如下图,没有陷阱方格,不可达方格有4个,分别是(4, 0) (4, 1) (5, 0) (5, 1)
五、解题思路
用两个二维布尔数组做动态规划:
reachable[y][x] 表示从起点(0,0)只向东/北能否到达该格
canReach[y][x] 表示从该格只向东/北能否到达终点(X-1,Y-1),等价于从终点反向只向西/南能否到达该格
算法:
- 正向DP求 reachable
- 反向DP求 canReach
- 统计非墙格:reachable为真且canReach为假 -> 陷阱;reachable为假 -> 不可达
复杂度 O(X*Y),适配 X,Y<=1000。
六、Python算法源码
import sys
def main():
data = sys.stdin.read().strip().split()
if not data:
return
it = iter(data)
X = int(next(it))
Y = int(next(it))
N = int(next(it))
wall = [[False] * X for _ in range(Y)]
for _ in range(N):
wx = int(next(it))
wy = int(next(it))
wall[wy][wx] = True
reachable = [[False] * X for _ in range(Y)]
# 正向DP:从起点只向东/北能否到达
for y in range(Y):
for x in range(X):
if wall[y][x]:
continue
if x == 0 and y == 0:
reachable[y][x] = True
else:
from_left = x > 0 and reachable[y][x - 1]
from_down = y > 0 and reachable[y - 1][x]
reachable[y][x] = from_left or from_down
can_reach = [[False] * X for _ in range(Y)]
# 反向DP:从终点反向向西/南能否到达
for y in range(Y - 1, -1, -1):
for x in range(X - 1, -1, -1):
if wall[y][x]:
continue
if x == X - 1 and y == Y - 1:
can_reach[y][x] = True
else:
from_right = x + 1 < X and can_reach[y][x + 1]
from_up = y + 1 < Y and can_reach[y + 1][x]
can_reach[y][x] = from_right or from_up
trap = 0
unreachable = 0
for y in range(Y):
for x in range(X):
if wall[y][x]:
continue
if not reachable[y][x]:
unreachable += 1
elif not can_reach[y][x]:
trap += 1
sys.stdout.write(f"{trap} {unreachable}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
七、JavaScript算法源码
const fs = require('fs');
const input = fs.readFileSync(0, 'utf8').trim();
if (input.length === 0) process.exit(0);
const data = input.split(/\s+/).map(Number);
let idx = 0;
const X = data[idx++];
const Y = data[idx++];
const N = data[idx++];
const wall = Array.from({ length: Y }, () => Array(X).fill(false));
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
const wx = data[idx++];
const wy = data[idx++];
wall[wy][wx] = true;
}
const reachable = Array.from({ length: Y }, () => Array(X).fill(false));
// 正向DP:从起点只向东/北能否到达
for (let y = 0; y < Y; y++) {
for (let x = 0; x < X; x++) {
if (wall[y][x]) continue;
if (x === 0 && y === 0) {
reachable[y][x] = true;
} else {
const fromLeft = x > 0 && reachable[y][x - 1];
const fromDown = y > 0 && reachable[y - 1][x];
reachable[y][x] = fromLeft || fromDown;
}
}
}
const canReach = Array.from({ length: Y }, () => Array(X).fill(false));
// 反向DP:从终点反向向西/南能否到达
for (let y = Y - 1; y >= 0; y--) {
for (let x = X - 1; x >= 0; x--) {
if (wall[y][x]) continue;
if (x === X - 1 && y === Y - 1) {
canReach[y][x] = true;
} else {
const fromRight = x + 1 < X && canReach[y][x + 1];
const fromUp = y + 1 < Y && canReach[y + 1][x];
canReach[y][x] = fromRight || fromUp;
}
}
}
let trap = 0;
let unreachable = 0;
for (let y = 0; y < Y; y++) {
for (let x = 0; x < X; x++) {
if (wall[y][x]) continue;
if (!reachable[y][x]) {
unreachable++;
} else if (!canReach[y][x]) {
trap++;
}
}
}
process.stdout.write(`${trap} ${unreachable}`);
八、C算法源码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int X, Y;
if (scanf("%d %d", &X, &Y) != 2) return 0;
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
int size = X * Y;
// 使用一维数组模拟二维
char *wall = (char *)calloc(size, sizeof(char));
char *reachable = (char *)calloc(size, sizeof(char));
char *canReach = (char *)calloc(size, sizeof(char));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int wx, wy;
scanf("%d %d", &wx, &wy);
wall[wy * X + wx] = 1;
}
// 正向DP:从起点只向东/北能否到达
for (int y = 0; y < Y; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < X; x++) {
int idx = y * X + x;
if (wall[idx]) continue;
if (x == 0 && y == 0) {
reachable[idx] = 1;
} else {
int fromLeft = (x > 0) && reachable[y * X + (x - 1)];
int fromDown = (y > 0) && reachable[(y - 1) * X + x];
reachable[idx] = (fromLeft || fromDown) ? 1 : 0;
}
}
}
// 反向DP:从终点反向向西/南能否到达
for (int y = Y - 1; y >= 0; y--) {
for (int x = X - 1; x >= 0; x--) {
int idx = y * X + x;
if (wall[idx]) continue;
if (x == X - 1 && y == Y - 1) {
canReach[idx] = 1;
} else {
int fromRight = (x + 1 < X) && canReach[y * X + (x + 1)];
int fromUp = (y + 1 < Y) && canReach[(y + 1) * X + x];
canReach[idx] = (fromRight || fromUp) ? 1 : 0;
}
}
}
int trap = 0, unreachable = 0;
for (int y = 0; y < Y; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < X; x++) {
int idx = y * X + x;
if (wall[idx]) continue;
if (!reachable[idx]) {
unreachable++;
} else if (!canReach[idx]) {
trap++;
}
}
}
printf("%d %d", trap, unreachable);
free(wall);
free(reachable);
free(canReach);
return 0;
}
九、C++算法源码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int X, Y;
if (!(cin >> X >> Y)) return 0;
int N;
cin >> N;
vector<vector<bool>> wall(Y, vector<bool>(X, false));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int wx, wy;
cin >> wx >> wy;
wall[wy][wx] = true;
}
vector<vector<bool>> reachable(Y, vector<bool>(X, false));
// 正向DP:从起点只向东/北能否到达
for (int y = 0; y < Y; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < X; x++) {
if (wall[y][x]) continue;
if (x == 0 && y == 0) {
reachable[y][x] = true;
} else {
bool fromLeft = x > 0 && reachable[y][x - 1];
bool fromDown = y > 0 && reachable[y - 1][x];
reachable[y][x] = fromLeft || fromDown;
}
}
}
vector<vector<bool>> canReach(Y, vector<bool>(X, false));
// 反向DP:从终点反向向西/南能否到达
for (int y = Y - 1; y >= 0; y--) {
for (int x = X - 1; x >= 0; x--) {
if (wall[y][x]) continue;
if (x == X - 1 && y == Y - 1) {
canReach[y][x] = true;
} else {
bool fromRight = x + 1 < X && canReach[y][x + 1];
bool fromUp = y + 1 < Y && canReach[y + 1][x];
canReach[y][x] = fromRight || fromUp;
}
}
}
int trap = 0, unreachable = 0;
for (int y = 0; y < Y; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < X; x++) {
if (wall[y][x]) continue;
if (!reachable[y][x]) {
unreachable++;
} else if (!canReach[y][x]) {
trap++;
}
}
}
cout << trap << " " << unreachable;
return 0;
}
🏆下一篇:华为OD机试真题 - 简易内存池(Python/JS/C/C++ 双机位C卷 200分)
🏆本文收录于,华为OD机试真题(Python/JS/C/C++)
刷的越多,抽中的概率越大,私信哪吒,备注华为OD,加入华为OD刷题交流群,每一题都有详细的答题思路、详细的代码注释、3个测试用例、为什么这道题采用XX算法、XX算法的适用场景,发现新题目,随时更新。























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










